How to Check if a Function returns True in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Check if a Function returns True in JavaScript
To check if a function returns true:
- Call the function and check if its return value is equal to
true. - If the condition is met, the function returns
true.
function doWork() { // logic ... return true; } // 👇️ Check if returns explicitly `true` if (doWork() === true) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ function returns true'); } else { console.log('the function does NOT return true'); }
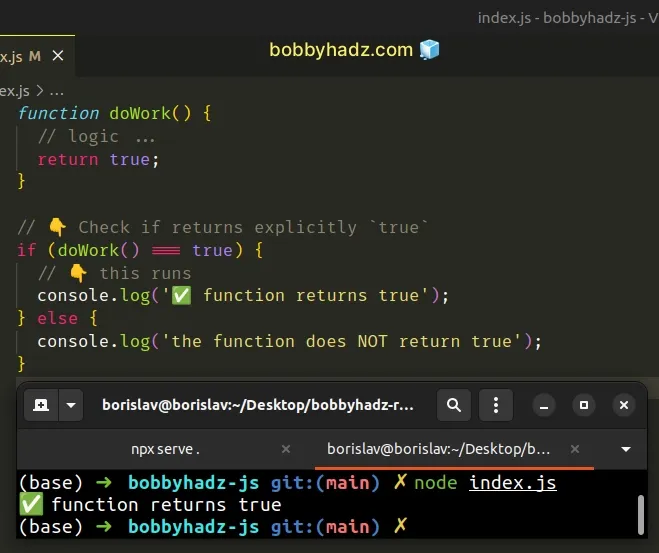
The only way to check if a function returns true is to call the function and
check if its return value is equal to true.
If the condition is met, the if block is run, otherwise, the else block
runs.
Alternatively, you can check if a function returns a truthy value.
# Check if a Function returns a Truthy value in JavaScript
To check if a function returns a truthy value:
- Call the function and use its return value in an
ifstatement. - The
ifblock is only run if the function returns a truthy value.
function doWork() { // logic ... return true; } // 👇️ Check if returns Truthy value if (doWork()) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ function returns TRUTHY value'); } else { console.log('The function does NOT return a truthy value'); }
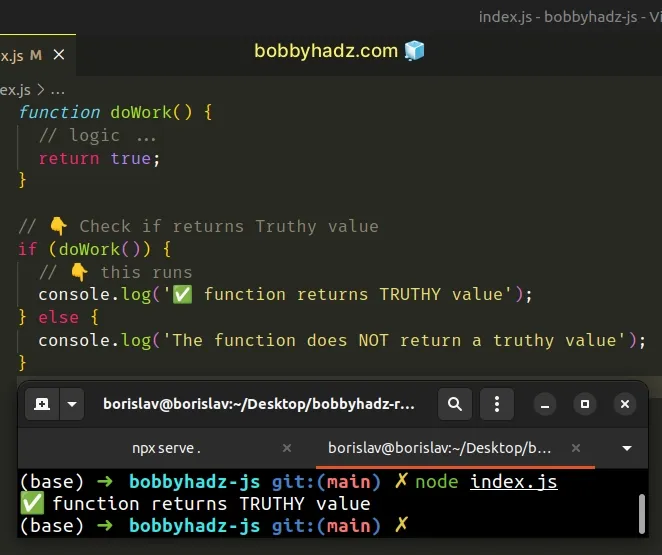
The falsy values in JavaScript are: false, null, undefined, 0, ""
(empty string), NaN (not a number).
All other values are truthy.
The if statement
checks if the return value of the function is truthy.
if block is run if the function returns any other than the aforementioned 6 falsy values.function doWork() { // logic ... return 'bobbyhadz.com'; } // 👇️ Check if returns Truthy value if (doWork()) { console.log('✅ function returns TRUTHY value'); } else { console.log('The function does NOT return a truthy value'); }
The function in the example returns a string and all non-empty strings are
truthy values, so the if block runs.
If you pass a value to the Boolean() constructor and it returns true, then
the if condition will be met and the if block will run.
Here are some examples of passing truthy and falsy values to the Boolean()
constructor.
