Check if Value is Negative or Positive Number in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·8 min

# Table of Contents
- Check if Value is a Negative Number
- Check if a Number is a Negative Integer
- Check if a Value is a Positive Number in JavaScript
- Check if String is a Positive Integer in JavaScript
# Check if Value is a Negative Number
Use the Math.sign() method to check if a value is a negative number.
The Math.sign() method returns -1 if the provided argument is a negative
number or can be converted to one.
function isNegative(num) { if (Math.sign(num) === -1) { return true; } return false; } console.log(isNegative(-5)); // 👉️ true console.log(isNegative(5)); // 👉️ false console.log(isNegative('-5')); // 👉️ true console.log(isNegative('test')); // 👉️ false // ------------------------------------------------------ function checkNumberSign(num) { if (Math.sign(num) === 1) { console.log('The value is a positive number'); } else if (Math.sign(num) === -1) { console.log('The value is a negative number'); } } checkNumberSign(5); // 👉️ The value is a positive number checkNumberSign(-5); // 👉️ The value is a negative number
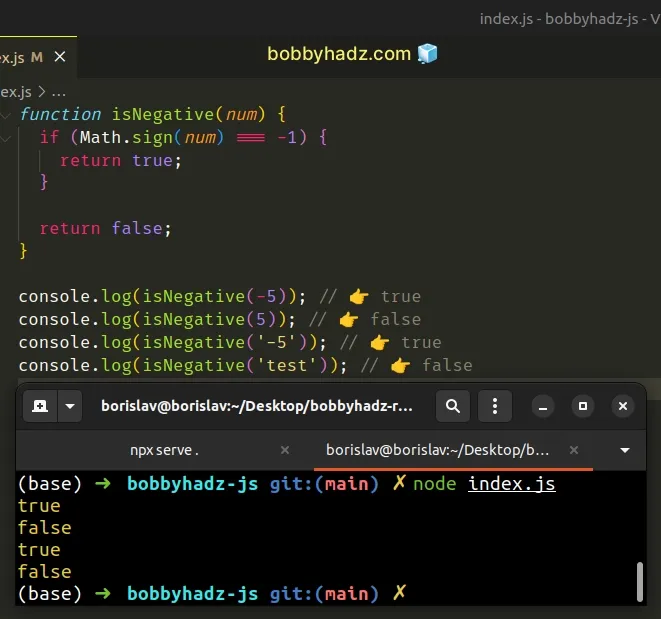
We used the Math.sign() method to check if a value is a negative number.
If the provided argument is not a number, it gets converted to a number.
Math.sign() method returns -1, then the provided argument is a negative number or could be converted to one.If you want to make sure the passed-in parameter is of type number, use the
typeof operator.
function isNegative(num) { if (typeof num === 'number' && Math.sign(num) === -1) { return true; } return false; }
We use the logical AND (&&) operator to chain another condition.
We check if the provided argument is a number before calling the Math.sign()
method.
The Math.sign() method has 5 possible return values:
- it returns
1if the argument is positive - it returns
-1if the argument is negative - it returns
0if the argument is0 - it returns
-0if the argument is-0 - in all other cases it returns
NaN(not a number)
Here are some examples of calling the Math.sign() method directly.
console.log(Math.sign(-5)); // 👉️ -1 console.log(Math.sign(5)); // 👉️ 1 console.log(Math.sign('-5')); // 👉️ -1 console.log(Math.sign('test')); // 👉️ NaN console.log(Math.sign(0)); // 👉️ 0
If the provided value is not a number, the method attempts to convert it to one.
# Check if a Value is a Negative Number using comparison operators
Alternatively, you can use the comparison operators.
