Set CSS styles on an Element using TypeScript
Last updated: Feb 29, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Set CSS styles on an Element using TypeScript
To set CSS styles on an element in TypeScript:
- Select the specific element.
- Set properties on the
styleobject of the element to update its styles. - For example,
el.style.backgroundColor = 'lime'.
Here is the HTML for the examples.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div id="box">Hello world</div> <script src="./src/index.ts"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related TypeScript code.
// 👇️ const box: HTMLElement | null const box = document.getElementById('box'); if (box != null) { box.style.backgroundColor = 'lime'; box.style.color = 'white'; box.style.fontSize = '2em'; }
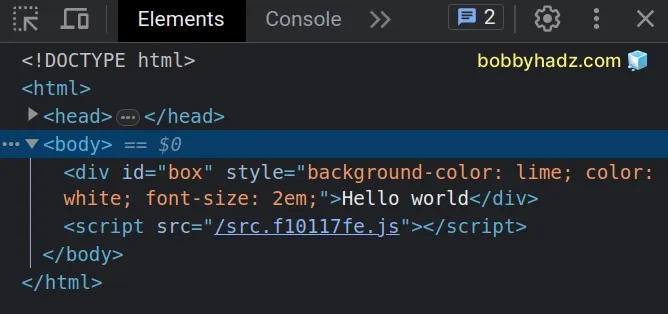
We used the document.getElementById
method to select the element. The method returns null if no element with the
provided id exists in the DOM, so we had to make sure the box variable
doesn't store a null value before accessing any properties on it.
# Using document.getElementsByClassName()
If you use the document.getElementsByClassName method instead, type the elements as a collection of HTML elements.
const boxes = Array.from( document.getElementsByClassName('box') as HTMLCollectionOf<HTMLElement>, ); boxes.forEach(box => { box.style.backgroundColor = 'lime'; box.style.color = 'white'; box.style.fontSize = '2em'; });
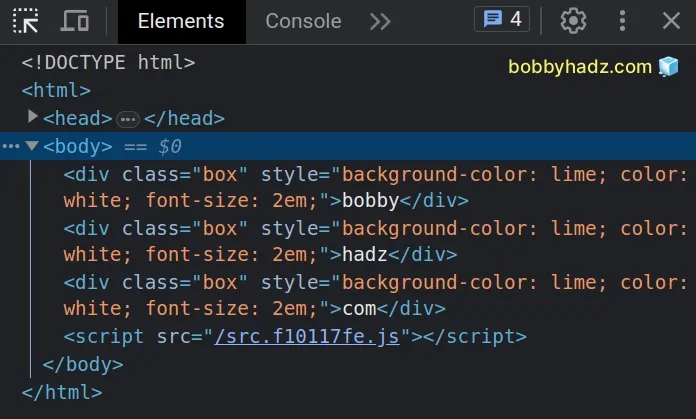
The getElementsByClassName method returns a type of
HTMLCollectionOf<Element> and the Element
interface doesn't contain the
style property.
This is why we used a
type assertion
to type the collection as HTMLCollectionOf<HTMLElement>.
We used the style object to set CSS properties on the element.
style object.# Using the setProperty() method instead
If you don't like CSS property names being camel-cased, you can use the setProperty method instead.
// 👇️ const box: HTMLElement | null const box = document.getElementById('box'); if (box != null) { box.style.setProperty('background-color', 'lime'); box.style.setProperty('color', 'white'); }
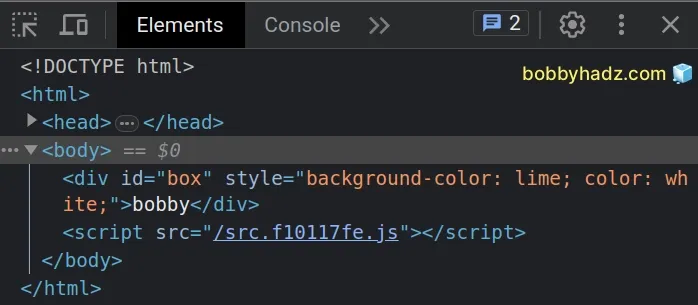
The setProperty method takes the following 3 parameters:
propertyName- the name of the CSS property we want to modify. Note that property names of multiple words must be hyphenated.value- the new value for the CSS property.priority- can be set toimportantor an empty string.
I've also written an article on how to pass CSS styles as props in React TypeScript.
# Using the style property to read CSS property values
You can also use the style object to read CSS property values from the
element.
// 👇️ const box: HTMLElement | null const box = document.getElementById('box'); if (box != null) { box.style.setProperty('background-color', 'lime'); // 👇️ "lime" console.log(box.style.backgroundColor); // 👇️ "16px" console.log(window.getComputedStyle(box).fontSize); }
The first example reads the value of the background color property on the element.
However, this wouldn't work if the property was not set as an inline style on the element.
window.getComputedStyle method instead.The getComputedStyle method returns an object that contains the values of all
CSS properties of the passed-in element, after applying stylesheets.
I've also written an article on how to add a class to an element in React.
If you need to show/hide an element in TypeScript, check out the following article.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

