Convert Bytes to KB, MB, GB or TB using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 7, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Convert Bytes to KB, MB, GB or TB using JavaScript
- Convert Bytes to KB, MB, GB or TB using a while loop in JavaScript
- Using the
filesizepackage to convert bytes to KB, MB, GB or TB
# Convert Bytes to KB, MB, GB or TB using JavaScript
To convert bytes to KB, MB, GB or TB:
- If the supplied bytes are
0or an invalid number, return0bytes. - Store the possible sizes in an array.
- Calculate the index based on the supplied bytes.
- Convert the bytes based on the index.
function bytesToSize(bytes, decimals = 2) { if (!Number(bytes)) { return '0 Bytes'; } const kbToBytes = 1024; const dm = decimals < 0 ? 0 : decimals; const sizes = [ 'Bytes', 'KiB', 'MiB', 'GiB', 'TiB', 'PiB', 'EiB', 'ZiB', 'YiB', ]; const index = Math.floor( Math.log(bytes) / Math.log(kbToBytes), ); return `${parseFloat( (bytes / Math.pow(kbToBytes, index)).toFixed(dm), )} ${sizes[index]}`; } console.log(bytesToSize(1234)); // 1.21 KiB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567)); // 1.18 MiB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567890)); // 1.15 GiB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567891231)); // 1.12 TiB console.log(bytesToSize(12345678912312345)); // 10.97 PiB
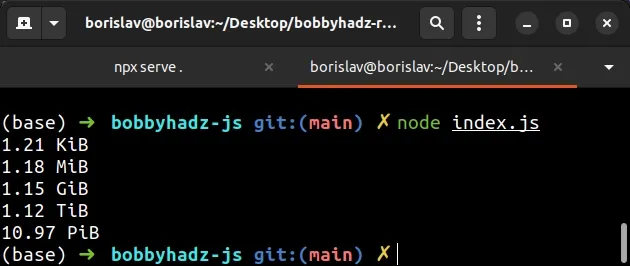
By default, the function rounds to 2 decimal places, you can pass a second argument if you want to round to N decimal places instead.
function bytesToSize(bytes, decimals = 2) { if (!Number(bytes)) { return '0 Bytes'; } const kbToBytes = 1024; const dm = decimals < 0 ? 0 : decimals; const sizes = [ 'Bytes', 'KiB', 'MiB', 'GiB', 'TiB', 'PiB', 'EiB', 'ZiB', 'YiB', ]; const index = Math.floor( Math.log(bytes) / Math.log(kbToBytes), ); return `${parseFloat( (bytes / Math.pow(kbToBytes, index)).toFixed(dm), )} ${sizes[index]}`; } console.log(bytesToSize(1234, 3)); // 1.205 KiB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567, 3)); // 1.177 MiB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567890, 3)); // 1.15 GiB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567891231, 3)); // 1.123 TiB console.log(bytesToSize(12345678912312345, 3)); // 10.965 PiB
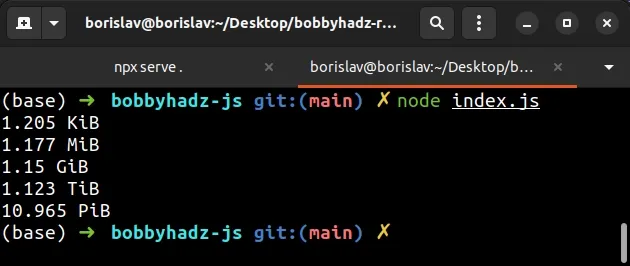
The examples above are rounded to 3 decimal places.
The code sample above assumes that 1 KB is equal to 1024 Bytes.
1 Kilobyte is equal to 1024 bytes in binary.
In decimal, 1 Kilobyte is equal to 1000 bytes.
You can update the value of the kbToBytes variable if you consider 1 KB to be
equal to 1000 bytes.
const kbToBytes = 1024;
If the user passed 0 bytes or an invalid number to the function, we return
0 bytes straight away.
if (!Number(bytes)) { return '0 Bytes'; }
Otherwise, the bytes get converted to the relevant unit of information
transmission and the corresponding string from the sizes array gets appended
to the end.
const sizes = [ 'Bytes', 'KiB', 'MiB', 'GiB', 'TiB', 'PiB', 'EiB', 'ZiB', 'YiB', ];
KiB, MiB, GiB stand for Kibibytes, Mebibytes, Gibibytes.
