Check if all Values in Array are True/False in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Check if all Values in an Array are True in JavaScript
- Check if all Values in an Array are False in JavaScript
# Check if all Values in an Array are True in JavaScript
To check if all values in an array are true:
- Use the
Array.every()method to iterate over the array. - Compare each value to
trueand return the result. - The
every()method will returntrueif all values in the array aretrue.
function allAreTrue(arr) { return arr.every(element => element === true); } console.log(allAreTrue([true, true])); // 👉️ true console.log(allAreTrue([true, false])); // 👉️ false if (allAreTrue([true, true])) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('All values are true'); } else { console.log('NOT all values are true'); }
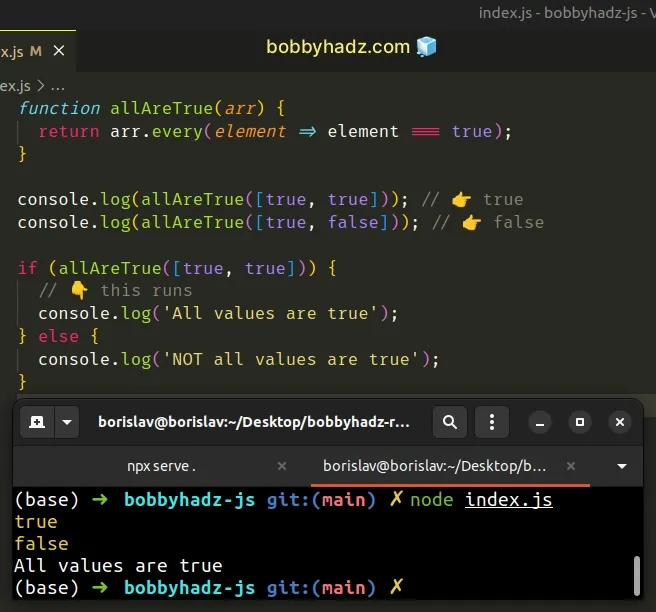
The same approach can be used to check if all values in an array pass a test.
The Array.every() method checks if all elements in the array pass the test implemented by the callback function.
On each iteration, we
check if the current element is equal to true
and return the result.
The method returns true if all elements pass the test and false otherwise.
every() method short-circuits and returns false.If the condition is met for all array elements, the every method returns
true.
Note that there is a distinction between a value being equal to true and a
value being truthy.
The falsy values in JavaScript are: false, null, undefined, 0, ""
(empty string), NaN (not a number).
All other values are truthy.
# Checking if all values in an array are null
If you need to check if all array values are null, compare each array element
to null.
function allAreNull(arr) { return arr.every(element => element === null); } console.log(allAreNull([null, null])); // 👉️ true console.log(allAreNull([null, undefined])); // 👉️ false if (allAreNull([null, null, null])) { console.log('All values are equal to null'); } else { console.log('Not all values are equal to null'); }
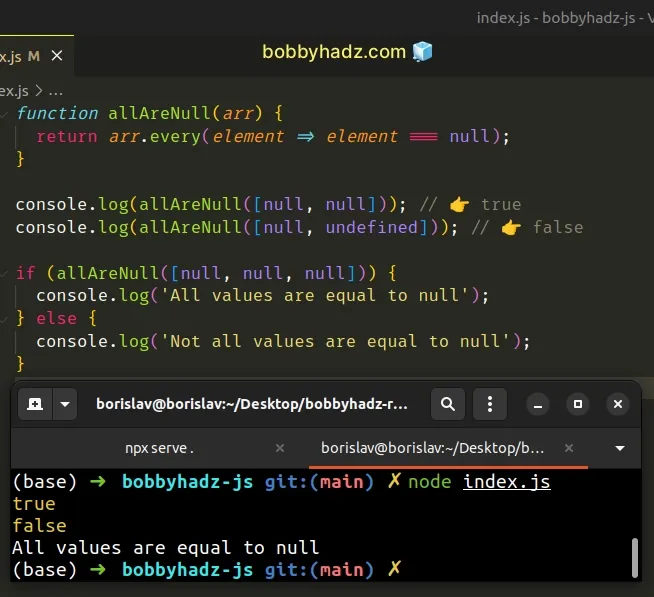
The function takes an array as a parameter and returns true if all values
values in the array are equal to null.
