How to disable a Button in TypeScript
Last updated: Feb 29, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Disable a button in TypeScript
To disable a button in TypeScript:
- Select the button element.
- Use the
setAttribute()method to set thedisabledattribute. - For example,
btn?.setAttribute('disabled', '').
Here is the HTML for the examples.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <input id="submit" type="submit" name="submit" /> <button id="btn">bobbyhadz</button> <script src="./src/index.ts"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related TypeScript code.
const input = document.getElementById('submit') as HTMLInputElement | null; // ✅ Set disabled attribute input?.setAttribute('disabled', ''); // ✅ Remove the disabled attribute // input?.removeAttribute('disabled') // ----------------------------------------------------------------- const btn = document.getElementById('btn') as HTMLButtonElement | null; // ✅ Set disabled attribute btn?.setAttribute('disabled', ''); // ✅ Remove the disabled attribute // btn?.removeAttribute('disabled');
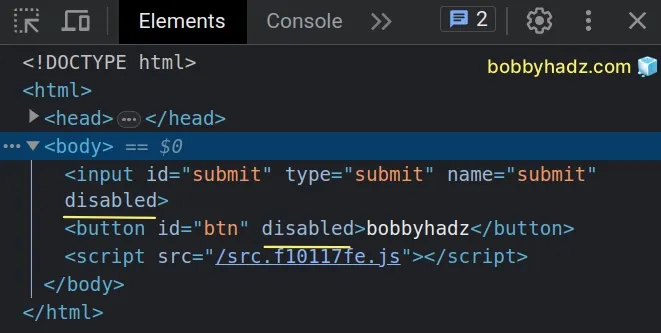
We selected the element using the document.getElementById method.
const input = document.getElementById('submit') as HTMLInputElement | null; const btn = document.getElementById('btn') as HTMLButtonElement | null;
We used a type assertion to type the input and button elements correctly.
Type assertions are used when we have information about the type of a value that TypeScript can't know about.
input variable stores anHTMLInputElement or a null value and not to worry about it.We used a union type to specify
that the variable could still be null because if an HTML element with the
provided id doesn't exist in the DOM, the getElementById() method returns a
null value.
We used the optional chaining (?.) operator to get around the possibly null value in the example.
input?.setAttribute('disabled', ''); btn?.setAttribute('disabled', '');
We used the
setAttribute
method to set the disabled attribute on the element.
The method takes the following 2 parameters:
name- the name of the attribute to be set.value- the value to assign to the attribute.
const input = document.getElementById('submit') as HTMLInputElement | null; // ✅ Set disabled attribute input?.setAttribute('disabled', ''); // ✅ Remove disabled attribute // input?.removeAttribute('disabled') // ----------------------------------------------------------------- const btn = document.getElementById('btn') as HTMLButtonElement | null; // ✅ Set disabled attribute btn?.setAttribute('disabled', ''); // ✅ Remove disabled attribute // btn?.removeAttribute('disabled');
The optional chaining (?.) operator short-circuits returning undefined if the
reference is equal to null or undefined.
input variable stores a null value, we won't attempt to call the setAttribute() method on null and get a runtime error.If the disabled attribute already exists on the element, the setAttribute
method will update the value, otherwise, a new attribute is added with the
specified name and value.
When setting the value of a boolean attribute, such as disabled, we can
specify any value for the attribute and it will work.
true.If a boolean attribute is not present, the value of the attribute is considered
to be false.

I've also written a detailed guide on how to get the value of an input element in TS.
# Removing the disabled attribute
If you need to remove an attribute from the element, use the removeAttribute
method.
const input = document.getElementById('submit') as HTMLInputElement | null; // ✅ Set disabled attribute input?.setAttribute('disabled', ''); // ✅ Remove disabled attribute input?.removeAttribute('disabled'); // ----------------------------------------------------------------- const btn = document.getElementById('btn') as HTMLButtonElement | null; // ✅ Set disabled attribute btn?.setAttribute('disabled', ''); // ✅ Remove disabled attribute btn?.removeAttribute('disabled');
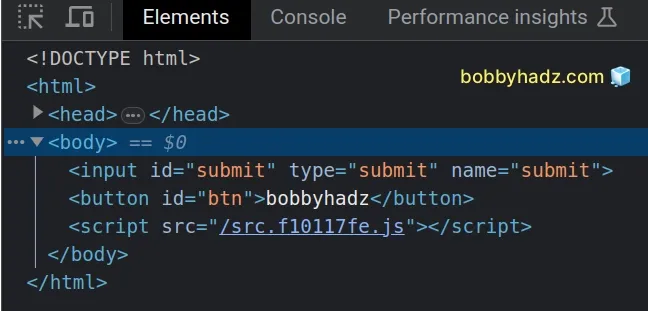
disabled attribute, we pass an empty string as the value for the attribute because it's a best practice to set boolean attributes without a value.If the attribute is not set on the element, the removeAttribute method returns
without throwing an error.
# Using an if statement as a type guard
If you don't want to use the optional chaining (?.) operator, you can use a
simple if statement that serves as a
type guard.
const input = document.getElementById('submit') as HTMLInputElement | null; // 👉️ input has type HTMLInputElement or null here if (input != null) { // 👉️ input has type HTMLInputElement here // ✅ Set disabled attribute input.setAttribute('disabled', ''); // ✅ Remove disabled attribute // input.removeAttribute('disabled'); }
We explicitly check that the input variable does not store a null value.
TypeScript knows that the input variable has a type of HTMLInputElement in
the if block and allows us to directly call the setAttribute() method.
Which approach you pick to exclude null from the type before calling the
setAttribute() method is a matter of personal preference.
However, it's always a best practice to include null in the type assertion,
because the getElementById method would return null if no element with the
provided id was found.
If you need to add a click event listener to a button, check out the following article.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

