How to Check the Type of a Variable in TypeScript
Last updated: Feb 28, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Check the Type of a Variable in TypeScript
- Check the Type of a Variable using
instanceof - Using a type predicate to check the type of a variable
- Checking if a variable stores an Array
- Checking if a variable stores a NaN value
- Checking if a variable stores
null - The
typeofoperator always returns a string
# Check the Type of a Variable in TypeScript
Use the typeof operator to check the type of a variable in TypeScript.
The typeof operator returns a string that indicates the type of the value
and can be used as a type guard in TypeScript.
const myVar: string | number = 'bobbyhadz.com'; console.log(typeof myVar); // 👉️ "string" if (typeof myVar === 'string') { console.log(myVar.toUpperCase()); // 👉️ "BOBBYHADZ.COM" }
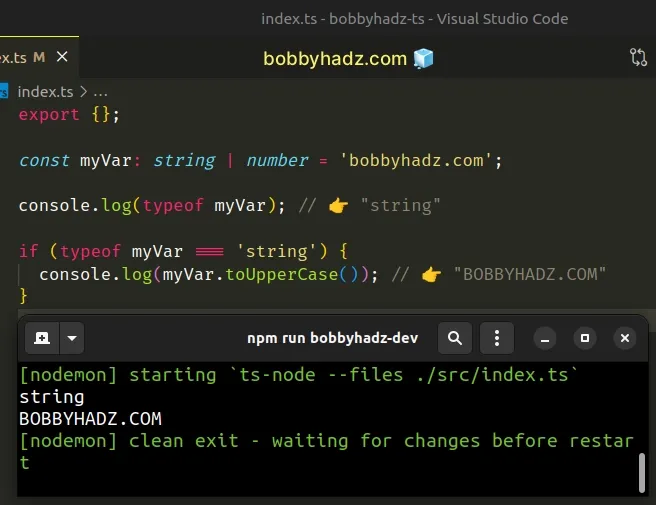
We used the typeof operator to check the type of a variable in TypeScript.
The operator returns a string that indicates the type of the value and can be
used as a
type guard.
const myVar: string | number = Math.random() > 0.5 ? 'Hello' : 1000; // 👉️ myVar has type string or number here if (typeof myVar === 'string') { // 👇️ myVar has type string here console.log(myVar.toUpperCase()); } else { // 👇️ myVar has type number here console.log(myVar.toFixed(2)); }
The variable is typed using a union and can have a type of string or number.
We can't directly access string built-in methods on the variable because it might be a number.
if statement checks if the type of the variable is a string, so TypeScript knows the variable stores a string in the if block.The only other possible type the variable might store is a number, so the
variable is typed as a number in the else block.
Here are some examples of using the typeof operator.
console.log(typeof 'bobbyhadz.com'); // 👉️ "string" console.log(typeof 100); // 👉️ "number" console.log(typeof true); // 👉️ "boolean" console.log(typeof [1, 2, 3]); // 👉️ "object" console.log(typeof {}); // 👉️ "object" console.log(typeof function example() {}); // 👉️ "function" console.log(typeof NaN); // 👉️ "number" console.log(typeof undefined); // 👉️ "undefined" console.log(typeof null); // 👉️ "object" console.log(typeof class A {}); // 👉️ "function"
Notice that using the typeof operator with an array returns object.
# Check the Type of a Variable using instanceof
If you need to check if a variable stores an instance of a specific class, use
the instanceof operator.
class Person {} const person = new Person(); if (person instanceof Person) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('value is an instance of Person'); }
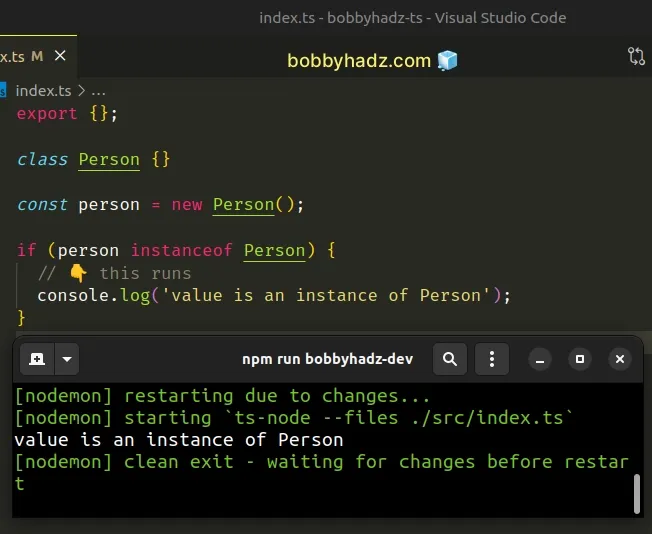
The syntax for the
instanceof
operator is object instanceof constructor.
The operator returns true if the prototype property of the constructor
appears anywhere in the prototype chain of the object.
person object was created using the Person class, so it is an instance of the class.The instanceof operator is very useful in TypeScript because it can be used as
a
type guard.
class Person { walk() { console.log('person is walking'); } } class Animal { run() { console.log('animal is running'); } } function example(x: Person | Animal) { // 👉️ x is type Person or Animal here if (x instanceof Person) { // 👇️ x is type Person here x.walk(); } else { // 👇️ x is type Animal here x.run(); } } const p1 = new Person(); const a1 = new Animal(); example(p1); // 👉️ "person is walking" example(a1); // 👉️ "animal is running"
The function takes a parameter of type Person or Animal, so before we access
a class-specific method, we have to check an instance of which class was passed
to the function.
