Check if Array Contains an Object in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 1, 2024
Reading time·9 min

# Table of Contents
- Check if an Array contains an Object with Array.some()
- Check if an Array Contains an Object with Array.find()
- Check if an Array Contains an Object with Array.findIndex()
- Check if an Array Contains an Object with Array.filter()
- Check if an Array Contains an Object with Array.includes()
- Check if an Array Contains an Object using a
for...ofloop - Check if an Array Contains an Object using a
forloop - Check if an Object is NOT contained in an array in JavaScript
- Check if a Value is NOT in an Array in JavaScript
- Check if a Value is NOT in an Array using indexOf
# Check if an Array contains an Object with Array.some()
To check if a JavaScript array contains an object:
- Use the
Array.some()method to iterate over the array. - Check if each object contains a property with the specified value.
Array.some()will returntrueif the object is contained in the array.
const people = [ {id: 1, name: 'John'}, {id: 2, name: 'Adam'}, ]; const isFound = people.some(element => { if (element.id === 1) { return true; } return false; }); console.log(isFound); // 👉️ true if (isFound) { // object is contained in the array }
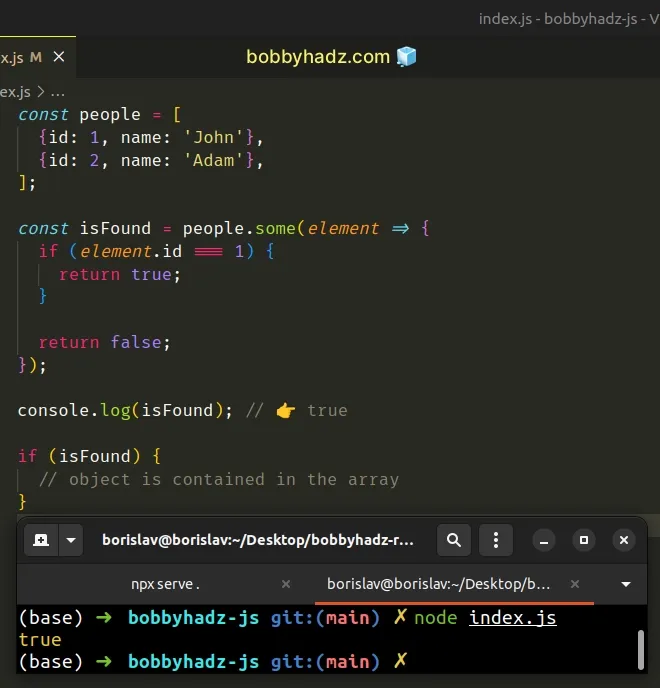
The function we passed to the Array.some() method gets called with each value (object) in the array.
Array.some method short-circuits and returns true.On each iteration, we check if the current object has an id property with a
value of 1.
If the condition is met, we return true, otherwise, we return false.
If the Array.some() method returns true, the object is contained in the
array.
If you need to get the matching object, use the Array.find() method.
# Check if an Array Contains an Object with Array.find()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Array.find()method to iterate over the array. - Check if each object contains a property with the specified value.
Array.find()will return the object if the object is contained in the array.
const people = [ {id: 1, name: 'John'}, {id: 2, name: 'Adam'}, ]; const person = people.find(element => { if (element.id === 1) { return true; } return false; }); console.log(person); // 👉️ { id: 1, name: 'John' } if (person !== undefined) { // 👉️ object is contained in the array }
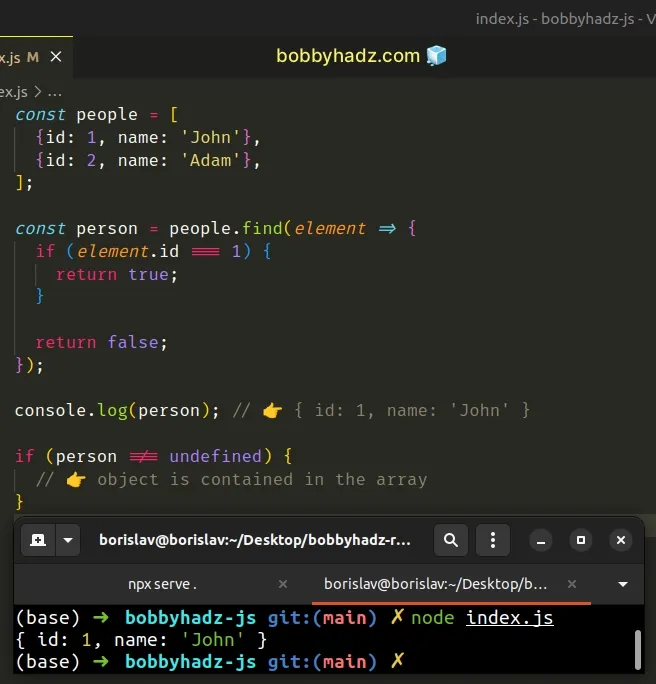
The function we passed to the Array.find() method gets called with each element in the array until it returns a truthy value or iterates over the entire array.
