How to check if a String is Empty in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 1, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Check if a String is Empty in JavaScript
Use the length property on the string to check if it is empty.
If the string's length is equal to 0, then it's empty, otherwise, it isn't
empty.
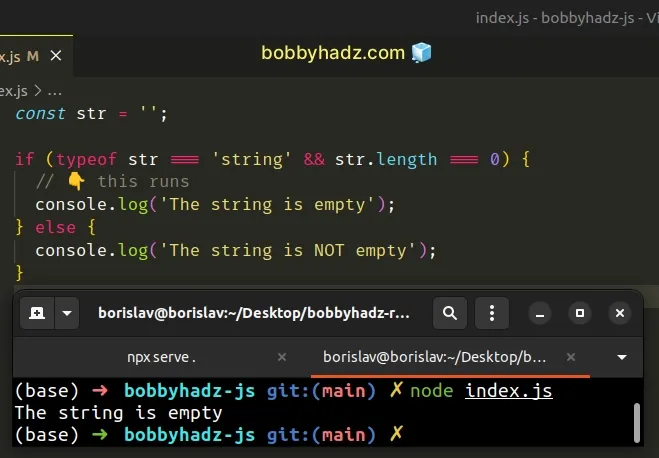
const str = ''; if (typeof str === 'string' && str.length === 0) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The string is empty'); } else { console.log('The string is NOT empty') }
The String.length property returns the number of characters in the string.
console.log(''.length); // 👉️ 0 console.log('a'.length); // 👉️ 1 console.log('ab'.length); // 👉️ 2
If accessing the string's length property returns 0, then the string is
empty.
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
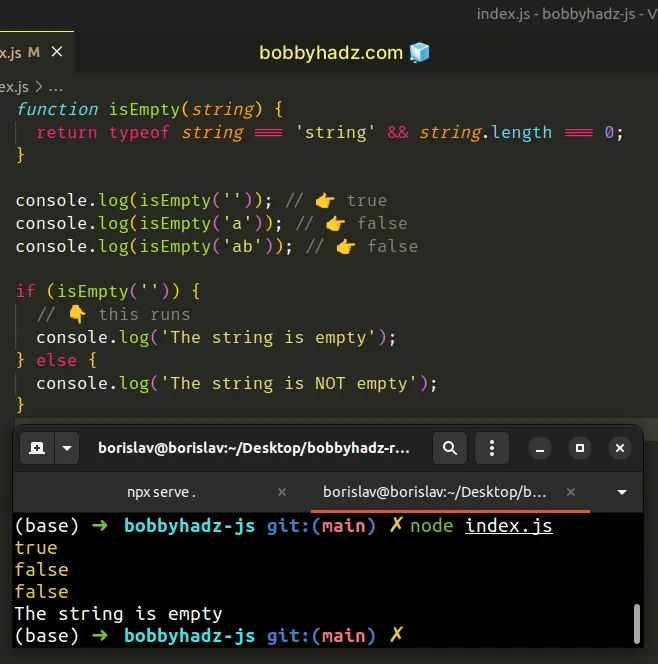
function isEmpty(string) { return typeof string === 'string' && string.length === 0; } console.log(isEmpty('')); // 👉️ true console.log(isEmpty('a')); // 👉️ false console.log(isEmpty('ab')); // 👉️ false if (isEmpty('')) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The string is empty'); } else { console.log('The string is NOT empty'); }
The function takes a string as a parameter and returns true if the string is
empty and false otherwise.
# Handling strings that only contain spaces
If you also consider an empty string one that contains only spaces, use the
String.trim() method before checking if the string is empty.
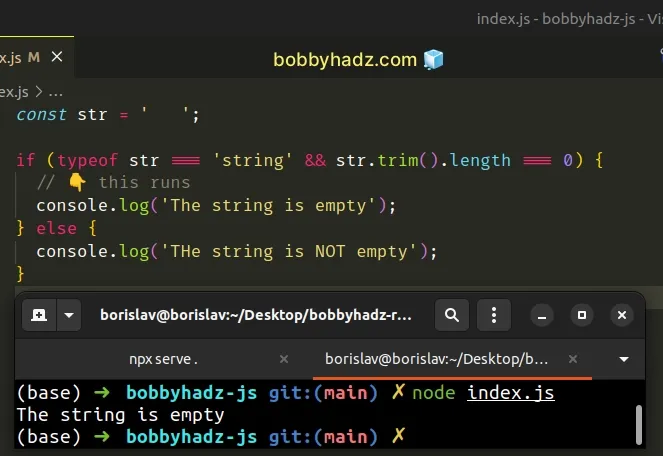
const str = ' '; if (typeof str === 'string' && str.trim().length === 0) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The string is empty'); } else { console.log('THe string is NOT empty'); }
The String.trim() method removes the leading and trailing whitespace from a string and returns a new string, without modifying the original string.
const str = ' '; console.dir(str.trim()); // 👉️ "" console.dir(str.length); // 👉️ 8 console.dir(str.trim().length); // 👉️ 0
The trim() method removes all whitespace characters including spaces, tabs and
newlines.