// 👇️ truthy values console.log(Boolean('hello')); // 👉️ true console.log(Boolean(1)); // 👉️ true console.log(Boolean([])); // 👉️ true console.log(Boolean({})); // 👉️ true // 👇️ falsy values console.log(Boolean('')); // 👉️ false console.log(Boolean(0)); // 👉️ false console.log(Boolean(undefined)); // 👉️ false console.log(Boolean(null)); // 👉️ false
# Check if a function returns a truthy value using logical AND (&&)
You can also use the logical AND (&&) operator to check if a function returns a truthy value.
function doWork() { // logic ... return true; } function sum(a, b) { return a + b; } const result = doWork() && sum(10, 15); console.log(result); // 👉️ 25
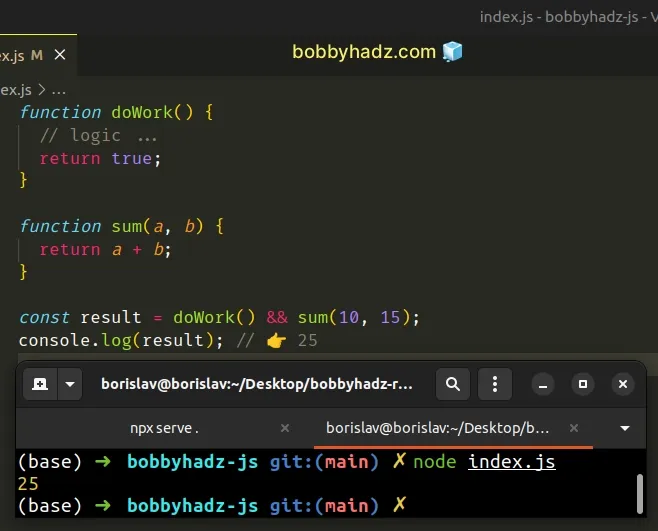
The logical AND (&&) operator returns the value to its left if it's falsy, otherwise, the value to its right is returned.
The doWork() function returns a truthy value, so the sum() function is
invoked and its value is returned.
You can also explicitly check if the value is equal to true even though this
is less common.
function doWork() { return 'bobbyhadz.com'; } function sum(a, b) { return a + b; } const result = doWork() === true && sum(10, 15); console.log(result); // 👉️ false
The function returns a truthy value, but it doesn't return true, so the
logical AND (&&) operator short-circuits returning the value to the left.
Here is an example of using the operator with a function that returns a falsy value.
function doWork() { // logic ... return false; } function sum(a, b) { return a + b; } const result = doWork() && sum(10, 15); console.log(result); // 👉️ false
If the value to the left of the logical AND (&&) operator is falsy, the expression to the right is not evaluated at all.
# Check if a function returns a truthy value using ternary operator
You can also use the ternary operator to check if a function returns true or a
truthy value.
function doWork() { return true; } function sum(a, b) { return a + b; } const result = doWork() ? sum(10, 10) : 'abcd'; console.log(result); // 👉️ 20
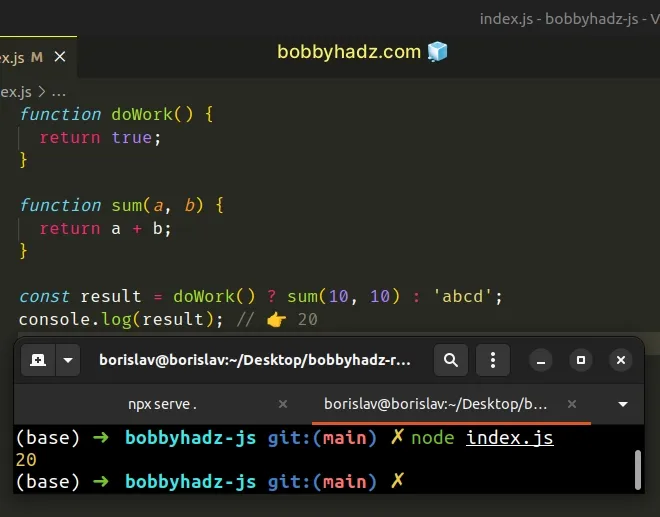
The ternary operator is
very similar to an if/else statement.
If the expression to the left of the question mark is truthy, the operator returns the value to the left of the colon, otherwise, the value to the right of the colon is returned.
You can also use this approach to check if the function returns true.
function doWork() { return true; } function sum(a, b) { return a + b; } const result = doWork() === true ? sum(10, 10) : 'abcd'; console.log(result); // 👉️ 20
Here is an example where the function returns a falsy value.
function doWork() { return ''; } function sum(a, b) { return a + b; } const result = doWork() ? sum(10, 10) : 'abcd'; console.log(result); // 👉️ 'abcd'
The function returns a falsy value, so the expression after the colon is returned.
You can imagine that the value before the colon is the if block and the value
after the colon is the else block.

