How to convert a Blob to an ArrayBuffer in JavaScript
Last updated: Apr 4, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# How to convert a Blob to an ArrayBuffer in JavaScript
Use the blob.arrayBuffer() method to convert a Blob to an ArrayBuffer in
JavaScript.
The arrayBuffer method returns a Promise that resolves with the contents of
the blob as binary data contained in an ArrayBuffer.
async function example() { const blob = new Blob(['bobbyhadz.com']); const buf = await blob.arrayBuffer(); console.log(buf); console.log(buf.byteLength); console.log(buf.slice(0, 5)); } example();
Running the code snippet above produces the following output.
ArrayBuffer { [Uint8Contents]: <62 6f 62 62 79 68 61 64 7a 2e 63 6f 6d>, byteLength: 13 } 13 ArrayBuffer { [Uint8Contents]: <62 6f 62 62 79>, byteLength: 5 }
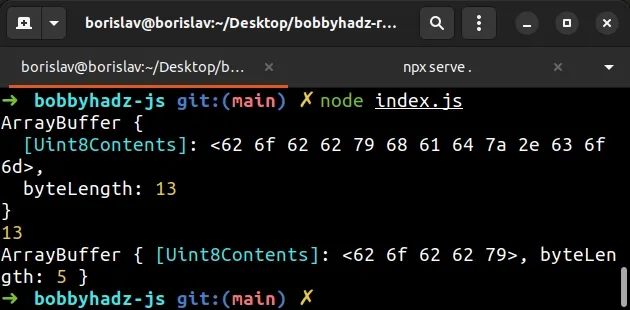
We used an async/await function
to await the Promise that is returned from the blob.arrayBuffer() method.
const buf = await blob.arrayBuffer();
The method returns a Promise that resolves with the contents of the blob as
binary data contained in an ArrayBuffer.
The byteLength property of the ArrayBuffer returns the length of the
ArrayBuffer in bytes.
console.log(buf.byteLength);
The ArrayBuffer.slice method returns a copy of the ArrayBuffer from the
specified start byte index, up to but not including the specified end byte
index.
You can use the new Blob() constructor if you need to convert the
ArrayBuffer back to a Blob.
async function example() { const blob = new Blob(['bobbyhadz.com']); const buf = await blob.arrayBuffer(); console.log(buf); console.log(buf.byteLength); console.log(buf.slice(0, 5)); const blobAgain = new Blob([buf]); const str = await blobAgain.text(); console.log(str); // 👉️ bobbyhadz.com } example();
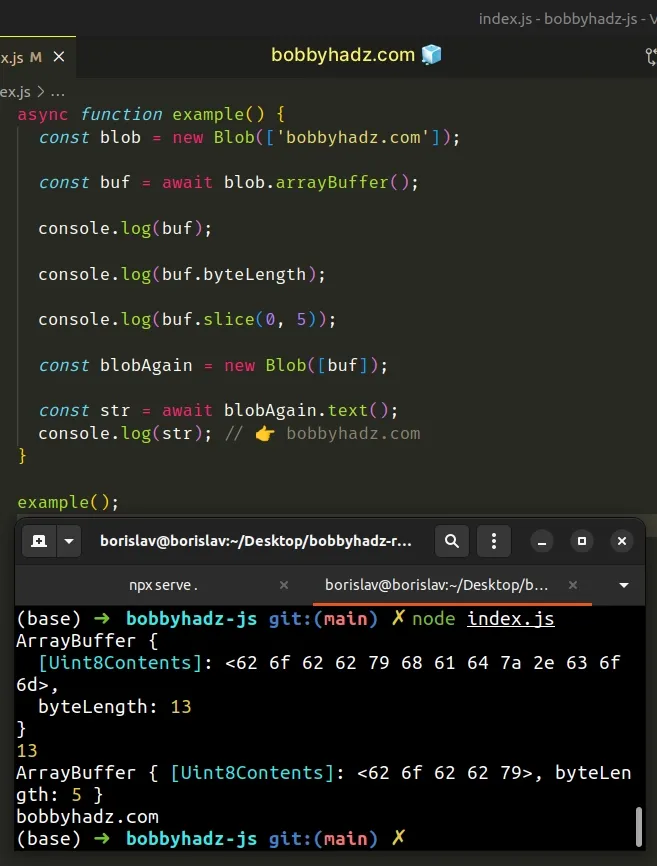
The new Blob() constructor returns a new Blob object.
