Check if a Value is Falsy or Truthy in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- Check if a Value is Falsy in JavaScript
- Check if multiple values are falsy
- Check if Falsy except Zero using JavaScript
- Check if a Value is Truthy in JavaScript
# Check if a Value is Falsy in JavaScript
Use the logical NOT (!) operator to check if a value is falsy, e.g.
if (!myValue).
The logical NOT operator returns true when it precedes falsy values, in all
other cases it returns false.
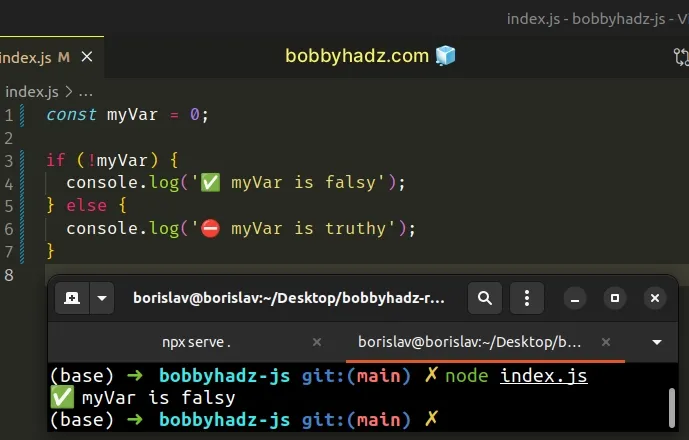
const myVar = 0; if (!myVar) { console.log('✅ myVar is falsy'); } else { console.log('⛔️ myVar is truthy'); }
If you need to check if a value is truthy, click on the following subheading.
We used the logical NOT (!) operator to check
if the myVar variable stores a falsy value.
The falsy values in JavaScript are: false, 0, -0, "" (empty string),
null, undefined, NaN (Not a number).
Our if block will run only if the value stored in the myVar variable is one
of the aforementioned 6 falsy values.
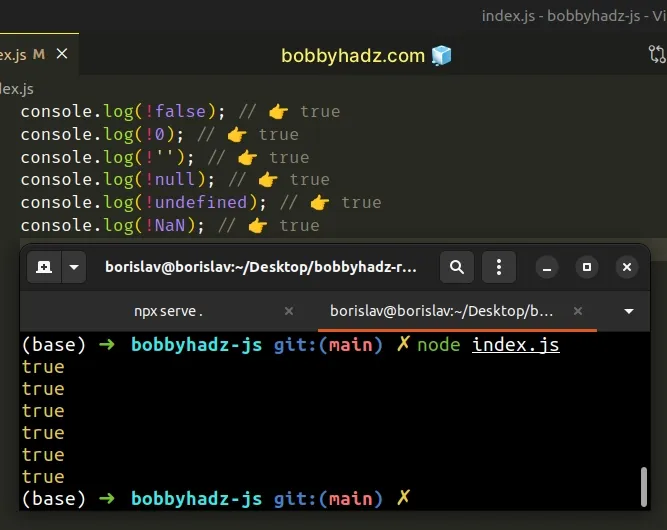
Here are examples of using the logical NOT (!) operator with falsy values:
console.log(!false); // 👉️ true console.log(!0); // 👉️ true console.log(!''); // 👉️ true console.log(!null); // 👉️ true console.log(!undefined); // 👉️ true console.log(!NaN); // 👉️ true
All other values are considered truthy.