You can also use the optional chaining (?.) operator if you need to handle
null and undefined values.
const str = ' '; if (str?.trim()) { console.log('The string is NOT empty'); } else { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The string is empty'); }
The optional chaining (?.) operator
short-circuits and returns undefined if the value to the left is nullish
(null or undefined).
This handles a scenario where the str variable stores an undefined value.
const str = undefined; if (str?.trim()) { console.log('The string is NOT empty'); } else { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The string is empty'); }
Instead of getting an error for trying to call the trim() method on an
undefined value, the call short-circuits, returning undefined because we
used the optional chaining (?.) operator.
# Checking if a string isn't empty
Use the value in an if statement to check if it is
truthy.
const str = 'bobbyhadz.com'; if (str) { // if this code block runs // str is NOT "", undefined, null, 0, false, NaN console.log('The value is truthy'); } else { console.log( 'The value is undefined, null 0, false, NaN or empty string', ); }
The code in the if block wouldn't run if the str variable is set to an empty
string, undefined, null, 0, false or NaN.
All other values are truthy.
You can also check that the value isn't equal to an empty string.
const str = ''; if (typeof str === 'string' && str !== '') { console.log('The string is NOT empty'); } else { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The string is empty'); }
We used the logical AND (&&) operator to chain 2 conditions. Both conditions
have to be met for the if block to run.
- The first condition checks that the value is a string.
- The second checks that the string isn't empty.
# Checking if a string isn't empty or contains only whitespace
This approach wouldn't work for a string that contains only spaces.
If you need to handle strings that contain only spaces, use the trim() method.
const str = ' '; if (typeof str === 'string' && str.trim() !== '') { console.log('The string is NOT empty'); } else { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The string is empty'); }
We first make sure that the str variable contains a string and then we call
the String.trim() method.
If we try to call the trim method on a variable that is set to undefined or
null, we'd get an error.
# Checking if a value is falsy
If you need to check for a falsy value, use the logical NOT (!) operator.
const str = 'bobbyhadz.com'; if (!str) { console.log( 'The value is undefined, null 0, false, NaN or empty string', ); } else { // 👉️ str is NOT "", undefined, null, 0, false, NaN console.log('The string is truthy'); }
The if block is only run if the str variable stores a falsy value.
The falsy values in JavaScript are: false, 0, empty string "", null,
undefined and NaN (not a number).
All other values are truthy.
# Checking if a value is an empty string, undefined or null
You can use the logical OR (||) operator if you want to explicitly check if a
variable stores an empty string, undefined or null.
const str = ''; if (typeof str === undefined || str === null || str === '') { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The value is undefined, null or empty string'); } else { console.log( 'The value is NOT undefined, null or empty string', ); }
We used the logical OR (||) operator, so the if block is run if either
condition is met.
The if block in the example runs if the str variable stores undefined,
null or an empty string.
# Checking if a value is NOT an empty string, undefined or null
Conversely, you can use the logical AND (&&) operator to check if a variable
doesn't store an empty string, null or undefined.
const str = 'bobbyhadz.com'; if (typeof str !== undefined && str !== null && str !== '') { // 👇️ this runs console.log( 'The value is NOT undefined, null or empty string', ); } else { console.log('The value is undefined, null or empty string'); }
We used the logical AND (&&) operator, so for the if block to run, all
conditions have to be met.
We check that:
- The variable doesn't store an
undefinedvalue. - The variable doesn't store a
nullvalue. - The variable is not an empty string.
# Checking if a value is empty using lodash
If you use the lodash module, you can also use the isEmpty() method to check
if a value is empty.
If you need to install lodash, run the following command.
# 👇️ initialize a package.json file npm init -y npm install lodash
You can now import and use the lodash.isEmpty() method.
import _ from 'lodash'; console.log(_.isEmpty(null)); // 👉️ true console.log(_.isEmpty(undefined)); // 👉️ true console.log(_.isEmpty('')); // 👉️ true console.log(_.isEmpty([])); // 👉️ true console.log(_.isEmpty({})); // 👉️ true console.log(_.isEmpty(true)); // 👉️ true console.log(_.isEmpty('abc')); // 👉️ false console.log(_.isEmpty(['a', 'b'])); // 👉️ false console.log(_.isEmpty({a: 'b'})); // 👉️ false
The isEmpty() method returns true if the value is an empty string, null,
undefined, an empty object, collection, Map or Set.
Array-like objects, buffers and strings are considered empty if they have a
length of 0.
Similarly, Map and Set objects are considered empty if they have a size of
0.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

