Get and set Account ID, Region & Availability Zones in CDK
Last updated: Jan 27, 2024
Reading time·7 min

# Table of Contents
- Getting AccountId and Region in AWS CDK
- Environment Agnostic Stacks in AWS CDK
- Getting the Availability Zones in CDK
# Getting AccountId and Region in AWS CDK
To access the accountId, region and availabilityZones properties in our
CDK code, we have to set the env property when instantiating our Stack.
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class MyCdkStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); console.log('accountId: ', cdk.Stack.of(this).account); console.log('region: ', cdk.Stack.of(this).region); console.log('availability zones: ', cdk.Stack.of(this).availabilityZones); } } const app = new cdk.App(); new MyCdkStack(app, `my-cdk-stack-dev`, { stackName: `my-cdk-stack-dev`, // 👇 now explicitly setting account and region env: { region: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_REGION, account: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT, }, });
If we run the npx aws-cdk synth command, we can see that we are now able to
access the accountId, region and availabilityZones at synthesis time in
our CDK code.
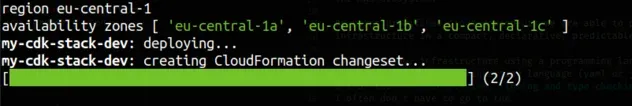
I have excluded the accountId property from the screenshot, but it too was resolved.
The
recommended way by the CDK team
to get access to the accountId and region properties is to use the
Stack.of(this).account and Stack.of(this).region API.
Notice that in our code snippet above, we used two environment variables that are available in our CDK environment.
{ region: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_REGION, account: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT, }
The value of these environment variables depends on whether we pass in a
--profile flag when we issue the npx aws-cdk deploy command.
For example, if we specify a profile, the values of CDK_DEFAULT_REGION and
CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT would correspond to the profile's region and account
properties.
npx aws-cdk deploy --profile myprofile my-stack
If we don't set the --profile flag, the values will correspond to the default
profile's region and account properties.
npx aws-cdk deploy my-stack
Either way, if we have the AWS CLI configured on our machine, by passing in the
CDK_DEFAULT_REGION and CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT properties we are explicitly
setting the environment, which enables us to access the properties at synthesis
time in our CDK code.
CDK_DEFAULT_REGION and CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT environment variables. The default profile of the different developers working on the project could be set to different regions and accounts.Instead, just pass the values as environment variables explicitly. You can hard code the values, manage them as secrets, etc.
# Table of Contents
# Environment Agnostic Stacks in AWS CDK
An environment-agnostic stack is a stack where we haven't explicitly set the
account and region properties.
const app = new cdk.App(); new MyCdkStack(app, `my-cdk-stack-dev`, { stackName: `my-cdk-stack-dev`, // 👇 we are not explicitly setting the region and account // env: { // region: 'us-east-1', // account: 123456789, // } });
Because we haven't explicitly set the env property in our stack, the account
and region properties will be resolved by CloudFormation at deployment time
rather than synthesis time.
Since we want access to these properties in our CDK code we have to find a way to resolve them at synthesis time.
Let's try to get the accountId, region and availabilityZones properties in
an environment agnostic stack, without explicitly setting the env property.
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class MyCdkStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // 👇 recommended way to get access to the properties console.log('accountId: ', cdk.Stack.of(this).account); console.log('region: ', cdk.Stack.of(this).region); console.log('availability zones: ', cdk.Stack.of(this).availabilityZones); } } const app = new cdk.App(); new MyCdkStack(app, `my-cdk-stack-dev`, { stackName: `my-cdk-stack-dev`, // 👇 we are not explicitly setting the region and account // env: { // region: 'us-east-1', // account: 123456789, // } tags: {env: 'dev'}, });
We only get unresolved token values that will eventually be resolved at deployment time by CloudFormation.
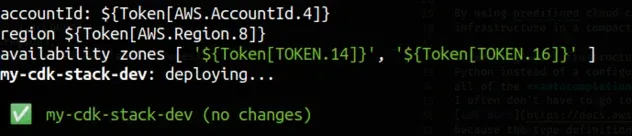
The solution is to explicitly set the account and region and call the
Stack.of APIs:
console.log('accountId:', cdk.Stack.of(this).account); console.log('region', cdk.Stack.of(this).region); console.log('availability zones', cdk.Stack.of(this).availabilityZones);
# Getting the Availability Zones in CDK
Every AWS Region consists of multiple Availability Zones. Usually when we provision resources we have to specify the region, and sometimes the availability zones, i.e. for EC2 or RDS instances.
We provision resources in multiple availability zones to avoid unexpected downtime in case of Availability Zone outages.
In order to get the Availability Zones in CDK we have to use the availabilityZones property on the core Stack construct.
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class MyCdkStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // 👇 get Availability Zones, Region, Account console.log('availability zones 👉', cdk.Stack.of(this).availabilityZones); console.log('region 👉', cdk.Stack.of(this).region); console.log('accountId 👉', cdk.Stack.of(this).account); } } const app = new cdk.App(); new MyCdkStack(app, 'my-cdk-stack', { stackName: 'my-cdk-stack', // 👇 Set the environment for the stack env: { region: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_REGION, account: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT, }, });
In the code sample:
We used the availabilityZones property on the Stack construct in order to get access to the availability zones of the region our CDK application is configured for.