# Check if all values in an array are Truthy in JavaScript
To check if all values in an array are truthy:
- Use the
Array.every()method to iterate over the array. - On each iteration, return the current element directly.
- The
every()method will returntrueif all array elements are truthy.
function allAreTruthy(arr) { return arr.every(element => element); } console.log(allAreTruthy([1, 'test', true])); // 👉️ true console.log(allAreTruthy([0, '', true])); // 👉️ false
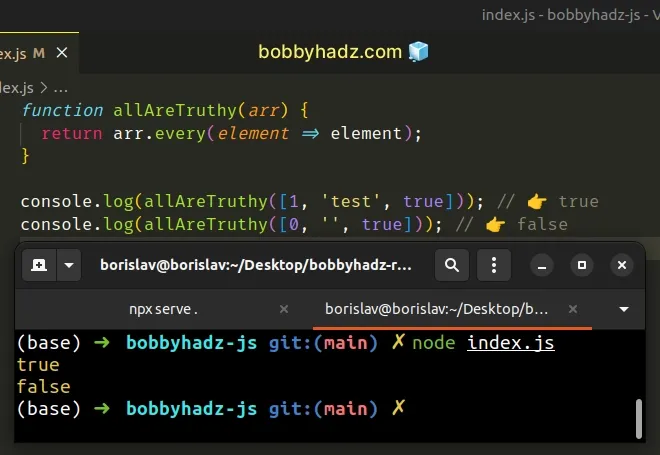
The every() method checks if the passed-in callback function returns a truthy
value, so we can directly return the current value.
An alternative and a little more concise approach is to use the Boolean()
constructor.
function allAreTruthy(arr) { return arr.every(Boolean); } console.log(allAreTruthy([1, 'test', true])); // 👉️ true console.log(allAreTruthy([0, '', true])); // 👉️ false
The Boolean() constructor gets passed each value in the array, converts the
value to its boolean representation and returns the result.
This achieves the same result but is a bit more implicit.
# Check if all Values in an Array are False in JavaScript
To check if all values in an array are false:
- Use the
Array.every()method to iterate over the array. - Compare each value to
falseand return the result. - The
every()method will returntrueif all array elements are equal tofalse.
function allAreFalse(arr) { return arr.every(element => element === false); } console.log(allAreFalse([false, false])); // 👉️ true console.log(allAreFalse([false, true])); // 👉️ false
The function we passed to the Array.every method gets called with each element of the array.
On each iteration, we check if the current element is equal to false and
return the result.
If all invocations of the callback function return a truthy value, then the
Array.every() method returns true, otherwise, false is returned.
If the callback function we passed to the Array.every() method returns a falsy
value, then Array.every() short-circuits also returning false.
The falsy values in JavaScript are: false, null, undefined, 0, ""
(empty string), NaN (not a number). All other values are truthy.
Note that checking if a value is equal to false is different than checking if
the value is falsy.
# Check if all Values in an Array are Falsy in JavaScript
To check if all values in an array are falsy:
- Use the
Array.every()method to iterate over the array. - Negate each value using the logical NOT (!) operator and return the result.
- The
every()method will returntrueif all values in the array are falsy.
function allAreFalsy(arr) { return arr.every(element => !element); } console.log(allAreFalsy([0, '', false])); // true console.log(allAreFalsy([1, 'test', true])); // false
On each iteration, we used the logical NOT (!) operator to convert each value to a boolean and invert the result.
Here are some examples of using the logical NOT (!) operator.
console.log(!true); // 👉️ false console.log(!false); // 👉️ true console.log(!'str'); // 👉️ false console.log(!''); // 👉️ true console.log(!null); // 👉️ true
If the array contains only falsy values, the function we passed to the every()
method would return true on all iterations.

