Make includes() case insensitive in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 1, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Make includes() case insensitive in JavaScript
- Ignoring case Check if Array contains String - Array.findIndex
- Ignoring Case Check if Array contains String - Array.some()
- Ignoring Case Check if Array contains String - Array.find()
- Perform a case-insensitive check if a string is in an array using filter()
# Make includes() case insensitive in JavaScript
To make the String.includes() method case insensitive, convert both of the
strings in the comparison to lowercase.
A case-insensitive comparison is done by converting the two strings to the same case.
const str = 'HELLO WORLD'; const substr = 'hELLo'; // 👇️ true console.log(str.toLowerCase().includes(substr.toLowerCase())); if (str.toLowerCase().includes(substr.toLowerCase())) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The substring is contained in the string'); } else { console.log('The substring is NOT contained in the string'); }
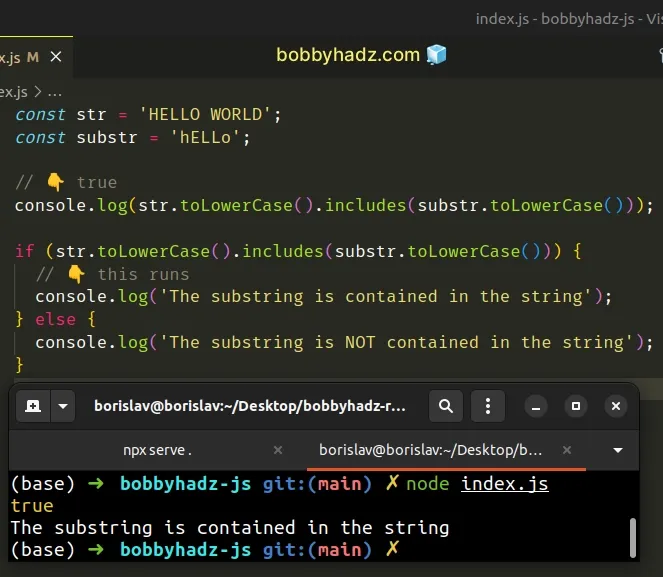
We converted both strings to lowercase to perform a case-insensitive lookup using the String.includes method.
We could achieve the same result by converting the strings to uppercase.
const str = 'HELLO WORLD'; const substr = 'hELLo'; // 👇️ true console.log(str.toUpperCase().includes(substr.toUpperCase())); if (str.toUpperCase().includes(substr.toUpperCase())) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The substring is contained in the string'); } else { console.log('The substring is NOT contained in the string'); }
We just need the strings to be in the same case to be able to determine if the substring is contained in the string.
# Ignoring case Check if Array contains String - Array.findIndex
To do a case insensitive check if an array contains a string:
- Use the
Array.findIndex()method to iterate over the array. - Convert each array element and the string to lowercase and check for equality.
- If the condition is met, the element's index is returned.
const names = ['John', 'Bob', 'Adam']; const name = 'ADAM'; const index = names.findIndex(element => { return element.toLowerCase() === name.toLowerCase(); }); console.log(index); // 👉️ 2 if (index !== -1) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The string is contained in the array'); } else { console.log('The string is NOT contained in the array'); }
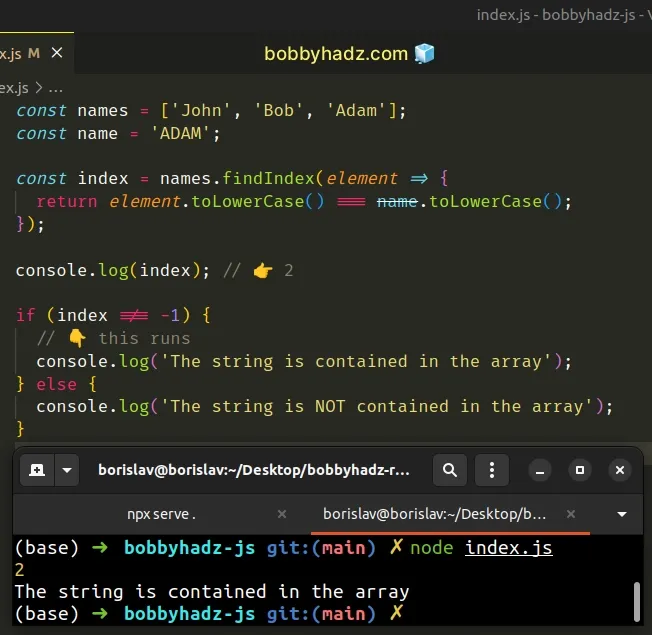
The function we passed to the Array.findIndex method gets called with each element in the array until it returns a truthy value or iterates over the entire array.
Once the callback function returns a truthy value, the element's index is
returned from findIndex().
