The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not dict
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·9 min

# Table of Contents
- The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not DICT
- The JSON object must be str or bytes not TextIOWrapper
- The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not LIST
- The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray not RESPONSE
Make sure to click on the correct subheading depending on your error message
# The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not dict
The Python "TypeError: the JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not
dict" occurs when we pass a dictionary to the json.loads() method.
To solve the error, remove the call to json.loads() and use the
json.dumps() method if trying to convert the dict to a JSON string.
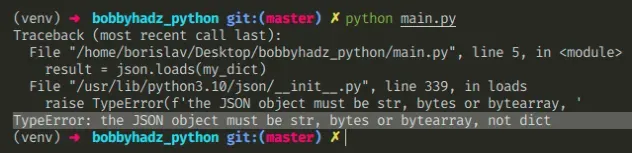
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import json my_dict = {'name': 'Bobby Hadz', 'age': 30} # ⛔️ TypeError: the JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not dict result = json.loads(my_dict)
The json.loads method parses a JSON string into a native Python object.
json.loads() method.# Converting a dictionary to a JSON string
If you need to convert a dictionary to a JSON string, use the json.dumps()
method.
import json my_dict = {'name': 'Bobby Hadz', 'age': 30} my_json_str = json.dumps(my_dict) print(my_json_str) # 👉️ '{"name": "Bobby Hadz", "age": 30}' print(type(my_json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
The json.dumps() method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
In other words, if you need to parse a JSON string into a native Python object,
you have to use the json.loads() method.
# Converting a JSON string to a native Python object
If you need to convert a Python object to a JSON string, you have to use the
json.dumps() method.
import json json_str = r'{"name": "Alice", "age": 30}' # ✅ Parse JSON string to a Python native dict my_dict = json.loads(json_str) print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'> # ✅ Convert Python native dict to a JSON string my_json_str = json.dumps(my_dict) print(type(my_json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
The json.loads() method helps us load a Python native object (e.g. a
dictionary or a list) from a JSON string.
# Using the json.load method to read from a JSON file
If you need to read from a JSON file, use the json.load() method.
import json file_name = 'example.json' with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: my_data = json.load(f) print(my_data) # 👉️ {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} print(my_data['name']) # 👉️ 'Alice' print(type(my_data)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'>
The code sample above assumes that you have an example.json file in the same
directory.
{"name": "Alice", "age": 30}
The json.load() method is used to deserialize a file to a Python object, whereas the json.loads() method is used to deserialize a JSON string to a Python object.
The json.load() method expects a text file or a binary file containing a JSON
document that implements a .read() method.
Here is the equivalent example if you use the open() function without the
with statement.
import json file_name = 'example.json' json_file = open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') json_data = json.load(json_file) print(json_data) # 👉️ {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} print(json_data['name']) # 👉️ 'Alice' print(type(json_data)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'> json_file.close()
The code sample achieves the same result but uses the
open() function
without the with statement.
The with statement takes care of automatically closing the file for us, but
when using the open() function directly, we have to close the file manually.
# You can convert the following Python objects to JSON
The JSONEncoder class supports the following objects and types by default.
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str | string |
| int, float, int and float derived Enums | number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
If you aren't sure what type of object a variable stores, use the built-in
type() class.
my_dict = {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'> print(isinstance(my_dict, dict)) # 👉️ True my_str = 'hello world' print(type(my_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'> print(isinstance(my_str, str)) # 👉️ True
The type class returns the type of an object.
The isinstance function returns
True if the passed-in object is an instance or a subclass of the passed-in
class.
# Table of Contents
- The JSON object must be str or bytes not TextIOWrapper
- The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not LIST
- The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray not RESPONSE
# The JSON object must be str or bytes not TextIOWrapper
The Python "TypeError: the JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not
TextIOWrapper" occurs when we pass a file object to the json.loads() method.
To solve the error, pass the file object to the json.load() method
instead.
