Check if Letter in String is Uppercase or Lowercase in JS
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·7 min

# Table of Contents
- Check if letter in String is Uppercase or Lowercase
- Check if letter in String is Uppercase or Lowercase using RegExp.test()
- Check if the First Letter of a String is Uppercase in JavaScript
- Capitalize the first letter of a string
# Check if letter in String is Uppercase or Lowercase
To check if a letter in a string is uppercase or lowercase:
- Use the
toUpperCase()method to convert the letter to uppercase. - Compare the letter to itself.
- If the comparison returns
true, the letter is uppercase, otherwise, it's lowercase.
const letter = 'A'; // ✅ Check if a letter is uppercase if (letter.toUpperCase() === letter) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ letter is uppercase'); } else { console.log('⛔️ letter is lowercase'); } // --------------------------------------- // ✅ Check if a letter is lowercase const letter2 = 'b'; if (letter2.toLowerCase() === letter2) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The letter is lowercase'); } else { console.log('The letter is uppercase'); }
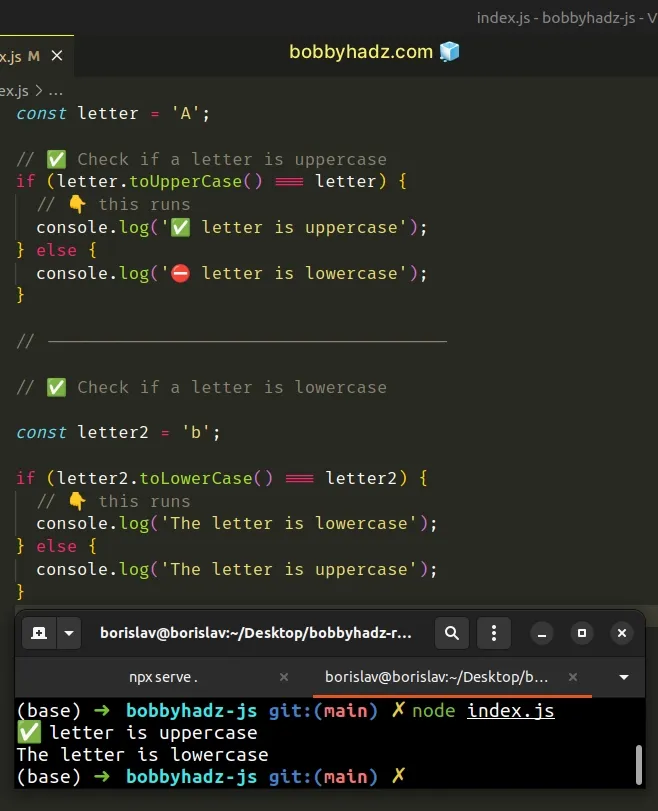
We used the String.toUpperCase() method to convert the character to uppercase so we can compare it.
If comparing the uppercase variant of the letter to the letter itself returns
true, then the letter is uppercase.
const char = 'B'; console.log(char.toUpperCase()); // 👉️ 'B' console.log(char === char.toUpperCase()); // 👉️ true
Otherwise, the letter is lowercase.
const char = 'b'; console.log(char.toUpperCase()); // 👉️ 'B' console.log(char === char.toUpperCase()); // 👉️ false
You can also access a specific letter in a string by accessing the string at an index.
const str = 'aBc'; const letter = str[1]; console.log(letter); // 👉️ 'B' if (letter.toUpperCase() === letter) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ letter is uppercase'); } else { console.log('⛔️ letter is lowercase'); }
0 and the last character has an index of str.length - 1.If you have to check if a letter is uppercase or lowercase often, define a reusable function.
function isUpperCase(string) { return string.toUpperCase() === string; } console.log(isUpperCase('ABC')); // 👉️ true console.log(isUpperCase('A')); // 👉️ true console.log(isUpperCase('b')); // 👉️ false console.log(isUpperCase('Ab')); // 👉️ false
The isUpperCase() function takes a string or a single letter and returns
true if the letter is uppercase and false otherwise.
The same approach can be used to define an isLowerCase function.
function isLowerCase(string) { return string.toLowerCase() === string; } console.log(isLowerCase('ABC')); // 👉️ false console.log(isLowerCase('A')); // 👉️ false console.log(isLowerCase('b')); // 👉️ true console.log(isLowerCase('Ab')); // 👉️ false
The isLowerCase() function takes a string or a single letter as a parameter
and returns true if the string is lowercase and false otherwise.
