Check if Two Arrays have the Same Elements in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Check if Two Arrays have the Same Elements in JavaScript
- Checking if the two arrays have same elements regardless of order
- Check if two arrays have the same elements using a
forloop - Check if two arrays have the same elements using
JSON.stringify()
# Check if Two Arrays have the Same Elements in JavaScript
To check if two arrays have the same elements:
- Check if the arrays have the same length.
- Use the
every()to check if the arrays contain the same element at the same index. - The
every()method will returntrueif the arrays have the same elements andfalseotherwise.
const arr1 = ['a', 'b', 'c']; const arr2 = ['a', 'b', 'c']; function areEqual(array1, array2) { if (array1.length === array2.length) { return array1.every((element, index) => { if (element === array2[index]) { return true; } return false; }); } return false; } console.log(areEqual(arr1, arr2)); // 👉️ true
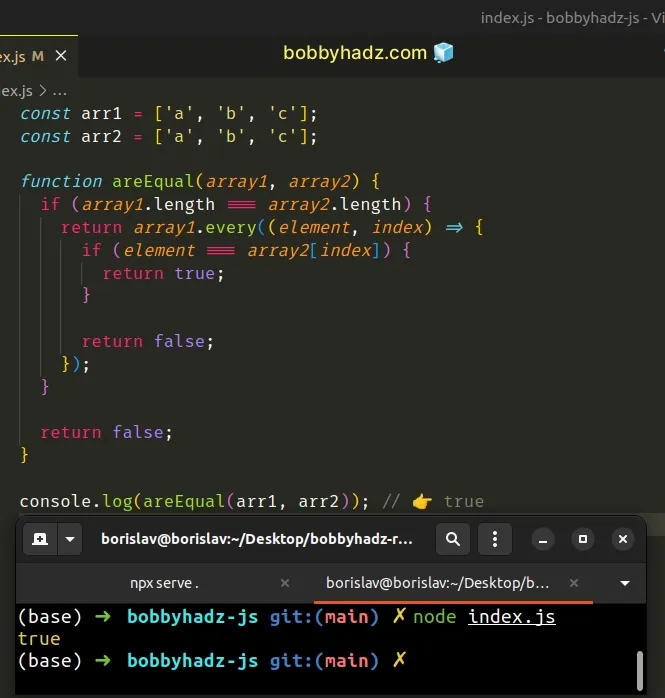
We first check if the arrays have the same length. If they don't, we return
false straight away.
The function we passed to the Array.every() method gets called with each element in the array until it returns a falsy value or iterates over the entire array.
On each iteration, we check if the current element is equal to the element at the same index in the other array.
every() method returns true only if the test function returns a truthy value on all iterations, otherwise, it returns false.If the test function returns false, the every method short-circuits
returning false.
areEqual() function only returns true if the passed-in arrays have the same length, their values are equal and in the same order.In this example, we call the areEqual() function with two arrays containing
the same elements in a different order and the function returns false.
const arr1 = ['c', 'b', 'a']; const arr2 = ['a', 'b', 'c']; function areEqual(array1, array2) { if (array1.length === array2.length) { return array1.every((element, index) => { if (element === array2[index]) { return true; } return false; }); } return false; } console.log(areEqual(arr1, arr2)); // 👉️ false
# Checking if the two arrays have same elements regardless of order
If you don't care about the ordering of the elements and you just want to check if two arrays contain the same elements, use this approach instead.
