Get the Max/Min Date in an Array of Objects in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 6, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Get the Max/Min Date in an Array of Objects in JavaScript
- Get the Min/Max Dates in an Array in JavaScript
# Get the Max/Min Date in an Array of Objects in JavaScript
To get the Max/Min date in an array of objects:
- Use the
map()method to get an array ofDateobjects. - Unpack the values from the array in a call to the
Math.max()orMath.min()functions. - Pass the result to the
Date()constructor.
const arr = [ {date: '2022-11-14T04:55:31.820Z'}, {date: '2022-09-24T07:25:31.820Z'}, {date: '2025-07-17T07:25:31.820Z'}, ]; // ✅ Get Max date const maxDate = new Date( Math.max( ...arr.map(element => { return new Date(element.date); }), ), ); // 👇️ Thu Jul 17 2022 console.log(maxDate); // ✅ Get Min date const minDate = new Date( Math.min( ...arr.map(element => { return new Date(element.date); }), ), ); // 👇️ Sat Sep 24 2022 console.log(minDate);
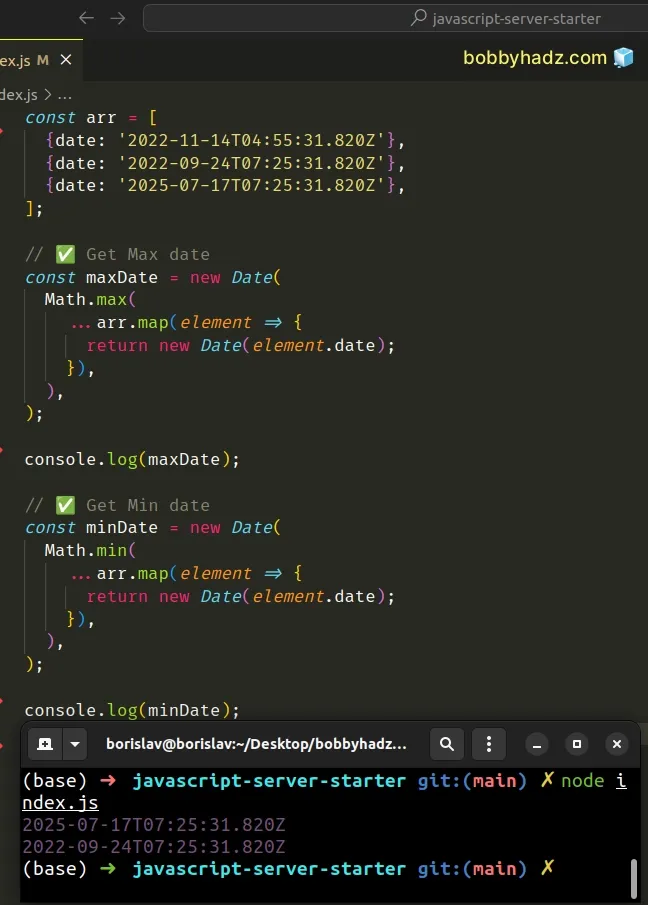
If you need to get the Min/Max dates in a flat array, scroll down to the next subheading.
We have an array of objects where each object has a date property that points
to a date and time string.
The date strings are formatted as ISO 8601 in the example, but this could be any
other valid string that the Date() constructor is able to parse.
Date objects for the date property and not date strings, then you don't have to pass the value to the Date() constructor like we did in the map() method.The function we passed to the Array.map() method gets called with each element (object) in the array.
On each iteration, we pass the date string to the
Date() constructor to create a
Date object.
At this point, we have an array of dates that we can unpack in a call to the Math.max() or Math.min() functions.
The Math.max() and Math.min() functions take multiple, comma-separated
numbers and return the max or min value, depending on which function you call.
const arr = [5, 10, 15, 3, 6, 9]; const min = Math.min(...arr); console.log(min); // 👉️ 3 const max = Math.max(...arr); console.log(max); // 👉️ 15
We used the
spread syntax (...),
because the Math.max() and Math.min() functions expect multiple,
comma-separated numbers and cannot directly get called with an array.
This works because under the hood each Date object stores a timestamp (the
number of milliseconds since the Unix Epoch).
// 👇️ 1643013648670 console.log(new Date().getTime());
If you try to compare two Date objects, they get converted to timestamps
before the comparison takes place.
