Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'map') in React
Last updated: Apr 6, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'map') in React
The "TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'map')" occurs
when we call the map() method on an undefined value, most often when the
map method is called before the data from an API request has arrived.
To solve the error, initialize the value you're mapping over to an empty array.

Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'map') Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read properties of null (reading 'map')

The solution is the same if you get the error "TypeError: Cannot read properties 'map' of null".
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import {useState, useEffect} from 'react'; function App() { // ⛔️ State is not initialized to an empty array const [users, setUsers] = useState(); useEffect(() => { async function getUsers() { const response = await fetch('https://randomuser.me/api/', { method: 'GET', headers: { accept: 'application/json', }, }); const data = await response.json(); setUsers(data.results); } getUsers(); }, []); console.log(users); return ( <div> {/* ⛔️ users is `undefined` because API has not responded yet */} {/* ⛔️ Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'map') */} {users.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> </div> ))} </div> ); } export default App;
We declared the users variable but didn't initialize it to an empty array.
When the App function is called it tries to call the
Array.map()
method on an undefined value and the error occurs.
null instead of an empty array.# Initialize your state variable to an empty array
To solve both errors, initialize the value for the users variable to an
empty array.
import {useState, useEffect} from 'react'; function App() { // ✅ State is initialized to an empty array const [users, setUsers] = useState([]); useEffect(() => { async function getUsers() { const response = await fetch('https://randomuser.me/api/', { method: 'GET', headers: { accept: 'application/json', }, }); const data = await response.json(); setUsers(data.results); } getUsers(); }, []); console.log(users); return ( <div> {/* ✅ Users is initially [] and then gets populated after API responds */} {users.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> </div> ))} </div> ); } export default App;
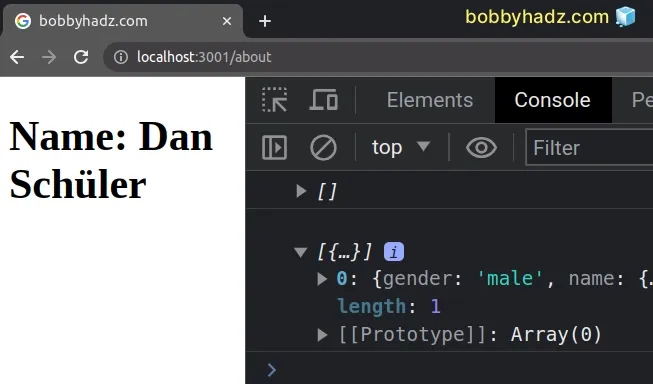
We provided an empty array as the initial value in our call to the useState method.
users variable is initially set to an empty array and the map method is called on an empty array instead of an undefined or a null value.After our useEffect hook is run and the remote API responds with the data, we update the state and our component rerenders.
At no point in time of the component's lifecycle is our users variable equal
to undefined or null and the error won't occur.
If you get the error TypeError: map() is not a function in React, click on the link and follow the instructions.
# Use the optional chaining operator (?.)
An alternative approach is to use the optional chaining (?.) operator to
short-circuit if the reference is equal to undefined or null.
<div> {/* ✅ Using optional chaining (?.) */} {users?.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> </div> ))} </div>
The optional chaining (?.) operator
short-circuits and returns undefined if the value to the left is nullish
(null or undefined).
If the users state variable stores an undefined or a null value, the
Array.map() method is not called at all.
Here is an example of how the optional chaining operator works in JavaScript.
const users = undefined; // 👇️ Logs undefined console.log( users?.map(user => { console.log(user); }), );
This solution works for both errors:
- TypeError: cannot read properties 'map' of undefined
- TypeError: cannot read properties 'map' of null
# Use the ternary operator to check if the value is an array
The following solution also works for both errors.
You conditionally check if the variable is an array before calling the map()
method, which would prevent you from getting the error.
<div> {/* ✅ Check if array before calling `map()` */} {Array.isArray(users) ? users.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> </div> )) : null} </div>
We used a ternary operator, which is very similar to an if/else statement.
