Check if Array has all Elements of Another Array - JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 1, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Check if Array has all Elements of Another Array
To check if an array contains all of the elements of another array:
- Call the
Array.every()method on the first array. - Check if each element in the array is contained in the second array.
- If the condition is met for all elements, the array has all elements of the other array.
const arr1 = ['pizza', 'cola']; const arr2 = ['pizza', 'cake', 'cola']; const containsAll = arr1.every(element => { return arr2.includes(element); }); console.log(containsAll); // 👉️ true
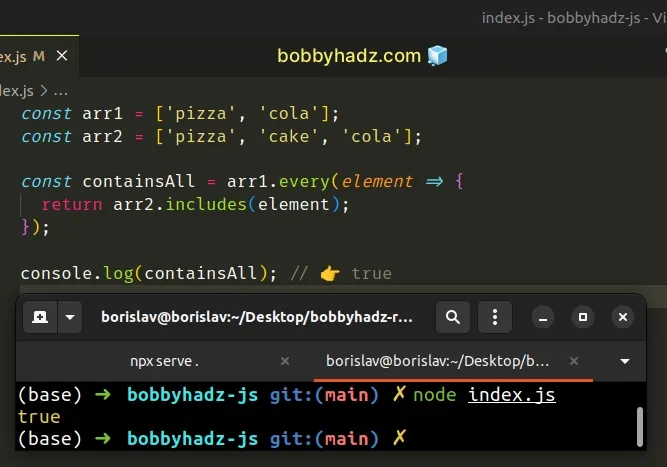
The function we passed to the Array.every method is invoked with each element of the array and should return a truthy or a falsy value.
If all invocations of the callback function return a truthy value, then the
Array.every() method returns true, otherwise false is returned.
Array.every method to iterate over the first array. To check if each value is contained in the second array, use the Array.includes method.const arr1 = ['pizza', 'cola']; console.log(arr1.includes('cola')); // 👉️ true console.log(arr1.includes('XYZ')); // 👉️ false
If the callback function we passed to the Array.every() method returns a falsy
value, then Array.every() also returns false.
falsy value, then the Array.every method short-circuits returning false.Alternatively, you can use the Array.indexOf() method.
# Check if Array has all Elements of Another Array using Array.every()
This is a three-step process:
- Call the
Array.every()method on the first array. - Check if the index of each element is found in the second array.
- If the condition is met for all elements, the array has all elements of the other array.
const arr1 = ['pizza', 'cola']; const arr2 = ['pizza', 'cake', 'cola'] const containsAll = arr1.every(element => { return arr2.indexOf(element) !== -1; }); console.log(containsAll); // 👉️ true
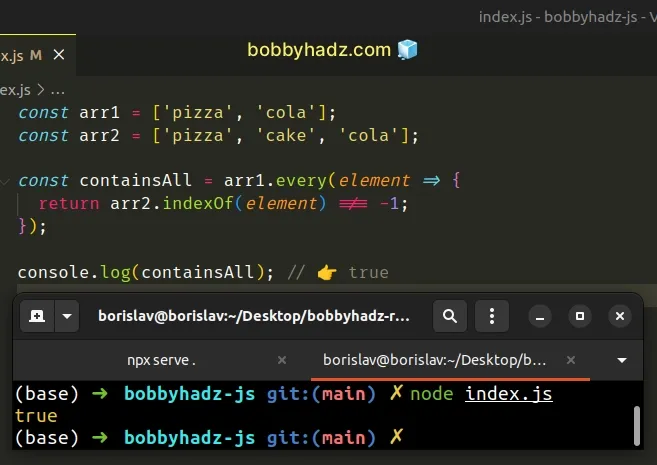
Array.every method returns true only if the condition is satisfied for all array elements.We used the Array.every() method to iterate over the first array.
On each iteration, we check if the current element is contained in the second array.
The Array.indexOf method
returns the index of the provided value in the array. If the value is not found
in the array, the method returns -1.
const arr1 = ['pizza', 'cake', 'cola']; console.log(arr1.indexOf('cola')); // 👉️ 2 console.log(arr1.indexOf('XYZ')); // 👉️ -1
The arr2 array contains all of the elements of arr1, therefore the return
value of the Array.indexOf() method will never be equal to -1.
After the Array.every() method finishes iterating, it returns true.