const arr1 = ['c', 'b', 'a']; const arr2 = ['a', 'b', 'c']; function areEqual(array1, array2) { if (array1.length === array2.length) { return array1.every(element => { if (array2.includes(element)) { return true; } return false; }); } return false; } console.log(areEqual(arr1, arr2)); // 👉️ true
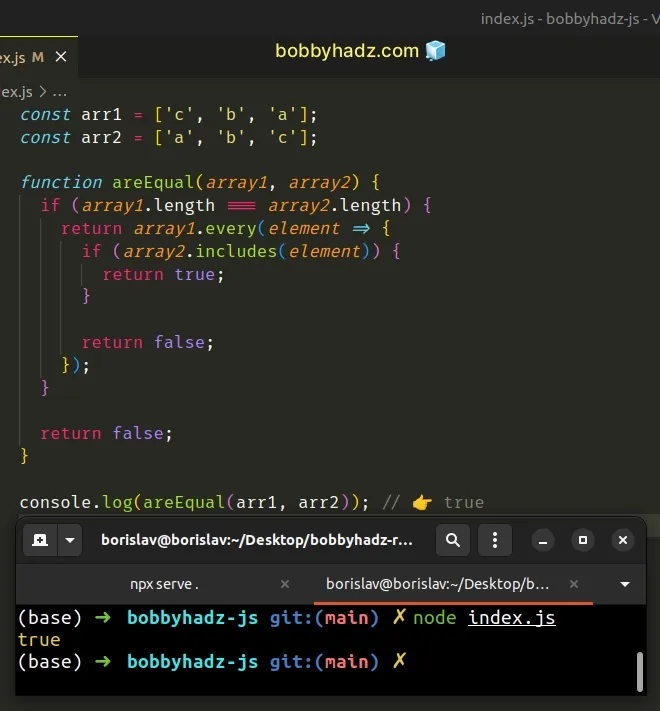
Instead of checking if the current element is equal to the element in the other array with the same index, we just check if the element is included in the other array.
We know that if the arrays have the same length and each element of one array is contained in the other array, we have 2 equal arrays with possibly different ordering.
If you need to find the array elements that are in both arrays, use the
Array.filter() method.
const arr1 = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']; const arr2 = ['a', 'b', 'c']; const intersection = arr1.filter(element => { return arr2.includes(element); }); console.log(intersection); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b', 'c' ]
The function we passed to the Array.filter() method gets called with each
element in the array.
On each iteration, we check if the element is contained in the other array and return the result.
The filter() method returns a new array that only contains the elements for
which the callback function returned true.
Alternatively, you can use a for loop.
# Check if two arrays have the same elements using a for loop
This is a three-step process.
- Check if the arrays don't have the same length and if the condition is met,
return
false. - Check if each element in the first array is not equal to the element at the same index in the second array.
- If the condition is met, return
false, otherwise, returntrue.
function areEqual(array1, array2) { if (array1.length !== array2.length) { return false; } for (let index = 0; index < array1.length; index++) { if (array1[index] !== array2[index]) { return false; } } return true; } const arr1 = ['a', 'b', 'c']; const arr2 = ['a', 'b', 'c']; const arr3 = ['z', 'x', 'y']; console.log(areEqual(arr1, arr2)); // 👉️ true console.log(areEqual(arr1, arr3)); // 👉️ false
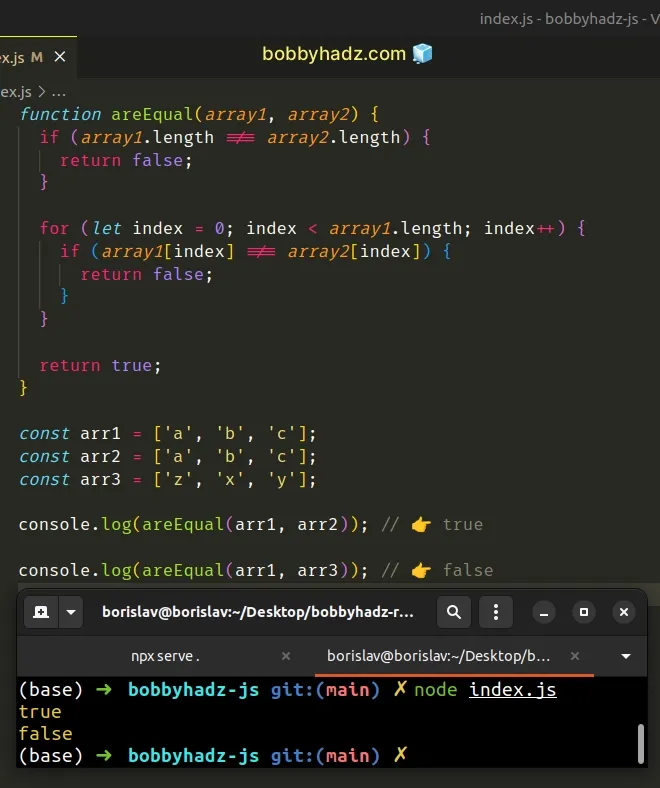
We first check if the two arrays don't have the same length.