Array.find() method returns the corresponding array element, otherwise, it returns undefined.There is an object with an id of 1, so the find() method returns the
object.
Array.find() method instead of Array.some() when you need to access additional properties on the object.If you need to get the index of the matching object, use the Array.findIndex()
method.
# Check if an Array Contains an Object with Array.findIndex()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Array.findIndex()method to iterate over the array. - Check if each object contains a property with the specified value.
- The
findIndex()method will return the index of the object in the array, or-1if the object isn't in the array.
const people = [ {id: 1, name: 'John'}, {id: 2, name: 'Adam'}, ]; const index = people.findIndex(element => { if (element.id === 1) { return true; } return false; }); console.log(index); // 👉️ 0 if (index !== -1) { // 👉️ object is contained in the array }
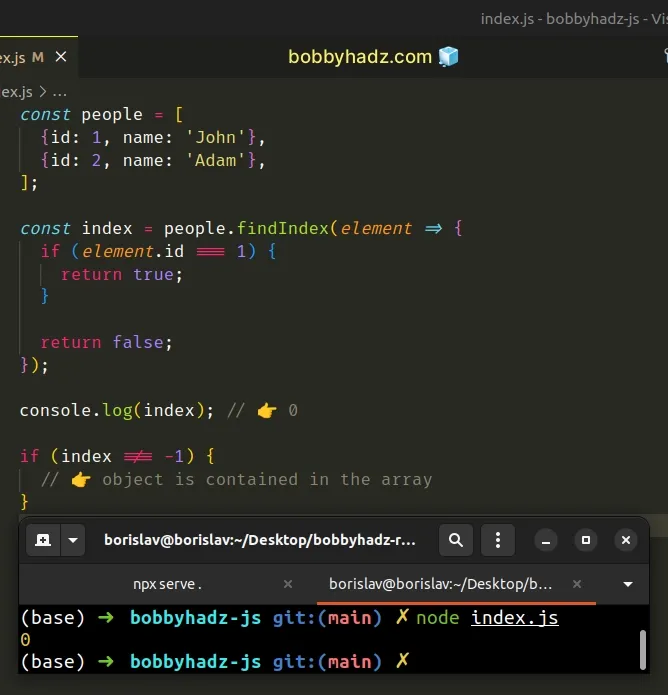
The Array.findIndex()
method is very similar to the Array.find() method, but it returns the index of
the element that satisfies the condition and not the element itself.
The Array.findIndex() method calls its callback function with each element in
the array until a truthy value is returned or the values in the array are
exhausted.
Array.findIndex() method returns -1 if all calls of the callback function return a falsy value.if you need to get all matching objects, use the Array.filter() method.
# Check if an Array Contains an Object with Array.filter()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Array.filter()method to iterate over the array. - Check if each object contains a property with the specified value.
- The
Array.filter()method will return an array containing the objects that meet the condition (if any).