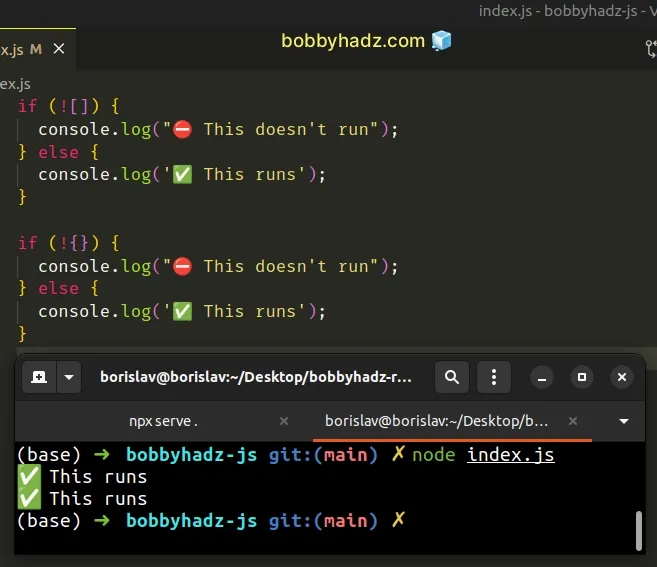
# Empty arrays and empty objects are truthy values
if (![]) { console.log("⛔️ This doesn't run"); } else { console.log('✅ This runs'); } if (!{}) { console.log("⛔️ This doesn't run"); } else { console.log('✅ This runs'); }
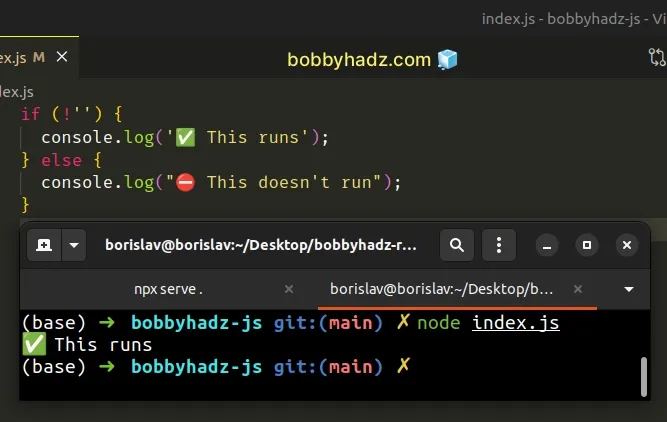
# Empty strings are falsy values
Even though the array and object are empty, they aren't falsy values as opposed to the empty string.
if (!"") { console.log('✅ This runs'); } else { console.log("⛔️ This doesn't run"); }
# Check if multiple values are falsy
You can use the Array.every() method to check if multiple values are falsy.
const value1 = false; const value2 = undefined; const value3 = null; const allFalsy = [value1, value2, value3].every( element => !element, ); console.log(allFalsy); // 👉️ true
The Array.every() method checks if all elements in the array pass the test implemented by the callback function.
On each iteration, we negate the current value and return the result.
The logical NOT (!) operator converts falsy values to truthy.
The every() method returns true if all elements pass the test and false
otherwise.
# Checking if an array or an object contains elements or key-value pairs
If you need to check if an array or an object contains elements or key-value pairs, do this instead:
if (['a'].length > 0) { // 👉️ array is not empty } if (Object.keys({a: 'b'}).length > 0) { // 👉️ object is not empty }
We used the length property to check if the array has more than 0 elements.
If the array has more than 0 elements, then it isn't empty.
console.log([].length); // 👉️ 0 console.log(['bobby', 'hadz', 'com'].length); // 👉️ 3
If you need to check if an object isn't empty, check if the object has more than
0 keys.
if (Object.keys({a: 'b'}).length > 0) { // 👉️ object is not empty }
The Object.keys() method returns an array containing the object's keys.
If the array contains more than 0 keys, the object isn't empty.
You could also do the check implicitly, e.g.:
if ([].length) { // 👉️ if this runs, the array is not empty }
In this example, we access the length property on an empty array, which
evaluates to 0.
0 is a falsy value, so the if block doesn't run.
If you want to check if the array is empty in an implicit way, use the logical NOT (!) operator.
if (![].length) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The array is empty'); } else { console.log('The array is NOT empty'); }
The [].length expression returns 0 which is a falsy value.