If the value to the left-hand side of the less-than operator is not already a
number, it will get converted to one and compared to 0. If the expression
returns true, the value is a negative number.
function isNegative(num) { if (num < 0) { return true; } return false; } console.log(isNegative(-5)); // 👉️ true console.log(isNegative(5)); // 👉️ false console.log(isNegative('-5')); // 👉️ true console.log(isNegative('test')); // 👉️ false
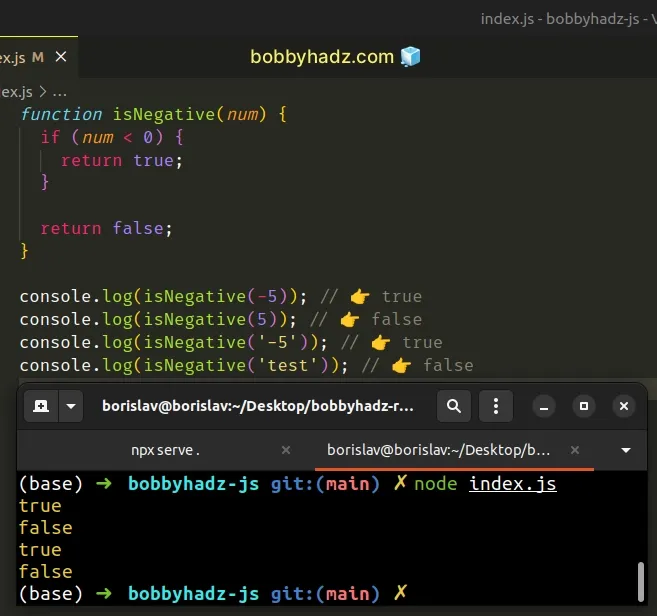
We used the
less than (<)
operator to compare the value on the left to 0.
If the value to the left is not a number, JavaScript will attempt to convert it to one.
If you only expect to take numbers as arguments, add another condition to the
if statement.
function isNegative(num) { if (typeof num === 'number' && num < 0) { return true; } return false; }
Here are some more examples of using the less-than operator.
console.log(-1 < 0); // 👉️ true console.log('-1' < 0); // 👉️ true console.log('test' < 0); // 👉️ false console.log('' < 0); // 👉️ false console.log(null < 0); // 👉️ false
If you're interested in reading more about how the "less-than" operator converts values that are not of the same type when comparing them, check out this section of the MDN docs.
# Check if a Number is a Negative Integer in JavaScript
To check if a number is a negative integer:
- Pass the number to the
Number.isInteger()method. - Check that the number is less than
0. - If both conditions are met, the number is a negative integer.
function isNegativeInteger(value) { if (Number.isInteger(value) && value < 0) { return true; } return false; } console.log(isNegativeInteger(0)); // 👉️ false console.log(isNegativeInteger(-1.5)); // 👉️ false console.log(isNegativeInteger(-1)); // 👉️ true console.log(isNegativeInteger('-1')); // false
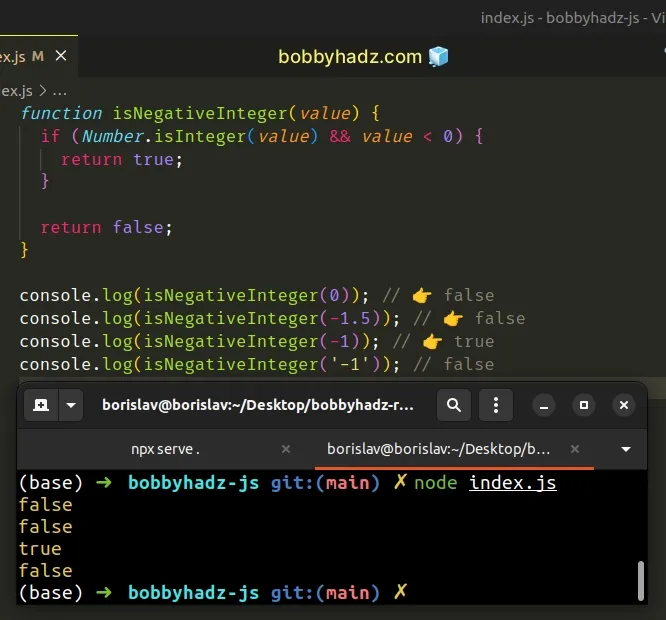
We used the Number.isInteger() method to determine if the passed-in value is an integer or not.
The method returns true if the value is an integer and false otherwise.
Here are some examples of using the Number.isInteger() method directly.
console.log(Number.isInteger(3)); // 👉️ true console.log(Number.isInteger(3.5)); // 👉️ false console.log(Number.isInteger('3')); // 👉️ false console.log(Number.isInteger(-3)); // 👉️ true
We then used the logical AND (&&) operator to chain another condition.