Here is a version of the function that considers 1 KB to be 1000 bytes and uses KB, MB, GB and TB instead.
function bytesToSize(bytes, decimals = 2) { if (!Number(bytes)) { return '0 Bytes'; } const kbToBytes = 1000; const dm = decimals < 0 ? 0 : decimals; const sizes = [ 'Bytes', 'KB', 'MB', 'GB', 'TB', 'PB', 'EB', 'ZB', 'YB', ]; const index = Math.floor( Math.log(bytes) / Math.log(kbToBytes), ); return `${parseFloat( (bytes / Math.pow(kbToBytes, index)).toFixed(dm), )} ${sizes[index]}`; } console.log(bytesToSize(1234)); // 1.23 KB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567)); // 1.23 MB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567890)); // 1.23 GB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567891231)); // 1.23 TB console.log(bytesToSize(12345678912312345)); // 12.35 PB
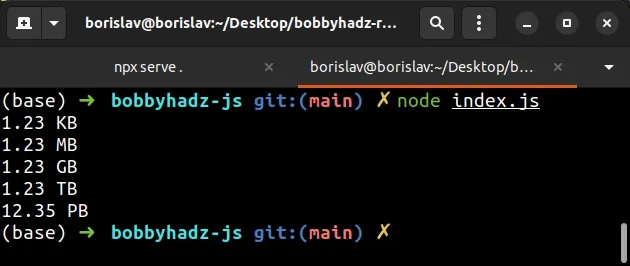
KB refers to base 1000, whereas KiB refers to base 1024.
# Convert Bytes to KB, MB, GB or TB using a while loop in JavaScript
You can also use a while loop to achieve the same result.
function bytesToSize(bytes) { if (!Number(bytes)) { return '0 Bytes'; } const sizes = [ 'Bytes', 'KiB', 'MiB', 'GiB', 'TiB', 'PiB', 'EiB', 'ZiB', 'YiB', ]; let index = 0; let n = parseInt(bytes, 10) || 0; const kbToBytes = 1024; while (n >= kbToBytes && ++index) { n = n / kbToBytes; } return `${n.toFixed(n < 10 && index > 0 ? 1 : 0)} ${ sizes[index] }`; } console.log(bytesToSize(1234)); // 1.21 KiB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567)); // 1.18 MiB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567890)); // 1.15 GiB console.log(bytesToSize(1234567891231)); // 1.12 TiB console.log(bytesToSize(12345678912312345)); // 10.97 PiB
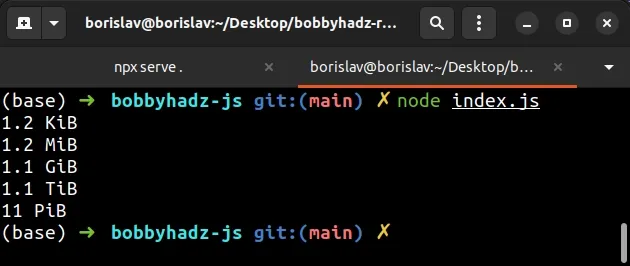
The example considers 1 KB to be equal to 1024 bytes.
const kbToBytes = 1024;
If you consider 1 KB to be equal to 1000 bytes, update the value of the
kbToBytes variable.
const kbToBytes = 1000; const sizes = [ 'Bytes', 'KB', 'MB', 'GB', 'TB', 'PB', 'EB', 'ZB', 'YB', ];
And update the strings in the sizes array.
# Using the filesize package to convert bytes to KB, MB, GB or TB
You can also use the popular filesize NPM package to convert bytes to KB, MB, GB or TB.