const people = [ {id: 1, name: 'John'}, {id: 2, name: 'Adam'}, ]; const filteredArray = people.filter(element => { if (element.id === 1) { return true; } return false; }); console.log(filteredArray); // 👉️ [ { id: 1, name: 'John' } ] if (filteredArray.length > 0) { // 👉️ object is contained in the array }
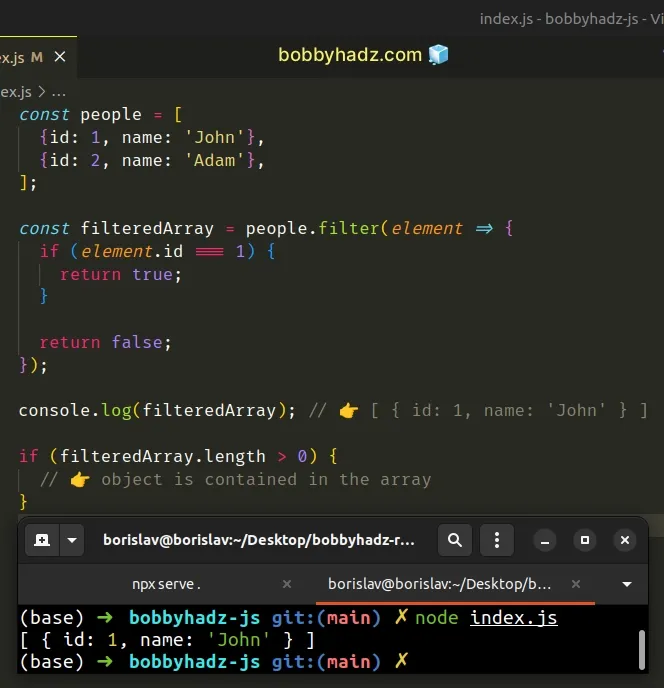
The function we passed to the Array.filter method gets called with each element in the array.
We check if each element (object) in the array contains an id property with a
value of 1. If the new array isn't empty, there are matching objects.
Note that the Array.filter() method returns an array with all of the elements
that meet the condition.
If we had multiple objects with an id equal to 1, all of them would get
included in the new array.
const people = [ {id: 1, name: 'John'}, {id: 2, name: 'Adam'}, {id: 1, name: 'Bobby'}, ]; const filteredArray = people.filter(element => { if (element.id === 1) { return true; } return false; }); // 👇️ [ { id: 1, name: 'John' }, { id: 1, name: 'Bobby' } ] console.log(filteredArray); if (filteredArray.length > 0) { // 👉️ object is contained in the array }
There are multiple objects in the array with an id of 1, so they all get
included in the new array.
You can also use the Array.includes() method to check if an object is
contained in an array.
# Check if an Array Contains an Object with Array.includes()
This is a three-step process:
- Store the object in a variable.
- Push the object into the array.
- Use the
Array.include()method to check if the object is contained in the array.
const obj = {id: 2, name: 'Adam'}; const people = [{id: 1, name: 'John'}]; people.push(obj); if (people.includes(obj)) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The object is contained in the array'); } else { console.log('The object is NOT contained in the array'); }
Note that this approach only works if you have access to the object that was pushed into the array.
The Array.includes() method returns true if the supplied value is contained
in the array and false otherwise.
However, when we use the includes() method with an object, it checks by
reference and not by value.
This wouldn't work if you have an object that has the same key-value pairs but has a different reference.
const people = [{id: 1, name: 'John'}]; // 👇️ false console.log(people.includes({id: 1, name: 'John'}));
The code sample returns false because the object we passed to the
Array.includes() method has a different reference, even though it has the same
key-value pairs.
Only use the includes() method to check if an array contains an object if you
have access to the same object (the same location in memory) that is stored in
the array.
const obj = {id: 2, name: 'Adam'}; const people = [{id: 1, name: 'John'}]; people.push(obj); if (people.includes(obj)) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The object is contained in the array'); } else { console.log('The object is NOT contained in the array'); }
You can also use a for...of loop to check if an array contains an object.
# Check if an Array Contains an Object using a for...of loop
This is a three-step process:
- Use a
for...ofloop to iterate over the array. - Check if each object has a property with the specified value.
- If the condition is met, set a boolean variable to
true.
const people = [ {id: 1, name: 'John'}, {id: 2, name: 'Adam'}, ]; let isContained = false; for (const obj of people) { if (obj.id === 1) { isContained = true; console.log(obj); // 👉️ { id: 1, name: 'John' } break; } } console.log(isContained); // 👉️ true
We declared a new variable and initialized it to false.
The for...of statement is
used to loop over iterable objects like arrays, strings, Map, Set and
NodeList objects and generators.
On each iteration, we check if the current object has an id property with a
value of 1.
isContained variable to true and use the break statement to exit the loop.The break statement helps us avoid iterating over the array needlessly once
we've found the matching object.
You can also use a basic for loop to check if an array contains an object.