Traceback (most recent call last): File "/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/main.py", line 7, in <module> my_data = json.loads(f) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ File "/usr/lib/python3.11/json/__init__.py", line 339, in loads raise TypeError(f'the JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, ' TypeError: the JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not TextIOWrapper
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import json file_name = 'example.json' with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: # ⛔️ TypeError: the JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not TextIOWrapper my_data = json.loads(f)
# Using the json.load() method to deserialize a JSON file
We can't pass a file object directly to the json.loads() method, but we can
use the json.load() method to deserialize a file to a Python object.
import json file_name = 'example.json' with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: my_data = json.load(f) print(my_data) # 👉️ {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} print(type(my_data)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'>
The code sample assumes that you have an example.json file in the same
directory.
{"name": "Alice", "age": 30}
The json.load() method is used to deserialize a file to a Python object, whereas the json.loads() method is used to deserialize a JSON string to a Python object.
The json.load() method expects a text file or a binary file containing a JSON
document that implements a .read() method.
# Manually calling the file.read() method with json.loads()
Alternatively, you manually call the read() method on the file object and use
the json.loads() method.
import json file_name = 'example.json' with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: # 👇️ make sure to call read() my_data = json.loads(f.read()) print(my_data) # 👉️ {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} print(type(my_data)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'>
The example above achieves the same result.
However, instead of relying on the json.load() method to call read() on the
file object for us, we manually do it and use the json.loads() method instead.
If you need to parse a JSON string into a native Python object, you have to use
the json.loads() method.
if you need to convert a Python object to a JSON string, you have to use the
json.dumps() method.
import json json_str = r'{"name": "Alice", "age": 30}' # ✅ Parse JSON string to Python native dict my_dict = json.loads(json_str) print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'> # ✅ Convert Python native dict to a JSON string my_json_str = json.dumps(my_dict) print(type(my_json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
The json.loads() method basically helps us load a Python native object (e.g. a
dictionary or a list) from a JSON string.
The JSONEncoder class supports the following objects and types by default.
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str | string |
| int, float, int and float derived Enums | number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
# Checking what type a variable stores
If you aren't sure what type of object a variable stores, use the built-in
type() class.
my_dict = {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'> print(isinstance(my_dict, dict)) # 👉️ True my_str = 'hello world' print(type(my_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'> print(isinstance(my_str, str)) # 👉️ True
The type class returns the type of an object.
The isinstance function returns
True if the passed-in object is an instance or a subclass of the passed-in
class.
# Table of Contents
- The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not LIST
- The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray not RESPONSE
# The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not list
The Python "TypeError: the JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not
list" occurs when we pass a list to the json.loads() method.
To solve the error, remove the call to json.loads() and use the
json.dumps() method if trying to convert the list to a JSON string.
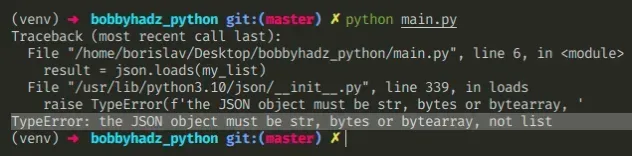
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import json my_list = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl'] # ⛔️ TypeError: the JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not list result = json.loads(my_list)
The json.loads() method parses a JSON string into a native Python object.
json.loads() method.# Converting the list to a JSON string
If you need to convert a list to a JSON string, use the json.dumps() method.
import json my_list = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl'] my_json_str = json.dumps(my_list) print(my_json_str) # 👉️ '["Alice", "Bob", "Carl"]' print(type(my_json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
The json.dumps() method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
If you need to parse a JSON string to a native Python object, you have to use
the json.loads() method.
If you need to convert a Python object to a JSON string, you have to use the
json.dumps() method.
import json json_str = r'["Alice", "Bob", "Carl"]' my_list = json.loads(json_str) print(type(my_list)) # 👉️ <class 'list'> my_json_str = json.dumps(my_list) print(type(my_json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
The json.loads() method basically helps us load a Python native object (e.g. a
list or a dictionary) from a JSON string.