The function in the example returned 2 because the 3rd element in the array
matched the string.
If the function we passed to findIndex never returns a truthy value, then
findIndex returns -1.
const names = ['John', 'Bob', 'Adam']; const name = 'Tim'; const result = names.findIndex(element => { return element.toLowerCase() === name.toLowerCase(); }); console.log(result); // 👉️ -1
Alternatively, you can use the Array.some() method.
# Ignoring Case Check if Array contains String - Array.some()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Array.some()method to iterate over the array. - Convert each array element and the string to lowercase and check for equality.
- If the condition is met,
trueis returned.
const names = ['John', 'Bob', 'Adam']; const name = 'JOHN'; const includesValue = names.some(element => { return element.toLowerCase() === name.toLowerCase(); }); console.log(includesValue); // 👉️ true
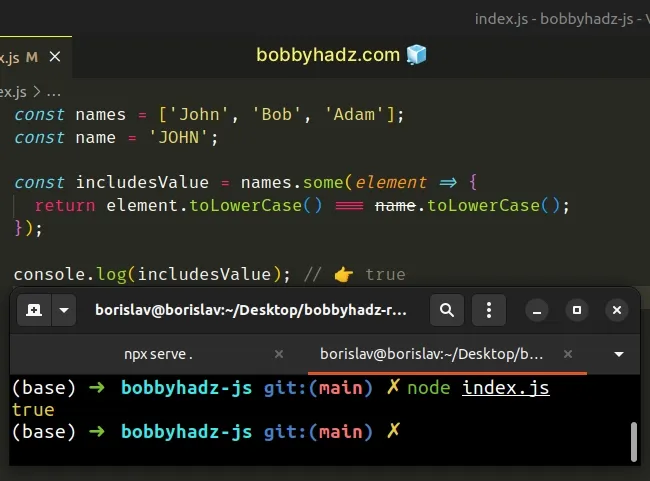
The difference between Array.findIndex() and Array.some() is that some
returns true or false, instead of the index of the array element or -1.
The function we passed to the Array.some() method is called with each element of the array until a truthy value is returned or the array's values are exhausted.
An alternative would be to convert both strings to uppercase to achieve the same result.
Alternatively, you can use the Array.find() method.
# Ignoring Case Check if Array contains String - Array.find()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Array.find()method to iterate over the array. - Convert each array element and the string to lowercase and check for equality.
- If the condition is met, the matching element is returned.
const names = ['John', 'Bob', 'Adam']; const name = 'ADAM'; const result = names.find(element => { return element.toLowerCase() === name.toLowerCase(); }); console.log(result); // 👉️ 'Adam'
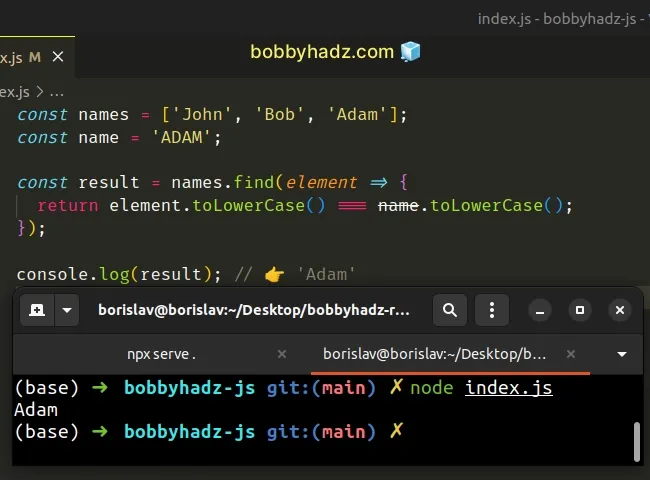
The function we passed to the Array.find method gets called with each element in the array until it returns a truthy value or iterates over the entire array.
If the callback function returns a truthy value, the corresponding element is
returned from the Array.find() method.
If all invocations of the callback function return a falsy value, the
Array.find() method returns undefined.
# Perform a case-insensitive check if a string is in an array using filter()
If you need to perform a case-insensitive check whether a string is contained in an array and get all matches:
- Use the
Array.filter()method to iterate over the array. - On each iteration, lowercase the array element and the string it should be compared to.
- The
Array.filtermethod will return an array of all of the elements that satisfy the condition
const arr = ['HELLO', 'HeLlO', 'WORLD']; const str = 'HeLLo'; const matches = arr.filter(element => { return element.toLowerCase() === str.toLowerCase(); }); console.log(matches); // 👉️ ['HELLO', 'HeLlO'] if (matches.length > 0) { // 👉️ at least 1 match found in the array }
The function we passed to the Array.filter method gets called with each element of the array.
The Array.filter() method does not stop iterating once the callback function
returns a truthy value. It returns an array of all elements that satisfy the
condition.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

