Create a Date from day, month, year in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 6, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# Create a Date from day, month, year in JavaScript
Use the Date() constructor to create a date from the day, month and year
values.
The Date() constructor takes the year, a zero-based value for the month and
the day as parameters and returns a Date object.
const date = new Date(2022, 0, 24); // 👇️ Mon Jan 24 2022 00:00:00 console.log(date);
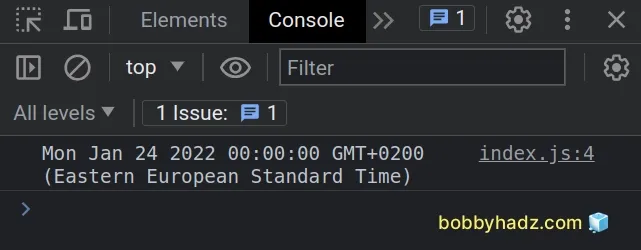
The 3 parameters we passed to the Date() constructor are:
year- an integer that represents the year, e.g.2022.monthIndex- a zero-based value that represents the month. For example, January is0, February is1, March is2, etc.day- an integer that represents the day of the month.
0 for the month, which is January.If you have the value for the month as a one-based value (January = 1), then
subtract 1 when passing it to the Date() constructor.
const str = '2022-01-24'; const [year, month, day] = str.split('-'); const date = new Date(+year, month - 1, day); // 👇️ Mon Jan 24 2022 00:00:00 console.log(date);
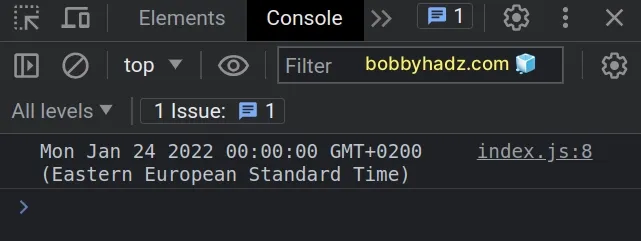
We have a date string that is formatted as YYYY-MM-DD in the example.
We split the string on each hyphen to get the values for the year, month and day.
const str = '2022-01-24'; // 👇️ ['2022', '01', '24'] console.log(str.split('-'));
1 when passing the month to the Date() constructor.Note that the Date() constructor automatically rolls the date over if
necessary.
const date = new Date(2022, 1, 29); // 👇️ Tue Mar 01 2022 00:00:00 console.log(date);
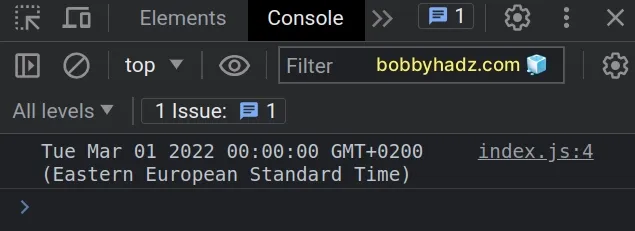
We passed 2022 as the year, 1 (February) as the month and 29 as the day of
the month.
February doesn't have 29 days in 2022, so the Date object automatically
adjusted the date to the 1st of March.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to Create a Date without Timezone in JavaScript
- Convert a Date or Date String to Timestamp in JavaScript
- Convert a Date to another Time Zone using JavaScript
- Convert an ISO Date to a Timestamp using JavaScript
- Convert an ISO string to a Date object in JavaScript
- How to generate a random Date in JavaScript