# Reading a list from a JSON file
If you need to read from a JSON file, use the json.load() method.
import json file_name = 'example.json' with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: my_data = json.load(f) print(my_data) # 👉️ ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl'] print(my_data[0]) # 👉️ 'Alice' print(type(my_data)) # 👉️ <class 'list'>
The code sample above assumes that you have an example.json file in the same
directory.
["Alice", "Bob", "Carl"]
The json.load() method is used to deserialize a file to a Python object, whereas the json.loads() method is used to deserialize a JSON string to a Python object.
The json.load() method expects a text file or a binary file containing a JSON
document that implements a .read() method.
The JSONEncoder class supports the following objects and types by default.
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str | string |
| int, float, int and float derived Enums | number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
# Checking the type of a variable
If you aren't sure what type of object a variable stores, use the built-in
type() class.
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] print(type(my_list)) # 👉️ <class 'list'> print(isinstance(my_list, list)) # 👉️ True my_str = 'hello' print(type(my_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'> print(isinstance(my_str, str)) # 👉️ True
The type class returns the type of an object.
The isinstance function returns
True if the passed-in object is an instance or a subclass of the passed-in
class.
# The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray not Response
The Python "TypeError: the JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not
Response" occurs when we pass a Response object to the json.loads()
method.
To solve the error, call the json() method on the Response object instead,
e.g. result = res.json().
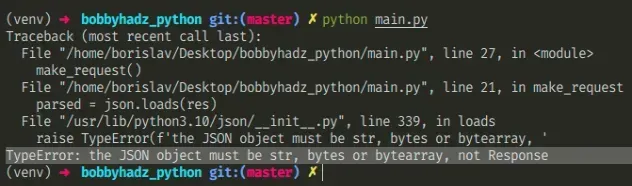
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import json import requests def make_request(): res = requests.get('https://reqres.in/api/users') # ⛔️ TypeError: the JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not Response parsed = json.loads(res) make_request()
We passed a Response object to the json.loads() method which caused the
error.
# Use the json() method to parse the response
To solve the error, use the json() method on the response object instead.
import requests def make_request(): res = requests.get('https://reqres.in/api/users') # ✅ call .json() method on Response object parsed = res.json() print(parsed) print(type(parsed)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'> make_request()
json() method on the Response object to parse it into a native Python object before accessing any of its keys.You should use the json() method to parse the data from all requests, not just
HTTP GET.
# Making an HTTP Post request with the requests module
Here is an example of a POST request with the requests module.
import requests def make_request(): res = requests.post( 'https://reqres.in/api/users', data={'name': 'John Smith', 'job': 'manager'} ) # ✅ Parse the JSON response to native Python object data = res.json() # 👇️ {'name': 'John Smith', 'job': 'manager', 'id': '649', 'createdAt': '2022-05-20T10:11:23.939Z'} print(data) print(data['name']) # 👉️ "John Smith" print(data['job']) # 👉️ "manager" print(data['id']) # 649 make_request()
If you are working with a JSON string or a native Python object, make sure to
use the json.loads() and json.dumps() methods.
If you need to parse a JSON string to a native Python object, you have to use
the json.loads() method.
If you need to convert a Python object into a JSON string, you have to use the
json.dumps() method.
import json json_str = r'{"name": "Alice", "age": 30}' # ✅ Parse the JSON string to Python native dict my_dict = json.loads(json_str) print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'> # ✅ Convert the Python native dict to a JSON string my_json_str = json.dumps(my_dict) print(type(my_json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
The json.loads() method basically helps us load a Python native object (e.g. a
dictionary or a list) from a JSON string.
The json.dumps() method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
The JSONEncoder class supports the following objects and types by default.
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str | string |
| int, float, int and float derived Enums | number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
# Checking the type of a variable
If you aren't sure what type of object a variable stores, use the built-in
type() class.
my_dict = {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'> print(isinstance(my_dict, dict)) # 👉️ True my_str = 'hello world' print(type(my_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'> print(isinstance(my_str, str)) # 👉️ True
The type class returns the type of an object.
The isinstance() function
returns True if the passed-in object is an instance or a subclass of the
passed-in class.

