TypeError: Object of type bytes is not JSON serializable
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# TypeError: Object of type bytes is not JSON serializable
The Python "TypeError: Object of type bytes is not JSON serializable" occurs when we try to convert a bytes object to a JSON string.
To solve the error, call the decode() method on the bytes object to decode
the bytes to a string before serializing to JSON.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import json my_bytes = 'bobbyhadz.com'.encode('utf-8') # ⛔️ TypeError: Object of type bytes is not JSON serializable json_str = json.dumps({'message': my_bytes})
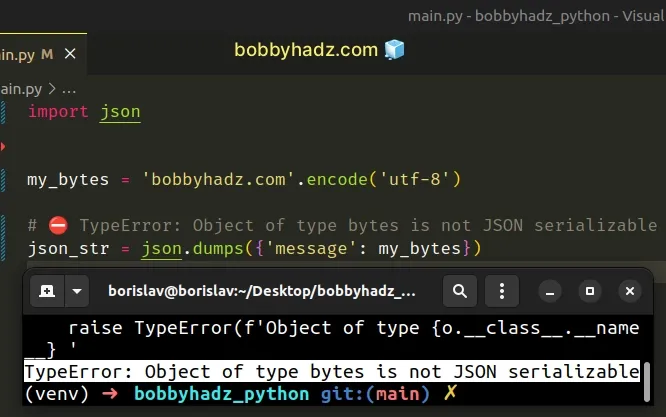
We tried passing a bytes object to the json.dumps() method but the method
doesn't handle bytes objects by default.
# Remove the call to encode to solve the error
To solve the error, either remove the call to the encode() method or use the
decode() method to decode the bytes object to a string.
import json my_bytes = 'bobbyhadz.com'.encode('utf-8') # ✅ Decode the bytes object json_str = json.dumps({'message': my_bytes.decode('utf-8')}) print(json_str) # 👉️ '{"message": "bobbyhadz.com"}' print(type(json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
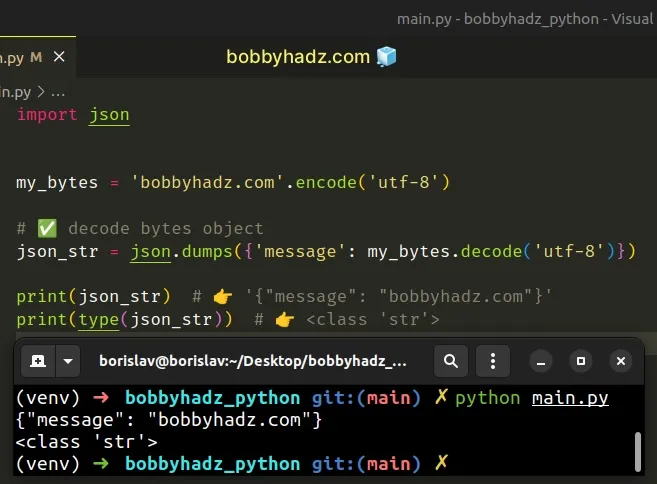
The default JSON encoder handles str values, so we can decode the bytes
object to a string before serializing to JSON.
The json.dumps() method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
The str.encode() method returns an
encoded version of the string as a bytes object. The default encoding is
utf-8.
The bytes.decode() method returns a
string decoded from the given bytes. The default encoding is utf-8.
# Create a custom BytesEncoder class to solve the error
Alternatively, you can extend from the JSONEncoder class and handle the
conversions in a default method.
import json class BytesEncoder(json.JSONEncoder): def default(self, obj): if isinstance(obj, bytes): return obj.decode('utf-8') return json.JSONEncoder.default(self, obj) my_bytes = 'hello world'.encode('utf-8') json_str = json.dumps({'message': my_bytes}, cls=BytesEncoder) print(json_str) # 👉️ '{"message": "hello world"}' print(type(json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
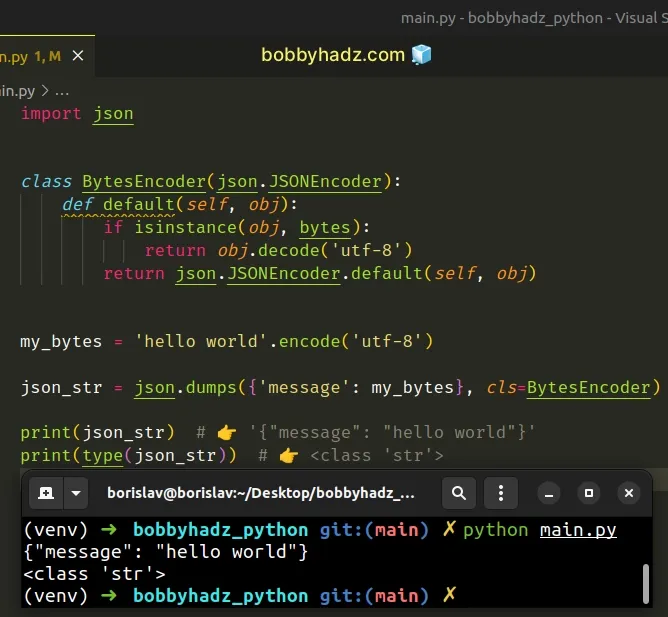
We extended from the JSONEncoder class.