For the if block to run, both conditions have to be met.
The second condition is only evaluated if the first condition returns true.
In our second condition, we check if the integer is less than 0. If the
value is an integer and it's less than 0, then it is a negative integer.
However, there is a caveat with the Number.isInteger() method. The method
returns true if the passed-in value:
- is an integer
- is a float that can be represented as an integer
Here are examples of floats that can be represented as integers:
// 👇️ true console.log(Number.isInteger(-5.0)); // 👇️ true console.log(Number.isInteger(-5.0000000000000000123));
It depends on your use case, however, most applications are ok with considering
numbers such as -5.0 and -3.0 to be negative integers.
# Check if Value is a Positive Number in JavaScript
Use the Math.sign() method to check if a value is a positive number.
The Math.sign() method will return 1 if the provided argument is a positive
number or can be converted to one.
function isPositive(num) { if (Math.sign(num) === 1) { return true; } return false; } console.log(isPositive(-5)); // 👉️ false console.log(isPositive(5)); // 👉️ true console.log(isPositive('5')); // 👉️ true console.log(isPositive('test')); // 👉️ false
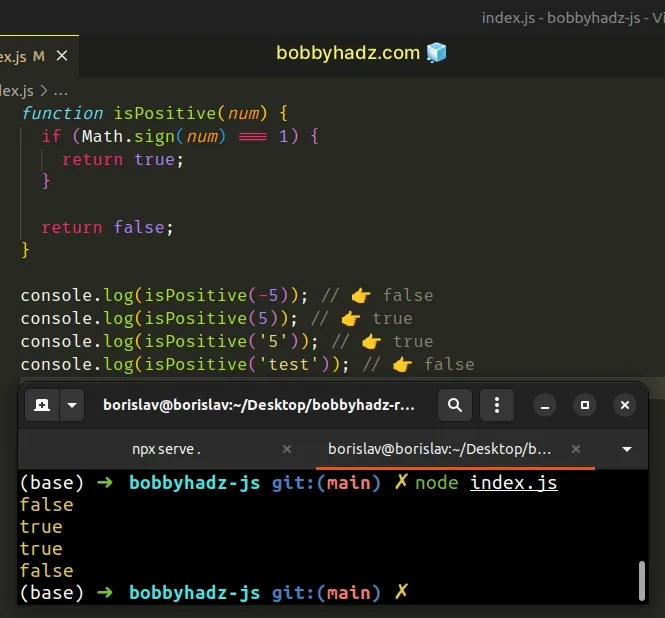
We use the Math.sign() method to check if a value is a positive number.
The only argument the method takes is a number. If the provided value is not a
number, it gets converted to one.
Math.sign() method returns 1, then the provided argument is a positive number or could be converted to one.If you want to make sure the passed-in parameter is of type number, you can
add an additional check to the if statement.
function isPositive(num) { if (typeof num === 'number' && Math.sign(num) === 1) { return true; } return false; }
We used the logical AND (&&) operator to chain another condition.
We check if the provided argument is a number before calling the Math.sign()
method.
The Math.sign() method has 5 possible return values:
- it returns
1if the argument is positive - it returns
-1if the argument is negative - it returns
0if the argument is0 - it returns
-0if the argument is-0 - in all other cases it returns
NaN(not a number)
Here are some examples of calling the Math.sign() method directly.
console.log(Math.sign(-5)); // 👉️ -1 console.log(Math.sign(5)); // 👉️ 1 console.log(Math.sign('-5')); // 👉️ -1 console.log(Math.sign('test')); // 👉️ NaN console.log(Math.sign(0)); // 👉️ 0
If the provided value is not a number, the method attempts to convert it to one.
# Check if Value is a Positive Number using comparison operators
Alternatively, you can use the comparison operators.
If the value on the left-hand side of the greater-than operator is not already a
number, it will get converted to one and compared to 0.