If the expression to the left of the question mark is truthy, the operator returns the value to the left of the colon, otherwise, the value to the right of the colon is returned.
You can imagine that the value before the colon is the if block and the value
after the colon is the else block.
users variable stores an array, and if it does, we return the result of calling the map() method, otherwise, we return null.# Use the logical AND (&&) operator
You can also solve the errors by using the logical AND (&&) operator.
<div> {/* ✅ Using logical AND (&&) */} {users && users.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> </div> ))} </div>
The logical AND (&&) operator returns the value to its left if it's falsy, otherwise, the value to its right is returned.
If the users variable stores an undefined or a null value, we don't
attempt to call the Array.map() method at all.
# Using an if statement
You can also use a simple if statement to solve the errors.
import {useState, useEffect} from 'react'; export default function App() { const [users, setUsers] = useState(); useEffect(() => { async function getUsers() { const response = await fetch('https://randomuser.me/api/', { method: 'GET', headers: { accept: 'application/json', }, }); const data = await response.json(); setUsers(data.results); } getUsers(); }, []); // ✅ Add this if statement to check if not undefined or null if (users == null) { return; } return ( <div> {users.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> </div> ))} </div> ); }
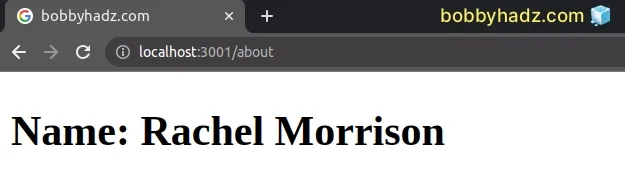
The if statement returns null if the users state variable stores an
undefined or a null value.
if (users == null) { return; }
This way the users.map() call in your return statement is never reached if the
users state variable has a value of null or undefined.
The if statement checks for both null and undefined because we used the
loose equality (==) operator.
// 👇️ true console.log(null == undefined); // 👇️ false console.log(null === undefined);
When you use the loose equality (==) operator, null is equal to undefined.
This is not the case when the strict equality (===) operator is used.
I've also written a detailed guide on how to check if a variable is null or undefined in React.
# Your API might be sending an empty response or a null value
If your API response is empty, you might be setting your state to an
undefined value, which can be a cause for the error.
Check if your API responds with a null value, you might be updating the
state variable to null from the API's response, which would cause the error.
# Trying to call Array.map() on array-like objects
Another common cause of the error is trying to call the Map method on an
array-like object, e.g. a Set.
function App() { const users = new Set(['James', 'Jon', 'Jan']); return ( <div> {/* ✅ Check if array before calling `map()` */} {Array.from(users).map(user => ( <div key={user}>{user}</div> ))} </div> ); } export default App;
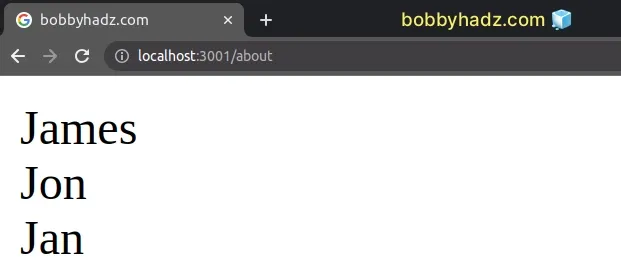
Had we tried to call the map() method directly on the Set object, we would
get an error, so we had to convert the Set to an array using the Array.from
method before calling map().
This would also be the case when working with other array-like objects like a
NodeList.
# Conclusion
The "TypeError: cannot read properties 'map' of null" error occurs when we
call the map() method on a null value, most often when initializing a state
variable to null.
To solve the error, initialize the value you're mapping over to an empty array.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Cannot read property 'setState' of undefined in React.js
- How to Render nested array using map() in React
- Update nested properties in a State object in React
- How to Loop (or map()) through an Object in React
- Using a condition inside map() in React
- Cannot update a component while rendering a different component
- React not reading .env file Environment Variables [Solved]
- No QueryClient set, use QueryClientProvider to set one