The JSONEncoder class supports the following objects and types by default.
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str | string |
| int, float, int and float derived Enums | number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
Notice that the JSONEncoder class doesn't support bytes to JSON conversion
by default.
We can handle this by extending from the class and implementing a default()
method that returns a serializable object.
import json class BytesEncoder(json.JSONEncoder): def default(self, obj): if isinstance(obj, bytes): return obj.decode('utf-8') return json.JSONEncoder.default(self, obj)
If the passed-in value is a bytes object, we decode it to a str and return
the result.
The isinstance function returns
True if the passed-in object is an instance or a subclass of the passed-in
class.
To use a custom JSONEncoder, specify it with the cls keyword argument in
your call to the json.dumps() method.
import json class BytesEncoder(json.JSONEncoder): def default(self, obj): if isinstance(obj, bytes): return obj.decode('utf-8') return json.JSONEncoder.default(self, obj) my_bytes = 'hello world'.encode('utf-8') # ✅ Pass the cls keyword argument json_str = json.dumps({'message': my_bytes}, cls=BytesEncoder) print(json_str) # 👉️ '{"message": "hello world"}' print(type(json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
If you don't provide the cls kwarg, the default JSONEncoder is used.
# Using the default keyword argument to solve the error
You can also use the default keyword argument in the call to the
json.dumps() method.
import json my_bytes = 'hello world'.encode('utf-8') def json_serializer(obj): if isinstance(obj, bytes): return obj.decode('utf-8') return obj json_str = json.dumps(my_bytes, default=json_serializer) print(json_str) # "hello world" print(type(json_str)) # <class 'str'>
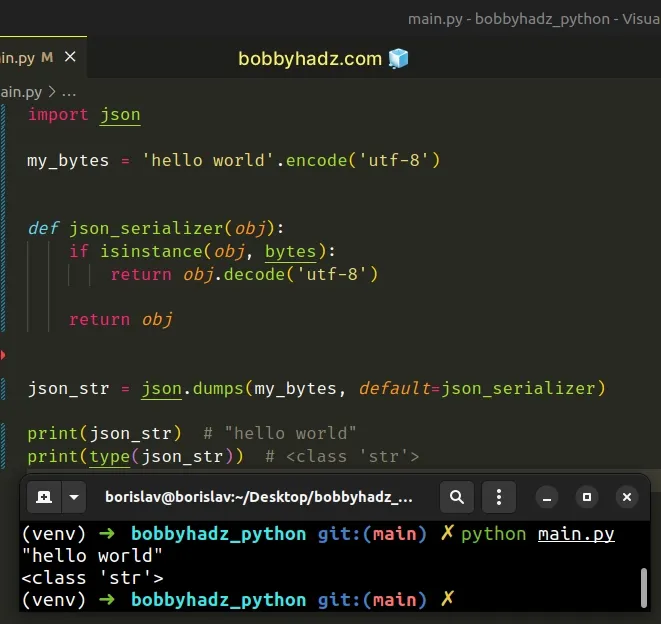
default keyword argument can be set to a function that gets called for objects that can't otherwise be serialized.We defined a custom json_serializer function that checks if the supplied value
is a bytes object.
If the value is a bytes object, we use the decode() method to convert it to a
string.
Otherwise, the value is returned as is.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not dict
- AttributeError: 'bytes' object has no attribute 'encode'
- Cannot use a string pattern on a bytes-like object in Python
- How to convert Bytes to Dictionary in Python
- Generate random bytes of length N in Python
- Get the length of a Bytes object in Python
- TypeError: a bytes-like object is required, not 'str'
- Expected str, bytes or os.PathLike object, not NoneType
- How to convert Dataclass to JSON in Python