# Using a type predicate to check the type of a variable
You can also use a type predicate to check the type of a variable.
const person = { name: 'Bobby Hadz', country: 'Chile', }; type Person = { name: string; country: string; }; // 👇️ checks if obj has properties of Person function isPerson(obj: Person): obj is Person { return 'name' in obj && 'country' in obj; } let bobby; if (isPerson(person)) { // 👉️ person has type of Person here bobby = person; } else { bobby = { name: '', country: '' }; } console.log(bobby); // 👉️ {name: 'Bobby Hadz', country: 'Chile'}
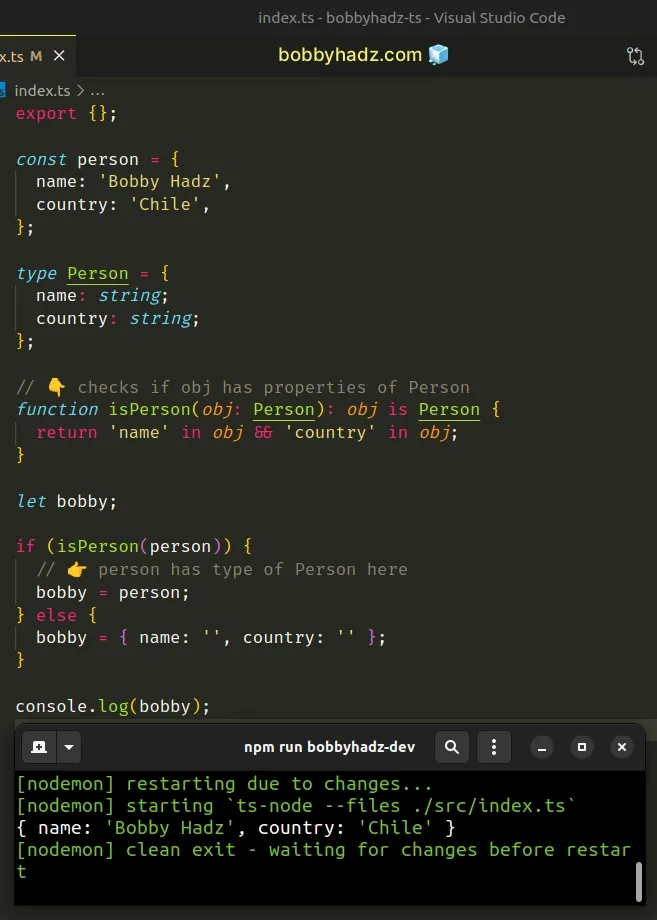
The obj is Person syntax is a
type predicate.
parameter is Type, where parameter is the name of a parameter from the function signature.In the example, we check if the passed-in value has the properties of an object
of type Person.
If the condition is met, we return true from the isPerson function and the
variable gets typed as Person.
# Checking if a variable stores an array
To check if a variable stores an array, use the Array.isArray() method.
const arr: string[] = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']; console.log(Array.isArray(arr)); // 👉️ true
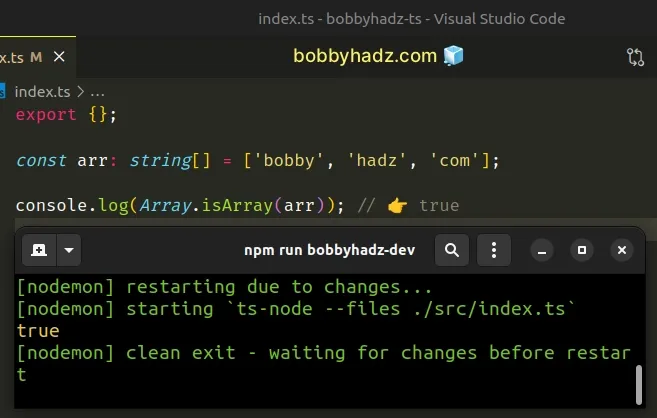
The Array.isArray() method returns true if the passed-in value is an array
and false otherwise.
I've also written an article on how to check if a value is an array of a specific type.
# Checking if a variable stores a NaN value
The type of NaN (not a number) is number. If you need to check if a specific
value is NaN, use the Number.isNaN method.
const example = Number('bobbyhadz.com'); console.log(example); // 👉️ NaN if (Number.isNaN(example)) { console.log('Passed in value is NaN'); }
The Number.isNaN method will return true if the passed-in value has a type
of number and is NaN.
# Checking if a variable stores null
The typeof operator returns "object" when you do typeof null.
console.log(typeof null); // 👉️ "object"
If you are checking whether a variable stores a null value, don't use the
typeof operator, instead check directly.
const example = null; if (example === null) { console.log('Variable stores a null value'); }
# The typeof operator always returns a string
Note that the typeof operator always returns a string. A very common mistake
is to do something like the following.
const myVar = undefined; if (typeof myVar === undefined) { console.log('myVar is undefined'); } else { console.log('👉️ This block runs'); }
The else block in the example is run because we are checking if the type of
myVar is equal to the value undefined.
This evaluates to false because typeof myVar returns a string of
"undefined" and not the value undefined.
The typeof operator returns "function" for classes. This is because classes
in JavaScript (and TypeScript) are just syntactic sugar for functions.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