The contents of the blob consist of the concatenation of the values in the supplied array.
The constructor takes an array whose contents are put inside the created Blob.
The Blob.text() method returns a Promise that resolves with a string containing the contents of the blob.
# Convert a Blob to an ArrayBuffer using .then() in JavaScript
The example used the async/await syntax, however, you can also use the
.then syntax to wait for the Promise
to resolve.
const blob = new Blob(['bobbyhadz.com']); blob.arrayBuffer().then(buf => { console.log(buf); console.log(buf.byteLength); console.log(buf.slice(0, 5)); });
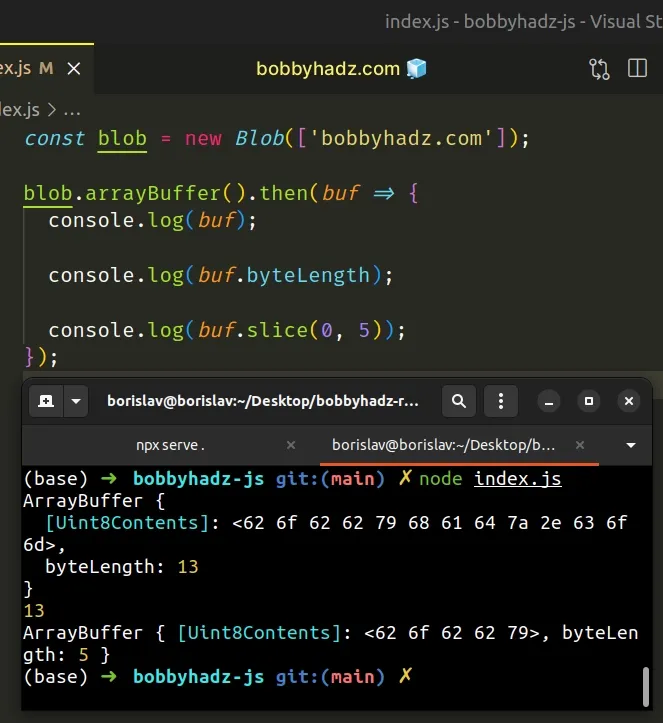
Running the code sample above produces the same output.
ArrayBuffer { [Uint8Contents]: <62 6f 62 62 79 68 61 64 7a 2e 63 6f 6d>, byteLength: 13 } 13 ArrayBuffer { [Uint8Contents]: <62 6f 62 62 79>, byteLength: 5 }
However, this time we used the .then() syntax to wait for the
blob.arrayBuffer() method to resolve with the contents of the blob as binary
data contained in an ArrayBuffer.
If you want to convert the ArrayBuffer back to a blob, use the new Blob()
constructor.
const blob = new Blob(['bobbyhadz.com']); blob.arrayBuffer().then(buf => { console.log(buf); console.log(buf.byteLength); console.log(buf.slice(0, 5)); const blobAgain = new Blob([buf]); blobAgain.text().then(str => { // 👇️ bobbyhadz.com console.log(str); }); });
We used the new Blob() constructor to convert the ArrayBuffer to a Blob.
The Blob.text() method returns a Promise that resolves with a string
containing the contents of the blob.
