Get the length of a Bytes object in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
# Get the length of a Bytes object in Python
Use the len() function to get the length of a bytes object.
The len() function returns the length (the number of items) of an object and
can be passed a sequence (a bytes, string, list, tuple or range) or a collection
(a dictionary, set, or frozen set).
my_bytes = 'hello'.encode('utf-8') print(type(my_bytes)) # 👉️ <class 'bytes'> print(len(my_bytes)) # 👉️ 5
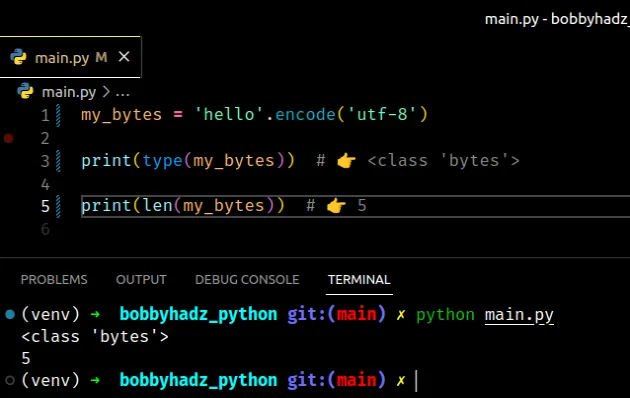
The len() function returns the length (the number of items) of an object.
Here is another example with some special characters.
my_bytes = 'éé'.encode('utf-8') print(type(my_bytes)) # 👉️ <class 'bytes'> print(len(my_bytes)) # 👉️ 4
The same approach can be used to get the length of a bytearray.
my_byte_array = bytearray('hello', encoding='utf-8') print(len(my_byte_array)) # 👉️ 5
If you need to get the size of an object, use the sys.getsizeof() method.
import sys my_bytes = 'hello'.encode('utf-8') print(sys.getsizeof(my_bytes)) # 👉️ 38 print(sys.getsizeof('hello')) # 👉️ 54
The sys.getsizeof() method returns the size of an object in bytes.
The object can be any type of object and all built-in objects return correct results.
The getsizeof method only accounts for the direct memory consumption of the
object, not the memory consumption of objects it refers to.
The getsizeof() method calls the __sizeof__ method of the object, so it
doesn't handle custom objects that don't implement it.
# Get the size of a String in Python
If you need to get the size of a string:
- Use the
len()function to get the number of characters in the string. - Use the
sys.getsizeof()method to get the size of the string in memory. - Use the
string.encode()method andlen()to get the size of the string in bytes.
import sys string = 'bobby' # ✅ Get the length of the string (number of characters) print(len(string)) # 👉️ 5 # ------------------------------------------ # ✅ Get the memory size of the object in bytes print(sys.getsizeof(string)) # 👉️ 54 # ------------------------------------------ # ✅ Get size of string in bytes my_bytes = len(string.encode('utf-8')) print(my_bytes) # 👉️ 5 print(len('őŴœ'.encode('utf-8'))) # 👉️ 6
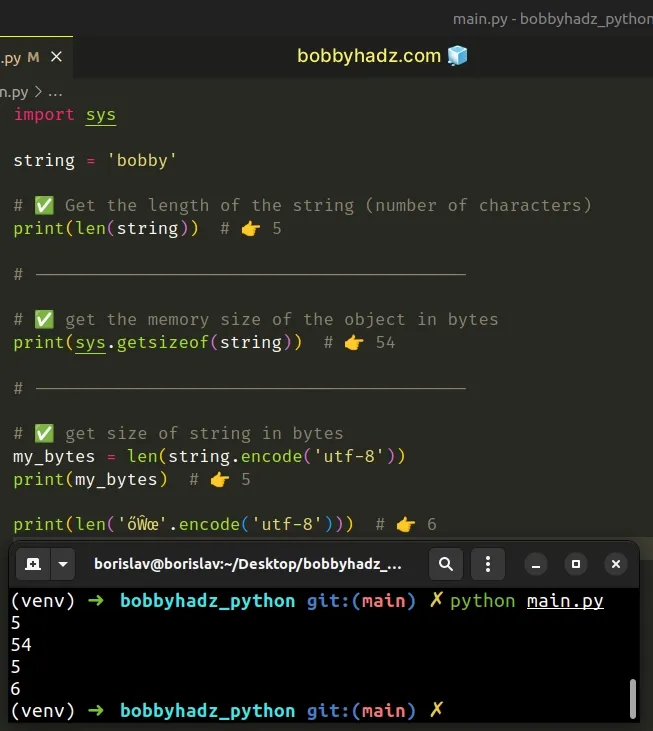
Use the len() function if you need to get the number of characters in a
string.
print(len('ab')) # 👉️ 2 print(len('abc')) # 👉️ 3
The len() function returns the length (the number of items) of an object.
The argument the function takes may be a sequence (a string, tuple, list, range or bytes) or a collection (a dictionary, set, or frozen set).
sys.getsizeof() method.import sys print(sys.getsizeof('bobby')) # 👉️ 54 print(sys.getsizeof('a')) # 👉️ 50
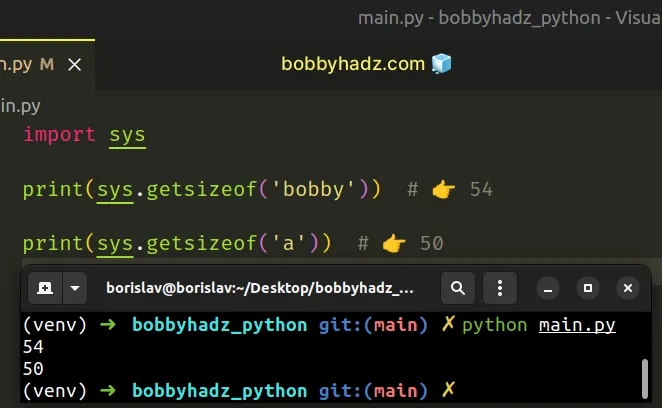
The sys.getsizeof() method returns the size of an object in bytes.
The object can be any type of object and all built-in objects return correct results.
The getsizeof method only accounts for the direct memory consumption of the
object, not the memory consumption of objects it refers to.
The getsizeof() method calls the __sizeof__ method of the object, so it
doesn't handle custom objects that don't implement it.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Generate random bytes of length N in Python
- How to convert Bytes to Dictionary in Python
- Cannot use a string pattern on a bytes-like object in Python
- AttributeError: 'bytes' object has no attribute 'encode'
- The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not dict
- Python binascii.Error: Incorrect padding
- How to convert from HEX to ASCII in Python [5 Ways]