If the expression returns true, the value is a positive number.
function isPositive(num) { if (num > 0) { return true; } return false; } console.log(isPositive(-5)); // 👉️ false console.log(isPositive(5)); // 👉️ true console.log(isPositive('5')); // 👉️ true console.log(isPositive('test')); // 👉️ false
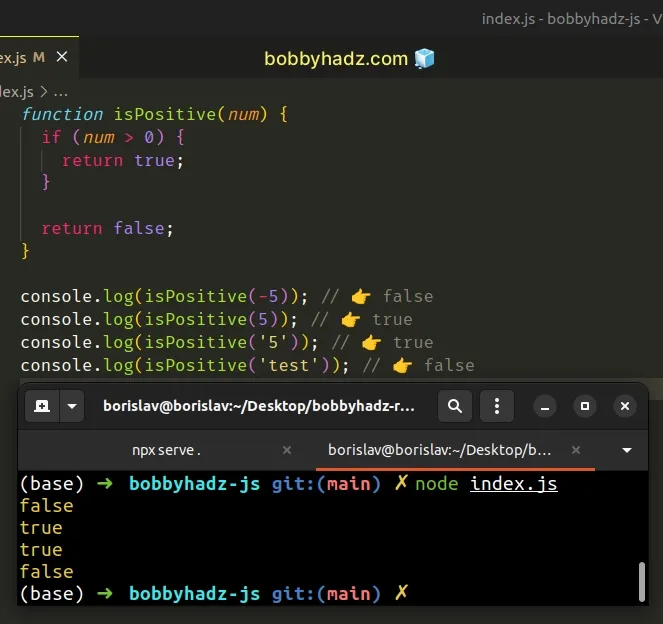
We used the
greater than (>)
operator to compare the value on the left to 0.
If the value to the left is not a number, JavaScript will attempt to convert it to one.
If you only expect to take numbers as arguments, add another condition to the
if statement.
function isPositive(num) { if (typeof num === 'number' && num > 0) { return true; } return false; }
Here are some more examples of using the greater than operator.
console.log(1 > 0); // 👉️ true console.log('1' > 0); // 👉️ true console.log('test' > 0); // 👉️ false console.log('' > 0); // 👉️ false console.log(null > 0); // 👉️ false
If you're interested in reading more about how the "greater-than" operator converts values that are not of the same type when comparing them, check out this section of the MDN docs.
# Check if String is a Positive Integer in JavaScript
To check if a string is a positive integer:
- Convert the string to a number and pass it to the
Number.isInteger()method. - Check if the number is greater than
0. - If the string is a valid integer and is greater than
0, the string is a valid positive integer.
function isPositiveInteger(str) { if (typeof str !== 'string') { return false; } const num = Number(str); if (Number.isInteger(num) && num > 0) { return true; } return false; } console.log(isPositiveInteger('0')); // 👉️ false console.log(isPositiveInteger('1')); // true console.log(isPositiveInteger('-1')); // 👉️ false console.log(isPositiveInteger('1.5')); // 👉️ false console.log(isPositiveInteger('test')); // false console.log(isPositiveInteger('')); // 👉️ false console.log(isPositiveInteger(' ')); // 👉️ false
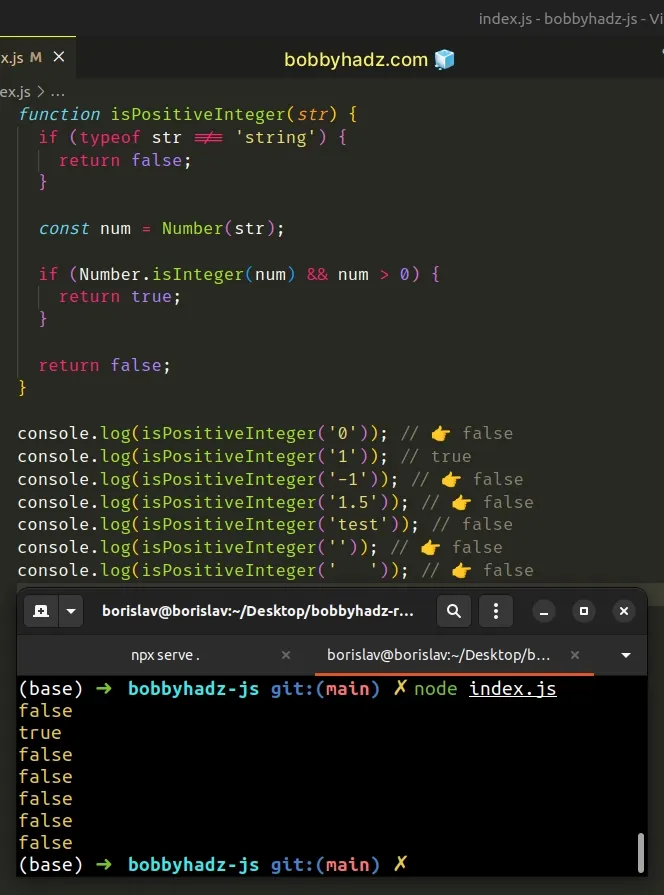
We first check if the passed-in value isn't a string. In this case, we return
false straight away because the function only handles strings.
