Set a Checkbox to Checked/Unchecked using TypeScript
Last updated: Feb 29, 2024
Reading time·4 min
# Table of Contents
- Set a Checkbox to Checked/Unchecked using TypeScript
- Check if a checkbox element is checked using TypeScript
# Set a Checkbox to Checked/Unchecked using TypeScript
To set a checkbox to checked/unchecked in TypeScript:
- Select the checkbox element.
- Type the element as
HTMLInputElementusing a type assertion. - Use the element's
checkedproperty to set the checkbox to checked or unchecked.
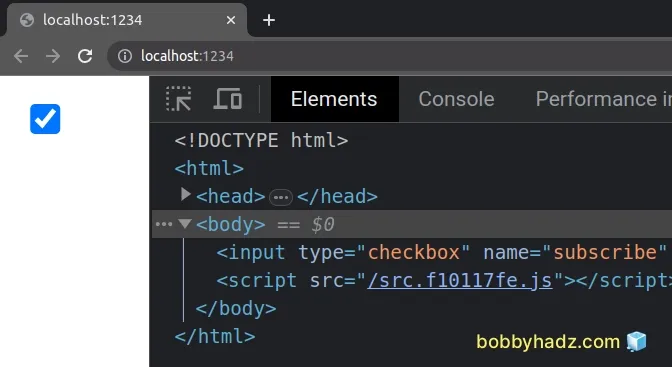
This is the index.html file for the examples.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <input type="checkbox" name="subscribe" id="subscribe" /> <script src="./src/index.ts"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related TypeScript code.
const checkbox = document.getElementById( 'subscribe', ) as HTMLInputElement | null; if (checkbox != null) { // ✅ Set checkbox checked checkbox.checked = true; // ✅ Set checkbox unchecked // checkbox.checked = false; }
We used a type assertion to type the checkbox variable as HTMLInputElement
or null.
If you're working with an option or select element, you can use the
HTMLOptionElement or HTMLSelectElement types.
The reason we included null in the type is that the
document.getElementById method will
return null if no element with the provided id is found in the DOM.
checkbox variable does not store a null value before accessing its checked property.Once we enter the if block, TypeScript knows that the type of the checked
variable is HTMLInputElement and not HTMLInputElement | null.
null from the type in the type assertion.Now we are able to access the checked property on the element because we've
typed it correctly.
The property can be used to read or set the checked state of the checkbox element.
If you need to uncheck the checkbox, set its checked property to false.
const checkbox = document.getElementById( 'subscribe', ) as HTMLInputElement | null; if (checkbox != null) { // ✅ Set checkbox checked checkbox.checked = true; // 👇️ true console.log(checkbox.checked); // ✅ Set checkbox unchecked checkbox.checked = false; }
It's always a best practice to include null in the type assertion because the
getElementById() method would return null if no element with the provided
id was found.
# Check if a checkbox element is checked using TypeScript
To check if a checkbox element is checked in TypeScript:
- Type the element as
HTMLInputElementusing a type assertion. - Use the
checkedproperty to see if the element is checked. - The property will return
trueif it is checked andfalseotherwise.
This is the index.html file for the examples.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <input type="checkbox" name="subscribe" id="subscribe" /> <script src="./src/index.ts"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related TypeScript code.
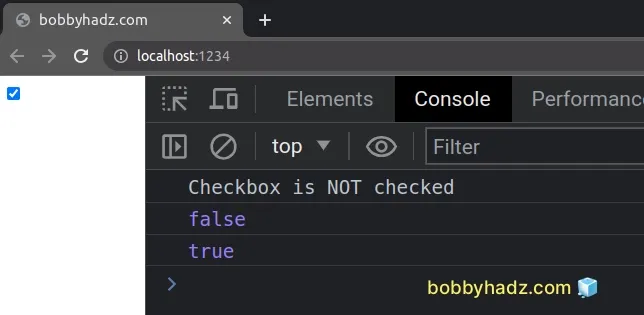
const checkbox = document.getElementById( 'subscribe', ) as HTMLInputElement | null; if (checkbox?.checked) { console.log('Checkbox is checked'); } else { console.log('Checkbox is NOT checked'); } console.log(checkbox?.checked); // 👉️ false if (checkbox != null) { checkbox.checked = true; } console.log(checkbox?.checked); // 👉️ true
We used a type assertion to type the checkbox variable as HTMLInputElement
or null.
If you're working with an option or select element, you can use the
HTMLOptionElement or HTMLSelectElement types.
The reason we included null in the type is that the
document.getElementById method will
return null if no element with the provided id is found in the DOM.
null from the type in the type assertion.Now we are able to access the checked property on the element because we've
typed it correctly.
The checked property returns a boolean result - true if the checkbox is
checked and false otherwise.
We used the optional chaining (?.)
operator to short-circuit if the reference is null or undefined.
const checkbox = document.getElementById( 'subscribe', ) as HTMLInputElement | null; // 👇️ optional chaining if (checkbox?.checked) { console.log('Checkbox is checked'); } else { console.log('Checkbox is NOT checked'); }
The optional chaining (?.) operator short-circuits returning undefined if the
reference is nullish.
checkbox variable stores a null value, we won't attempt to access the checked property and get a runtime error.# Using a simple if statement as a type guard
We could have also used a simple if statement that serves as a
type guard.
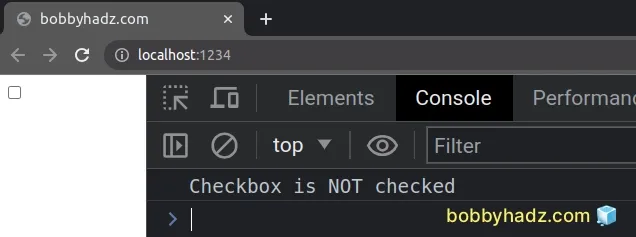
const checkbox = document.getElementById( 'subscribe', ) as HTMLInputElement | null; if (checkbox != null) { if (checkbox.checked) { console.log('Checkbox is checked'); } else { console.log('Checkbox is NOT checked'); } }
We explicitly make sure that the checkbox variable
does not store a null value before accessing
its checked property.
Once we enter the if block, TypeScript knows that the type of the checked
variable is HTMLInputElement and not HTMLInputElement | null.
It's always a best practice to include null in the type assertion because the
getElementById() method would return null if no element with the provided
id was found.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