# Dealing with digits and punctuation
However, this approach wouldn't work with digits or punctuation because they can't be uppercase or lowercase.
const letter = '?'; if (letter.toUpperCase() === letter) { // 👉️ this runs... console.log('✅ letter is uppercase'); } else { console.log('⛔️ letter is lowercase'); }
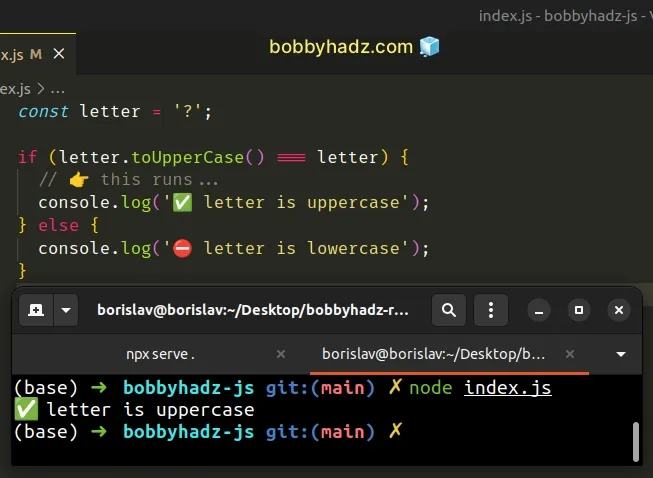
To resolve this issue, we have to check if the letter has uppercase and lowercase variants.
const letter = '?'; if (letter.toUpperCase() === letter && letter !== letter.toLowerCase()) { console.log('✅ letter is uppercase'); } else { // 👉️ this runs console.log('⛔️ letter is lowercase'); }
There are 2 conditions in our if statement:
- Check if the letter's uppercase variant is equal to the letter.
- Check if the letter is not equal to its lowercase variant.
If both conditions are met, the letter is uppercase.
const str = '4'; // 👇️️ true console.log(str.toLowerCase() === str.toUpperCase());
If we know that the letter is uppercase and it's not equal to its lowercase variant, then we have an uppercase letter.
Otherwise, we have a lowercase letter, a digit or punctuation.
If you have to do this often, define reusable functions.
function isUpperCase(letter) { if ( letter.toUpperCase() === letter && letter !== letter.toLowerCase() ) { console.log('✅ letter is uppercase'); return true; } console.log('⛔️ letter is lowercase'); return false; } const str = 'BObby'; console.log(isUpperCase(str[0])); // 👉️ true console.log(isUpperCase(str[1])); // 👉️ true console.log(isUpperCase(str[2])); // 👉️ false console.log(isUpperCase(str)); // 👉️ false
The isUpperCase function takes a letter and returns true if the letter is
uppercase and false otherwise.
isUpperCase function, it doesn't have to be a single letter.The same approach can be used to check if a letter (or a string) is lowercase.
function isLowerCase(letter) { if ( letter.toLowerCase() === letter && letter !== letter.toUpperCase() ) { return true; } return false; } const str = 'BObby'; console.log(isLowerCase(str[0])); // 👉️ false console.log(isLowerCase(str[1])); // 👉️ false console.log(isLowerCase(str[2])); // 👉️ true console.log(isLowerCase(str)); // 👉️ false
The isLowerCase() function takes a string as a parameter and returns true if
the string is lowercase and false otherwise.
# Check if letter in String is Uppercase or Lowercase using RegExp.test()
Alternatively, you can use the RegExp.test() method.
The test() method will return true if the letter is uppercase and false if
the letter is lowercase.
function isUpperCase(string) { return /^[A-Z]+$/.test(string); } console.log(isUpperCase('')); // 👉️ false console.log(isUpperCase('A')); // 👉️ true console.log(isUpperCase('b')); // 👉️ false console.log(isUpperCase('Ab')); // 👉️ false console.log(isUpperCase('ABC')); // 👉️ true
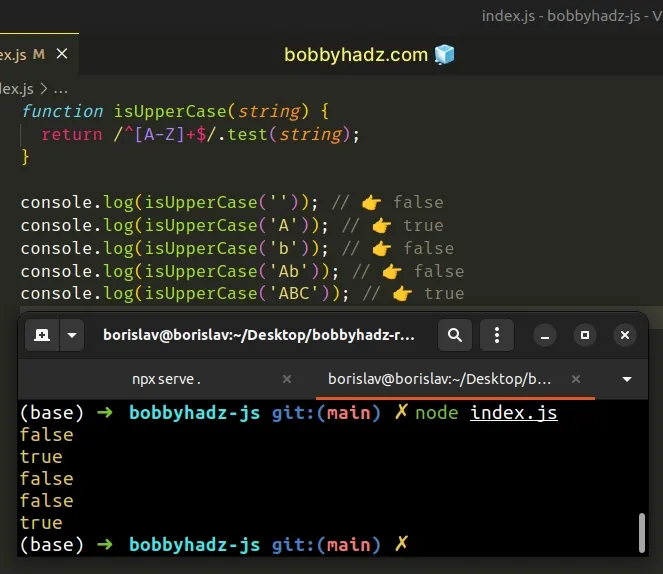
If you want to check if a letter is lowercase, you just have to lowercase the
A-Z letters in the range.
function isLowerCase(string) { return /^[a-z]+$/.test(string); } console.log(isLowerCase('')); // 👉️ false console.log(isLowerCase('A')); // 👉️ false console.log(isLowerCase('b')); // 👉️ true console.log(isLowerCase('Ab')); // 👉️ false console.log(isLowerCase('ABC')); // 👉️ false
Note that this approach only works for ASCII letters. If you have to handle all letters, use the approach from the previous subheading.