If the arrays don't have the same length, then they aren't equal, so we return
false straight away.
We used a for loop to iterate over the first array.
If the condition is met, the arrays aren't equal, so we return false.
Otherwise, the function returns true.
Alternatively, you can use the JSON.stringify() method.
# Check if two arrays have the same elements using JSON.stringify()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
JSON.stringify()method to convert the arrays to JSON strings. - Use the strict equality operator (===) to compare the strings.
- If the strings are equal, the two arrays have the same elements.
function areEqual(array1, array2) { return JSON.stringify(array1) === JSON.stringify(array2); } const arr1 = ['a', 'b', 'c']; const arr2 = ['a', 'b', 'c']; const arr3 = ['z', 'b', 'c']; console.log(areEqual(arr1, arr2)); // 👉️ true console.log(areEqual(arr3, arr2)); // 👉️ false
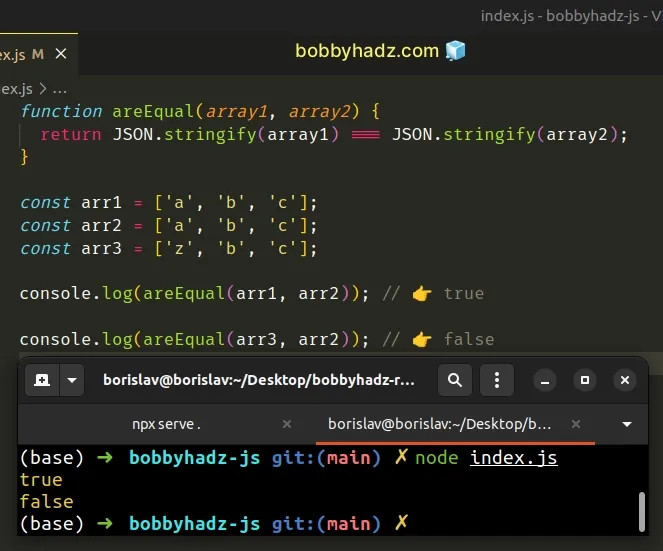
We used the JSON.stringify() method to convert the two arrays to JSON strings
and compared the strings.
If the areEqual() function returns true, the arrays have the same length and
contain the same elements, in the same order.
If you don't want to check for the order of the elements in the arrays, sort the
arrays before calling the JSON.stringify() method.
function areEqual(array1, array2) { const sortedArr1 = [...array1].sort(); const sortedArr2 = [...array2].sort(); return JSON.stringify(sortedArr1) === JSON.stringify(sortedArr2); } const arr1 = ['c', 'b', 'a']; const arr2 = ['b', 'a', 'c']; const arr3 = ['z', 'x', 'y']; console.log(areEqual(arr1, arr2)); // 👉️ true console.log(areEqual(arr3, arr2)); // 👉️ false
We used the Array.sort() method to sort the two arrays before comparing the
output of the JSON.stringify() method.
We used the spread syntax (...) to create a shallow copy of each array before
sorting them because the Sort() method sorts an array in place.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Check if Array contains any element of another Array in JS
- Check if Array Doesn't contain a Value in JavaScript
- Check if all Values in Array are Equal in JavaScript
- Check if Array has all Elements of Another Array - JavaScript
- How to Zip two or more Arrays in JavaScript - Complete Guide
- Check if a key exists in localStorage using JavaScript