You can also check if a number is a positive integer by using the
Number.isInteger() method and checking if the number is greater than 0.
const num = 5; if (Number.isInteger(num) && num > 0) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('num is an integer'); }
We used the Number() constructor to convert the string to a number and stored
the value into a variable.
function isPositiveInteger(str) { if (typeof str !== 'string') { return false; } const num = Number(str); if (Number.isInteger(num) && num > 0) { return true; } return false; }
Here are some examples of converting a string to a number.
console.log(Number('1')); // 👉️ 1 console.log(Number('1.5')); // 👉️ 1.5 console.log(Number('')); // 👉️ 0 console.log(Number(' ')); // 👉️ 0 console.log(Number('hello')); // 👉️ NaN
NaN (not a number) back.If the string is empty or contains spaces, we get 0 back.
The first condition in our second if statement checks if the value is a valid
integer.
function isPositiveInteger(str) { if (typeof str !== 'string') { return false; } const num = Number(str); if (Number.isInteger(num) && num > 0) { return true; } return false; }
The
Number.isInteger()
method returns true if the provided value is an integer and false otherwise.
Here are some examples of using the Number.isInteger() method directly.
console.log(Number.isInteger(1)); // 👉️ true console.log(Number.isInteger(1.5)); // 👉️ false console.log(Number.isInteger('1')); // 👉️ false console.log(Number.isInteger(-1)); // 👉️ true
We used the
logical AND (&&)
operator to chain another condition. The if block is only run if both
conditions are true.
The second condition checks if the number is greater than 0.
0, we have a positive integer.However, there is a caveat with the Number.isInteger() method. The method
returns true if the passed-in value:
- is an integer
- is a float that can be represented as an integer
Here are examples of floats that can be represented as integers:
// 👇️ true console.log(Number.isInteger(10.0)); // 👇️ true console.log(Number.isInteger(10.000000000000000123));
This shouldn't matter as most applications are OK with considering numbers such
as 1.0 and 2.0 as integers.
You can also use the Math.sign() method to check if a string is a positive
integer.
# Check if String is a Positive Integer using Math.sign()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Number()constructor to convert the string to a number. - Use the
Number.isInteger()method to check if the number is an integer. - Use the
Math.sign()method to check if the number is positive.
function isPositiveInteger(str) { const num = Number(str); if (Number.isInteger(num) && Math.sign(num) === 1) { return true; } return false; } console.log(isPositiveInteger('0')); // 👉️ false console.log(isPositiveInteger('1')); // true console.log(isPositiveInteger('-1')); // 👉️ false console.log(isPositiveInteger('1.5')); // 👉️ false console.log(isPositiveInteger('test')); // false console.log(isPositiveInteger('')); // 👉️ false console.log(isPositiveInteger(' ')); // 👉️ false
We used the Number() constructor to convert the argument to a number.
The Number.isInteger() method returns true if the passed-in number is an
integer and false otherwise.
The last step is to use the Math.sign() method to check if the number is
positive.
The
Math.sign()
method takes a number as a parameter and returns 1 if the number is positive
and -1 if the number is negative.
The Math.sign() method has 5 possible return values:
- it returns
1if the argument is positive - it returns
-1if the argument is negative - it returns
0if the argument is0 - it returns
-0if the argument is-0 - in all other cases it returns
NaN(not a number)
If the Number.isInteger() method returns true and the Math.sign() method
returns 1, then the string is a positive integer.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

