Unexpected `await` inside a loop.eslint no-await-in-loop
Last updated: Mar 7, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Unexpected
awaitinside a loop.eslint no-await-in-loop - Using the
Promise.all()method to await all Promises at the same time - Disabling the
no-await-in-looprule globally
# Unexpected await inside a loop.eslint no-await-in-loop
The ESLint error "Unexpected await inside a loop. eslint no-await-in-loop"
is raised when you use the await keyword to await each Promise in a loop.
To resolve the issue, use the Promise.all() method to await all Promises at
the same time or disable the ESLint rule for a line.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
const p1 = Promise.resolve(1); const p2 = Promise.resolve(2); async function example() { for (const promise of [p1, p2]) { // ⛔️ Unexpected `await` inside a loop. eslint no-await-in-loop await promise; } }
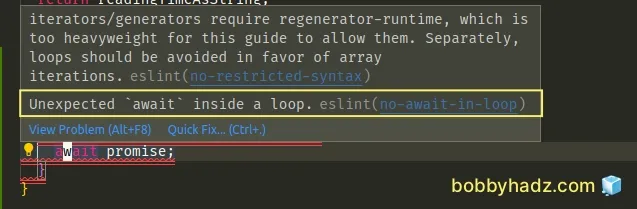
The issue in the code sample is that we are awaiting each promise in the array separately, on each iteration.
If you need to await the promises separately, one at a time, then you have to disable the ESLint rule.
The following comment disables the rule for a single line.
const p1 = Promise.resolve(1); const p2 = Promise.resolve(2); async function example() { for (const promise of [p1, p2]) { // eslint-disable-next-line no-await-in-loop await promise; } }
The comment has to be placed directly above your await statement in the loop.
Alternatively, you can disable the ESLint rule for a block of code.
const p1 = Promise.resolve(1); const p2 = Promise.resolve(2); async function example() { /* eslint-disable no-await-in-loop */ for (const promise of [p1, p2]) { await promise; } /* eslint-enable no-await-in-loop */ }
The first comment disables the rule and the second comment enables it.
If you need to disable the rule for an entire file, add the comment at the top of your file.
/* eslint-disable no-await-in-loop */ const p1 = Promise.resolve(1); const p2 = Promise.resolve(2); async function example() { for (const promise of [p1, p2]) { await promise; } }
# Using the Promise.all() method to await all Promises at the same time
If you don't necessarily have to await each Promise separately, one at a time, you can use the Promise.all() method to await all Promises at the same time and improve performance.
const p1 = Promise.resolve(1); const p2 = Promise.resolve(2); async function example() { const promisesArray = [p1, p2]; const result = await Promise.all(promisesArray); console.log(result); // 👉️ [ 1, 2 ] } example()
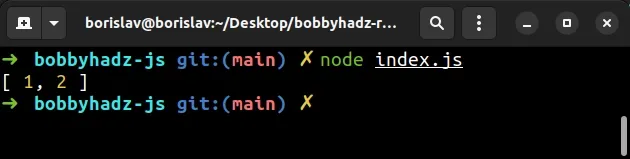
The Promise.all() method takes an iterable of Promises and returns a single
Promise.
The returned Promise fulfills when all of the supplied Promises fulfill.
As shown in the example, the method returns a Promise that resolves with an array containing the resolved values of the Promises from the iterable.
The await Promise.all() syntax awaits all of the Promises in the iterable at
the same time, so it is much more performant than awaiting each Promise
separately.
Here is another example that constructs an array of Promises in a for...of loop.
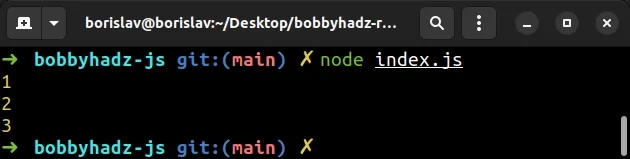
async function example() { const arr = [1, 2, 3] const promisesArray = [] for (const element of arr) { promisesArray.push(Promise.resolve(element)) } const result = await Promise.all(promisesArray); console.log(result); // 👉️ [ 1, 2, 3 ] } example()
We used a for...of loop to iterate over the array of numbers.
On each iteration, we use the Promise.resolve() method to construct an array of Promises.
The last step is to await the array of Promises using the Promise.all()
method.
The Promise.all() method returns an array so you can use
destructuring assignment to assign
the values of the array to variables.
async function example() { const arr = [1, 2, 3] const promisesArray = [] for (const element of arr) { promisesArray.push(Promise.resolve(element)) } const [a, b, c] = await Promise.all(promisesArray); console.log(a); // 👉️ 1 console.log(b); // 👉️ 2 console.log(c); // 👉️ 3 } example()
Note that you have to declare exactly as many variables as there are values in the array on the right-hand side.
# Disabling the no-await-in-loop rule globally
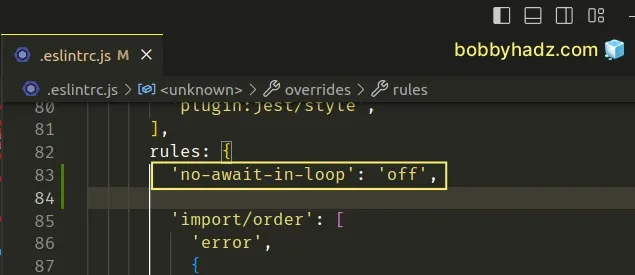
If you'd like to disable the no-await-in-loop ESLint rule globally, you have
to edit your .eslintrc.js config file.
module.exports = { rules: { 'no-await-in-loop': 'off', }, };
If you use a JSON config file (e.g. .eslintrc or .eslintrc.json), make sure
to double-quote all properties and values.
{ "rules": { "no-await-in-loop": "off" } }
Note that you shouldn't have trailing commas in a JSON config file.
If you still see the ESLint error after making the change, try to restart your IDE.
In general, it is better to just disable the rule when you need to await multiple Promises in a loop separately.
const p1 = Promise.resolve(1); const p2 = Promise.resolve(2); async function example() { for (const promise of [p1, p2]) { // eslint-disable-next-line no-await-in-loop await promise; } }
The following comments can also be used to disable the rule for a block of code or for an entire file.
const p1 = Promise.resolve(1); const p2 = Promise.resolve(2); async function example() { /* eslint-disable no-await-in-loop */ for (const promise of [p1, p2]) { await promise; } /* eslint-enable no-await-in-loop */ }
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- TypeScript ESLint: Unsafe assignment of an any value [Fix]
- ESLint error Unary operator '++' used no-plusplus [Solved]
- ESLint Prefer default export import/prefer-default-export
- Assignment to property of function parameter no-param-reassign
- Expected parentheses around arrow function argument arrow-parens
- Arrow function should not return assignment. eslint no-return-assign