Alternatively, you can use a for...of loop.
# Check if Array has all Elements of Another Array using for...of
This is a three-step process:
- Declare a boolean variable setting it to
true. - Use a
for...ofloop to iterate over the first array. - If a value is not contained in the second array, set the variable to
false.
const arr1 = ['pizza', 'cola']; const arr2 = ['pizza', 'cake', 'cola']; let containsAll = true; for (const element of arr1) { if (!arr2.includes(element)) { containsAll = false; break; } } console.log(containsAll); // 👉️ true
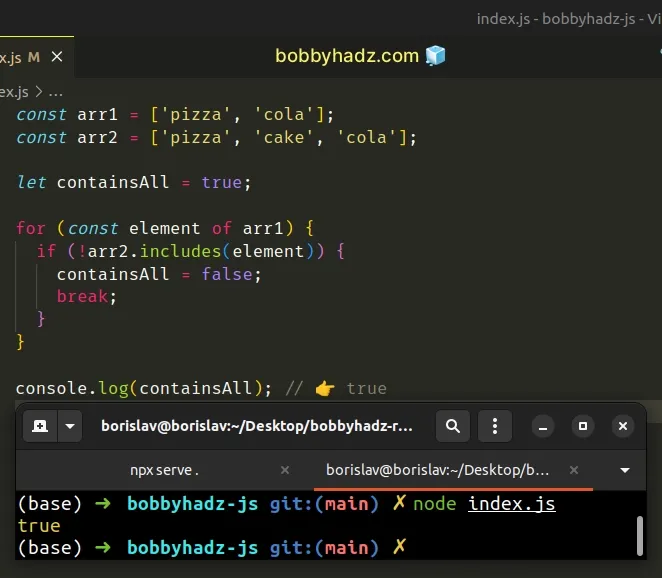
We used a for...of loop to iterate over the first array.
The for...of statement is
used to loop over iterable objects like arrays, strings, Map, Set and
NodeList objects and generators.
On each iteration, we use the Array.includes() method to check if the second
array contains the current value.
If the condition is not met, we set the containsAll variable to false and
break out of the loop.
Notice that we declared the variable using the let keyword.
let containsAll = true;
This is necessary because variables declared using const cannot be reassigned.
The break statement is used to exit the loop to avoid unnecessary iterations.
You can also use a basic for loop to check if all elements in an array exist
in another array.
# Check if Array has all Elements of Another Array using for
Here is an example of using a basic for loop to achieve the same result.
const arr1 = ['pizza', 'cola']; const arr2 = ['pizza', 'cake', 'cola']; let containsAll = true; for (let index = 0; index < arr1.length; index++) { if (!arr2.includes(arr1[index])) { containsAll = false; break; } } console.log(containsAll); // 👉️ true
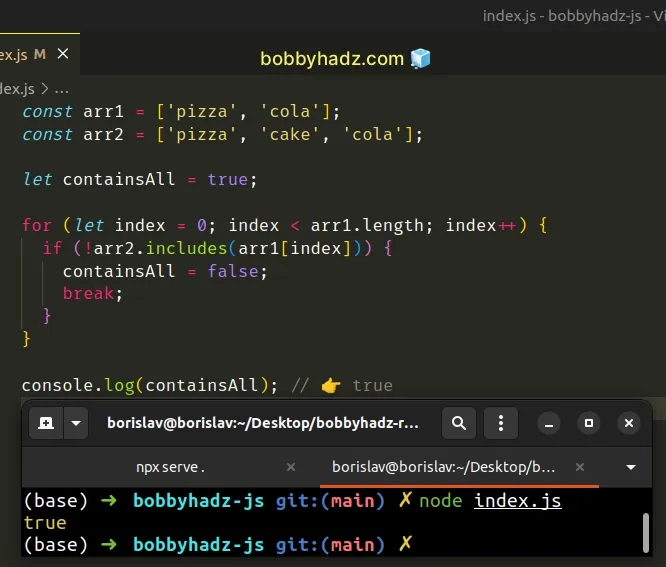
The code sample is very similar to the previous one.
However, instead of using for...of to iterate over the array, we used a basic
for loop.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I'd use the
Array.every() method because I find it quite intuitive and direct.
I've also written an article on how to check if an array contains any element of another array.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