We set the
envproperty when instantiating our CDK stack. This sets the environment (account, region), where our CDK stack will be deployed.
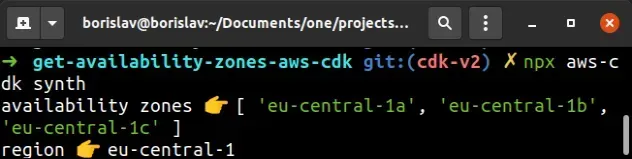
I'll issue the synth command to run my CDK code and print the values for the
Availability Zones and region.
npx aws-cdk synth
The output shows all of the Availability Zones for my default region -
eu-central-1.
If you get dummy values the first time you run the command, simply re-run
npx aws-cdk synth.
However, there are a couple of caveats with setting environments in CDK.
# Availability Zones Resolution in CDK
Every CDK stack we deploy belongs to a specific region and account. If
we don't explicitly set the region and account using the env property when
instantiating the stack, the stack is considered environment agnostic.
To better illustrate this scenario I'll comment out the env prop I've passed
to the stack upon instantiation:
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class MyCdkStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // 👇 accessing the same values console.log('availability zones 👉', cdk.Stack.of(this).availabilityZones); console.log('region 👉', cdk.Stack.of(this).region); console.log('accountId 👉', cdk.Stack.of(this).account); } } const app = new cdk.App(); new MyCdkStack(app, 'my-cdk-stack', { stackName: 'my-cdk-stack', // ❌️ NOT setting env // env: { // region: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_REGION, // account: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT, // }, });
I'll now issue the synth command to run my CDK code and print the outputs.
npx aws-cdk synth
The result shows the values as Tokens:
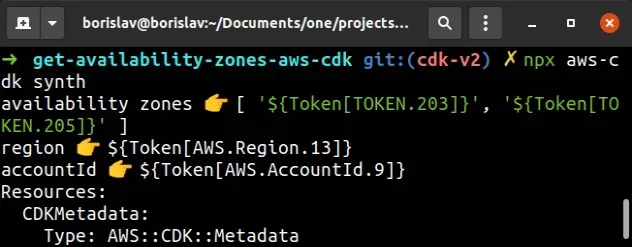
Tokens in CDK are encoded values that get resolved at deployment time by CloudFormation. This means we can't access the resolved version of these values in our CDK code, i.e. in conditional statements.
# Environment-Agnostic Stacks
The reason we're getting token values back is that we haven't set the env
property upon stack instantiation, which makes our stack environment-agnostic.
Environment-agnostic stacks resolve the values of region, account and
availability zones at deployment time, rather than synthesis time. This means
that we don't have access to the resolved values in our CDK code.
In the screenshot we can see only 2 Availability Zones, the reason being - there are AWS regions that only provide 2 availability zones and CDK doesn't know if we'll be deploying to one of them. The safe bet on CDK's part is to just allow us to use 2 Availability Zones.
The account and region in an environment-agnostic stack get resolved to the
account and region of the profile we've set using the --profile flag, for
example:
npx aws-cdk deploy --profile my-profile
If we don't explicitly set the --profile flag the account and region values
are resolved to the default AWS CLI profile's account and region:
npx aws-cdk deploy
# Best Practice - Explicitly set Env
In order to get access to all of the Availability Zones of a region, the best
practice is to explicitly specify the env property when instantiating a stack.
const app = new cdk.App(); new MyCdkStack(app, 'my-cdk-stack', { stackName: 'my-cdk-stack', // 👇 explicitly set Env env: { region: 'us-east-1', account: '123456789', }, });
By doing that we are able to set a consistent environment for our stack deployments, regardless of the machine we're deploying from.
Now we can get access to all of the Availability Zones for the region our stack is configured for.
An alternative approach is to use the environment variables that CDK provides for us, i.e.:
const app = new cdk.App(); new MyCdkStack(app, 'my-cdk-stack', { stackName: 'my-cdk-stack', // 👇 Implicitly set env env: { region: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_REGION, account: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT, }, });
The CDK_DEFAULT_REGION and CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT
environment variables are made available
for us in the CDK environment. They resolve at synthesis time, which means we
are able to access all of the Availability Zones for the region.
However, they rely on behavior specific to local machine configuration:
if we don't pass a
--profileflag when issuing thedeploycommand, these environment variables resolve (at synthesis time) to our default AWS Profile's account and region.if we provide the
--profileflag when deploying, the environment variables are set to the profile's account and region at synthesis time.The problem with this behavior is that local profile configuration may vary between your machine and the machines of other developers on your team, which might lead to deploying the CDK Stack to multiple accounts and regions.
# Summary
To access the availability zones of an AWS region we have to:
- Set the
envproperty when instantiating the CDK stack - use the availabilityZones property on the core Stack construct
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