# Check if an Array Contains an Object using a for loop
This is a three-step process:
- Use a
forloop to iterate over the array. - Check if the object at the current index has a property with the specified value.
- Set a boolean variable to
trueif the condition is met.
const people = [ {id: 1, name: 'John'}, {id: 2, name: 'Adam'}, ]; let isContained = false; for (let index = 0; index < people.length; index++) { if (people[index].id === 1) { isContained = true; console.log(people[index]); // 👉️ { id: 1, name: 'John' } break; } } console.log(isContained); // 👉️ true
We used a basic for loop to iterate over the array.
On each iteration, we check if the object at the current index has an id
property with a value of 1.
If the condition is met, we set the isContained variable to true and exit
the for loop.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I'd use the
Array.some() method as I find it quite direct and intuitive.
# Check if an Object is NOT contained in an array in JavaScript
To check if an object is not contained in an array:
- Use the
Array.every()method to iterate over the array. - Check if each object doesn't have a property equal to the specified value.
- The
every()method will returntrueif the object is not contained in the array.
const arr = [ {id: 1, name: 'Alice'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bobby'}, {id: 3, name: 'Carl'}, ]; const notInArray = arr.every(obj => { return obj.id !== 4; }); console.log(notInArray); // 👉️ true if (notInArray) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The object is NOT contained in the array'); } else { console.log('The object is contained in the array'); }
The function we passed to the Array.every method gets called with each element (object) of the array.
On each iteration, we check if the current object doesn't have an id property
with a value of 4.
If all invocations of the callback function return a truthy value, then the
Array.every() method returns true, otherwise, false is returned.
If the callback function we passed to the Array.every() method returns a falsy
value, then Array.every() short-circuits also returning false.
# Check if a Value is NOT in an Array in JavaScript
Use the logical NOT (!) operator to negate a call to the includes() method to
check if a value is not contained in an array.
The expression will return true if the value is not contained in the array and
false otherwise.
const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']; if (!arr.includes('XYZ')) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ value is not in array'); } else { console.log('⛔️ value is in array'); }
We used the logical NOT (!) operator to negate a call to the Array.includes() method to check if the specified value is not contained in the array.
The Array.includes() method returns true if the supplied value is contained
in the array and false otherwise.
Since we want to check if the value is NOT contained in the array, we have to negate (!) the result.
Here are some examples of using the logical NOT (!) operator.
console.log(!true); // 👉️ false console.log(!false); // 👉️ true console.log(!'hello'); // 👉️ false console.log(!''); // 👉️ true console.log(!null); // 👉️ true
You can imagine that the logical NOT (!) operator:
- converts the value to a
boolean - flips the
boolean
true, in all other cases it returns false.Falsy values are: null, undefined, "" empty string, NaN (Not a number),
0 and false.
If you have to check if a value is not contained in an array often, define a reusable function.
function notInArray(arr, value) { return !arr.includes(value); } const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']; console.log(notInArray(arr, 'bobby')); // 👉️ false console.log(notInArray(arr, 'XYZ')); // 👉️ true console.log(notInArray(arr, 'com')); // 👉️ false if (notInArray('XYZ')) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The value is NOT in the array'); } else { console.log('The value is in the array'); }
The notInArray function takes an array and a value as parameters and returns
true if the value is not in the array and false otherwise.
An alternative approach is to use the Array.indexOf method.
# Check if a Value is NOT in an Array using indexOf
If the indexOf method returns -1, the value is not contained in the array.
const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']; if (arr.indexOf('XYZ') === -1) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ value is not in array'); } else { console.log('⛔️ value is in array'); }
The Array.indexOf method returns the index of the first occurrence of the supplied value in the array.
If the value is not contained in the array, the method returns -1.
Our if statement checks if the method returned -1.
If it did, then the value is not contained in the array.
You can define a reusable function if you have to do this often.
function notInArray(arr, value) { return arr.indexOf(value) === -1; } const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']; console.log(notInArray(arr, 'bobby')); // 👉️ false console.log(notInArray(arr, 'XYZ')); // 👉️ true console.log(notInArray(arr, 'com')); // 👉️ false if (notInArray('XYZ')) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The value is NOT in the array'); } else { console.log('The value is in the array'); }
The function takes an array and a value as parameters and returns true if the
value is not contained in the array and false otherwise.