Open your terminal in your project's root directory and install the package.
npm init -y # 👇️ with NPM npm install filesize # 👇️ or with YARN yarn add filesize
You can import and use the package as follows.
import {filesize} from 'filesize'; // 👇️ 1.23 kB console.log(filesize(1234, {base: 10, standard: 'jedec'})); // 👇️ 1.23 MB console.log(filesize(1234567, {base: 10, standard: 'jedec'})); // 👇️ 1.23 GB console.log(filesize(1234567890, {base: 10, standard: 'jedec'})); // 👇️ 1.23 TB console.log( filesize(1234567891231, {base: 10, standard: 'jedec'}), ); // 👇️ 12.35 PB console.log( filesize(12345678912312345, {base: 10, standard: 'jedec'}), );
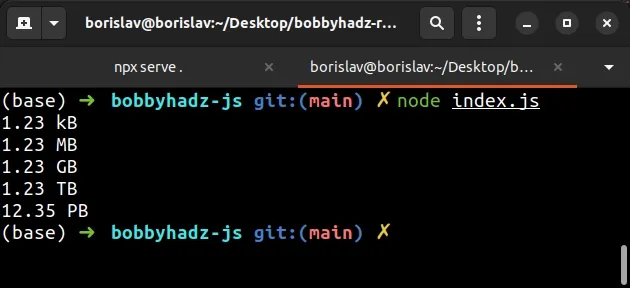
The filesize package enables us to get a human-readable file size string from
a number.
You can view all the available properties in the options object in
this section of the package's NPM page.
If you consider 1 KB to be equal to 1024 bytes, set the base property to 2.
import {filesize} from 'filesize'; // 👇️ 1.21 KB console.log(filesize(1234, {base: 2, standard: 'jedec'})); // 👇️ 1.18 MB console.log(filesize(1234567, {base: 2, standard: 'jedec'})); // 👇️ 1.15 GB console.log(filesize(1234567890, {base: 2, standard: 'jedec'})); // 👇️ 1.12 TB console.log( filesize(1234567891231, {base: 2, standard: 'jedec'}), ); // 👇️ 10.97 PB console.log( filesize(12345678912312345, {base: 2, standard: 'jedec'}), );
By default, the function rounds to 2 decimal places, you can set the round
property if you want to round to N decimal places instead.
import {filesize} from 'filesize'; // 👇️ 1.205 KB console.log( filesize(1234, {base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3}), ); // 👇️ 1.177 MB console.log( filesize(1234567, {base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3}), ); // 👇️ 1.15 GB console.log( filesize(1234567890, {base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3}), ); // 👇️ 1.123 TB console.log( filesize(1234567891231, { base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3, }), ); // 👇️ 10.965 PB console.log( filesize(12345678912312345, { base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3, }), );
You can view all the available properties in the options object in
this section of the package's NPM page.
You can also use the package in the browser.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <h2>bobbyhadz.com</h2> <script src="index.js" type="module"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript.
import {filesize} from 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/filesize@10.0.7/+esm'; // 👇️ 1.205 KB console.log( filesize(1234, {base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3}), ); // 👇️ 1.177 MB console.log( filesize(1234567, {base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3}), ); // 👇️ 1.15 GB console.log( filesize(1234567890, {base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3}), ); // 👇️ 1.123 TB console.log( filesize(1234567891231, { base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3, }), ); // 👇️ 10.965 PB console.log( filesize(12345678912312345, { base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3, }), );
You can issue the npx serve . command, open the page in your browser and open
the Console tab to view the output.
You can also use a CDN as follows.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <script src=" https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/filesize@10.0.7/dist/filesize.min.js "></script> </head> <body> <h2>bobbyhadz.com</h2> <h2 id="refresh-timer"></h2> <script src="index.js" type="module"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
// 👇️ 1.205 KB console.log( filesize.filesize(1234, { base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3, }), ); // 👇️ 1.177 MB console.log( filesize.filesize(1234567, { base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3, }), ); // 👇️ 1.15 GB console.log( filesize.filesize(1234567890, { base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3, }), ); // 👇️ 1.123 TB console.log( filesize.filesize(1234567891231, { base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3, }), ); // 👇️ 10.965 PB console.log( filesize.filesize(12345678912312345, { base: 2, standard: 'jedec', round: 3, }), );
Notice that we now access the filesize() method on the filesize global
object.
I've also written an article on how to get the size of a file in Node.js.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Download Images using JavaScript (Local and from URL)
- How to fetch Data on Button click in React
- TypeError: Failed to fetch and CORS in JavaScript [Solved]
- fetch() returns empty Response Body in JavaScript [Solved]
- How to Use an Image as a Link in React.js
- Import and use an Image in a React component
- Convert an HTML table to JSON and export it to a file in JS