// 👇️ 1668401731820 console.log( Math.max( ...[ new Date('2022-11-14T04:55:31.820Z'), new Date('2022-09-24T07:25:31.820Z'), ], ), );
The example above prints the timestamp of the latest date in the array.
If you need to convert this timestamp to a Date object, pass the timestamp as
a parameter to the Date() constructor.
// 👇️ Mon Nov 14 2022 console.log( new Date( Math.max( ...[ new Date('2022-11-14T04:55:31.820Z'), new Date('2022-09-24T07:25:31.820Z'), ], ), ), );
The Date() constructor is quite flexible when it comes to parsing dates.
The examples above use it to create a Date object from a date string and from
a timestamp.
# Get the Min/Max Dates in an Array in JavaScript
To get the Min/Max dates in an array:
- Unpack the arrays in a call to the
Math.min()orMath.max()functions. - Pass the result to the
Date()constructor. - The
Math.minandMath.maxfunctions will return the timestamp of the Min/Max date.
const arr = [ new Date('2022-11-14'), new Date('2022-09-24'), new Date('2025-07-17'), ]; const min = new Date(Math.min(...arr)); console.log(min); // 👉️ Sat Sep 24 2022 const max = new Date(Math.max(...arr)); console.log(max); // 👉️ Thu Jul 17 2025
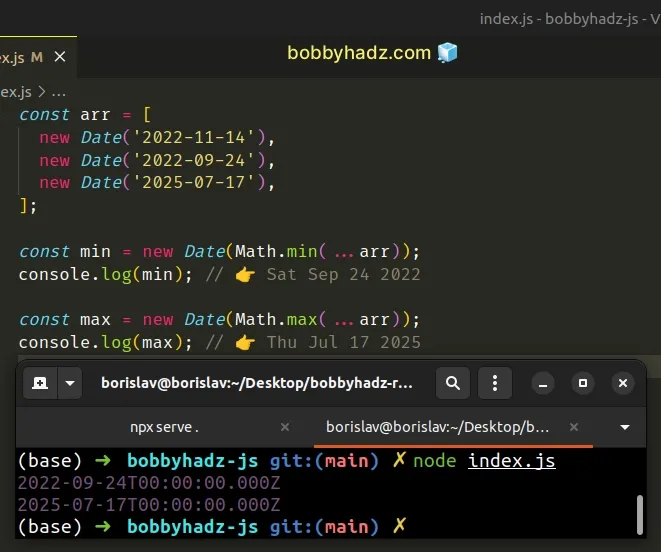
We have an array of Date objects in the example. If you have an array of date
strings, you can convert each date string to a Date object by passing it to
the Date() constructor.
const arrStrings = ['2022-11-14', '2022-09-24', '2025-07-17']; // 👇️ convert date strings to date objects const arrDates = arrStrings.map(str => new Date(str)); const min = new Date(Math.min(...arrDates)); console.log(min); // 👉️ Sat Sep 24 2022 const max = new Date(Math.max(...arrDates)); console.log(max); // 👉️ Thu Jul 17 2025
The example above uses the same approach as the first code snippet but has a
starting point of an array containing date strings and not Date objects.
We used the Math.max() and Math.min() functions to get the min and max dates in the array.
Math.max and Math.min functions take multiple, comma-separated numbers and return the max or min value, depending on which function you call.const arr = [5, 10, 15, 3, 6, 9]; const min = Math.min(...arr); console.log(min); // 👉️ 3 const max = Math.max(...arr); console.log(max); // 👉️ 15
We used the
spread syntax (...),
because the Math.max() and Math.min() functions expect multiple,
comma-separated numbers, which means we can't directly pass an array.
// 👇️ 1643015842501 console.log(new Date().getTime());
If you try to compare two Date objects, they get converted to timestamps
before the comparison takes place.
const arr = [ new Date('2022-11-14'), new Date('2022-09-24'), new Date('2025-07-17'), ]; // 👇️ 1752710400000 console.log(Math.max(...arr));
If you need to convert this timestamp to a Date object, so that you can take
advantage of some of the built-in functions, you can pass the timestamp as a
parameter to the Date() constructor.
const arr = [ new Date('2022-11-14'), new Date('2022-09-24'), new Date('2025-07-17'), ]; // 👇️ Thu Jul 17 2022 console.log(new Date(Math.max(...arr)));
The Date() constructor is quite flexible when it comes to parsing dates.
The example above uses it to create a Date object from a date string and a
timestamp.
I've also written an article on how to sort an array of objects by Date property.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