# Convert a Blob to an ArrayBuffer using the Response() constructor
You can also use the
Response()
constructor to convert a Blob to an ArrayBuffer.
async function example() { const blob = new Blob(['bobbyhadz.com']); const buf = await new Response(blob).arrayBuffer(); console.log(buf); console.log(buf.byteLength); console.log(buf.slice(0, 5)); } example();
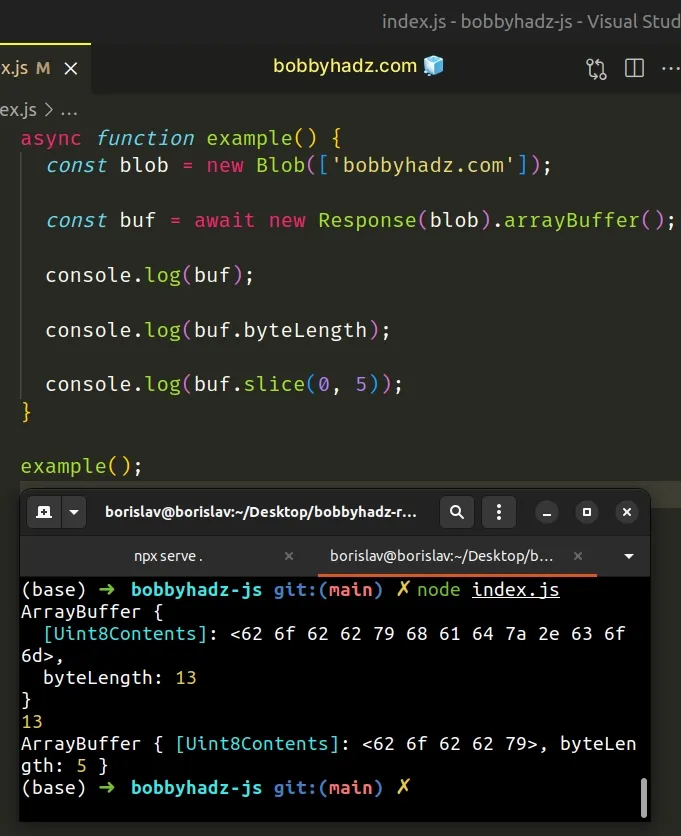
The code sample above produces the same output.
ArrayBuffer { [Uint8Contents]: <62 6f 62 62 79 68 61 64 7a 2e 63 6f 6d>, byteLength: 13 } 13 ArrayBuffer { [Uint8Contents]: <62 6f 62 62 79>, byteLength: 5 }
This time we used the Response constructor to create a Response object and called the Response.arrayBuffer() method.
The Response interface of the Fetch API represents the response to an HTTP
request.
The Response.arrayBuffer method is more widely supported than
buffer.arrayBuffer but this likely won't matter unless you have to support
very old browsers.
Here is the equivalent code sample but using .then().
const blob = new Blob(['bobbyhadz.com']); new Response(blob).arrayBuffer().then(buf => { console.log(buf); console.log(buf.byteLength); console.log(buf.slice(0, 5)); });
The Response.arrayBuffer method takes a Response stream and reads it to
completion.
The method returns a Promise that resolves with an ArrayBuffer.
If you need to convert the ArrayBuffer back to a Blob, pass it to the
new Blob() constructor.
const blob = new Blob(['bobbyhadz.com']); new Response(blob).arrayBuffer().then(buf => { console.log(buf); console.log(buf.byteLength); console.log(buf.slice(0, 5)); const blobAgain = new Blob([buf]); blobAgain.text().then(str => { // 👇️ bobbyhadz.com console.log(str); }); });
I've also written an article on how to set the filename of a blob in JavaScript.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Download Images using JavaScript (Local and from URL)
- How to fetch Data on Button click in React
- TypeError: Failed to fetch and CORS in JavaScript [Solved]
- fetch() returns empty Response Body in JavaScript [Solved]
- How to Use an Image as a Link in React.js
- Import and use an Image in a React component
- Convert an HTML table to JSON and export it to a file in JS