We used the logical NOT (!) operator to flip the falsy value, so the if block
runs.
Here are all the falsy values in JavaScript.
console.log(Boolean(false)); // 👉️ false console.log(Boolean(0)); // 👉️ false console.log(Boolean('')); // 👉️ false console.log(Boolean(null)); // 👉️ false console.log(Boolean(undefined)); // 👉️ false console.log(Boolean(NaN)); // 👉️ false
# Check if Falsy except Zero using JavaScript
To check if a value is falsy except zero:
- Check if the value is truthy or the value is zero.
- If neither condition is met, the value is falsy except zero.
const value = 0; if (value || value === 0) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ value is truthy or 0'); } else { console.log('⛔️ value is falsy except 0'); }
We used the logical OR (||) operator to chain multiple conditions.
If either condition returns a truthy value, our if block runs.
0.If either condition is met, then we have a truthy value or 0.
If neither condition is met, we have a falsy value that is not 0, and the
else block runs.
The falsy values in JavaScript are: null, undefined, false, 0, NaN
(not a number), "" (empty string).
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
function isTruthyOrZero(value) { return Boolean(value || value === 0); } console.log(isTruthyOrZero(0)); // 👉️ true console.log(isTruthyOrZero('bobbyhadz.com')); // 👉️ true console.log(isTruthyOrZero(null)); // 👉️ false console.log(isTruthyOrZero(undefined)); // 👉️ false console.log(isTruthyOrZero('')); // 👉️ false
The isTruthyOrZero function takes a value as a parameter and returns true if
the value is truthy or zero and false if the value is falsy except zero.
# Check if a Value is Truthy in JavaScript
To check if a value is truthy, pass the value to an if statement, e.g.
if (myValue).
If the value is truthy, it gets coerced to true and the if block runs.
const myVar = 'test'; if (myVar) { console.log('✅ the value is truthy'); } else { console.log('⛔️ the value is falsy'); }
The if statement checks if the value stored in the variable is
truthy. Truthy are
all values that are not falsy.
The falsy values in JavaScript are: false, 0, "" (empty string), null,
undefined, NaN (Not a number).
if block only runs if the variable stores any other than the aforementioned 6 falsy values.Truthy values in an if statement get coerced to true before the if block
is run.
# Examples of truthy values
Here are some examples of truthy values used in an if condition.
if ([]) { console.log('✅ This runs'); } if ({}) { console.log('✅ This runs'); } if (true) { console.log('✅ This runs'); } if ('test') { console.log('✅ This runs'); }
Notice that an empty array and an empty object are considered truthy, whereas an empty string is considered falsy.
if ('') { console.log("⛔️ this doesn't run"); }
# Checking if an array or an object contains elements
If you need to check if an array or object contains elements or key-value pairs, check if the array has elements and if the object has keys.
if ([1, 2, 3].length > 0) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The array is not empty'); } if (Object.keys({name: 'alice'}).length > 0) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The object is not empty'); }
We check if the array contains at least 1 element and if the object contains at least 1 key-value pair.
You could also do the check implicitly, e.g.:
if (['a'].length) { // 👉️ if this runs, the array is not empty }
We implicitly check for the length of the array. If the array is empty, its
length property will return 0, which is a falsy value, and our if block
wouldn't run.
If the array contains at least 1 element, the length property would return a
positive integer, which is a truthy value.
The value gets coerced to true and the if block runs.
Here are some examples of truthy values.
console.log(Boolean('a')); // 👉️ true console.log(Boolean(1)); // 👉️ true console.log(Boolean(-1)); // 👉️ true console.log(Boolean([])); // 👉️ true console.log(Boolean({})); // 👉️ true console.log(Boolean(new Set())); // 👉️ true console.log(Boolean(['a'])); // 👉️ true console.log(Boolean({a: 'b'})); // 👉️ true
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