The
RegExp.test()
method checks if the regular expression is matched in the string and returns
true if it is and false otherwise.
The forward slashes / / mark the beginning and end of the regular expression.
The caret ^ symbol matches the beginning of the input and the dollar sign
$ matches the end of the input.
The part between the square brackets [] is called a character class and
matches the uppercase or lowercase letters in the range.
The plus + matches the preceding item (the letter range) 1 or more times.
As previously noted, this approach only works for ASCII letters (A-Z).
# Check if the First Letter of a String is Uppercase in JavaScript
To check if the first letter of a string is uppercase:
- Use the
String.charAt()method to get the first letter of the string. - Use the
String.toUppercase()method to convert the letter to uppercase. - Compare the result to the letter.
function firstIsUppercase(str) { if (str.length === 0) { return false; } return str.charAt(0).toUpperCase() === str.charAt(0); } console.log(firstIsUppercase('Hello')); // 👉️ true console.log(firstIsUppercase('world')); // 👉️ false console.log(firstIsUppercase('')); // 👉️ false if (firstIsUppercase('Hello')) { console.log('✅ First letter is uppercase'); } else { console.log('⛔️ First letter is NOT uppercase'); }
We first
check if the supplied string is empty.
If it is, the function returns false.
The String.charAt() method returns the character at the specified index or an empty string if the index doesn't exist.
We used the String.toUpperCase() method to convert the first letter of the string to uppercase and then we compared it to itself.
0 and the last character has an index of str.length - 1.If comparing the uppercase variant of the first letter to the letter itself
returns true, then the first letter is uppercase.
const str = 'Hello'; console.log(str[0].toUpperCase()); // 👉️ H console.log(str[0].toUpperCase() === str[0]); // 👉️ true
Otherwise, the first letter is lowercase.
const str = 'hi'; console.log(str[0].toUpperCase()); // 👉️ H console.log(str[0].toUpperCase() === str[0]); // 👉️ false
# Capitalize the first letter of a string
To capitalize the first letter of a string:
- Use the
String.charAtmethod to get the first letter of the string. - Use the
String.toUpperCase()method to convert the letter to uppercase. - Use the
slice()method to append the rest of the string to the result.
function capitalizeFirst(str) { return str.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + str.slice(1); } console.log(capitalizeFirst('apple')); // 👉️ Apple console.log(capitalizeFirst('one two')); // 👉️ One two console.log(capitalizeFirst('')); // 👉️ ''
We used the String.charAt() method to get the first letter of the string and
converted it to uppercase.
The last step is to use the String.slice() method to append the remainder of
the string to the letter.
console.log('apple'.slice(1)); // 👉️ pple console.log('hello'.slice(1)); // 👉️ ello
The String.slice() method extracts a section of a string and returns it, without modifying the original string.
The String.slice() method takes the following arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| start index | The index of the first character to include in the returned substring |
| end index | The index of the first character to exclude from the returned substring |
String.slice() method, the slice goes to the end of the string.The addition (+) operator can be used to concatenate two or more strings.
# Check if the first letter of a string is uppercase using RegExp.test()
You can also use the RegExp.test method to check if the first letter of a
string is uppercase.
The test() method will return true if the first letter is uppercase and
false otherwise.
function firstIsUppercase(str) { return /[A-Z]/.test(str.charAt(0)); } console.log(firstIsUppercase('Hello')); // 👉️ true console.log(firstIsUppercase('world')); // 👉️ false console.log(firstIsUppercase('')); // 👉️ false
The RegExp.test() method matches a regular expression in a string.
If the regex is matched in the string, the method returns true, otherwise
false is returned.
The forward slashes / / mark the beginning and end of the regular expression.
The square brackets [] are called a character class and match a range of
uppercase letters from A to Z.
We accessed the first character of the string in the call to the test()
method.
You can tweak the regular expression to check if the string starts with one or more capital letters.
function startsWithUppercase(str) { return /^[A-Z]/.test(str); } console.log(startsWithUppercase('Hello')); // 👉️ true console.log(startsWithUppercase('HELLO world')); // 👉️ true console.log(startsWithUppercase('world')); // 👉️ false console.log(startsWithUppercase('')); // 👉️ false
The caret ^ matches the beginning of the input.
Notice that we passed the entire string to the RegExp.test() method.
In its entirety, the regular expression checks if the supplied string starts with one or more uppercase letters.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

