No QueryClient set, use QueryClientProvider to set one [Fix]
Last updated: Apr 7, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# No QueryClient set, use QueryClientProvider to set one [Fix]
The React Query error "No QueryClient set, use QueryClientProvider to set one"
occurs when you forget to wrap your React application in a QueryClientProvider
component.
To solve the error, wrap the entry point of your application (e.g. the App
component) in a QueryClientProvider.
Here is an example that shows how you should wrap your main component in a
QueryClientProvider.
import React from 'react'; import { QueryClient, QueryClientProvider, useQuery, } from 'react-query'; const queryClient = new QueryClient(); export default function App() { return ( <QueryClientProvider client={queryClient}> <Users /> </QueryClientProvider> ); } function Users() { return ( // ... Your users component here ) }
Note: if you use React-Query v4, you have to import from
@tanstack/react-queryinstead.
import { QueryClient, QueryClientProvider, useQuery, } from '@tanstack/react-query';
Notice that I wrapped the main component (App in this case) in a
QueryClientProvider.
import { QueryClient, QueryClientProvider } from 'react-query' const queryClient = new QueryClient() function App() { return ( <QueryClientProvider client={queryClient}> <YourMainComponent /> </QueryClientProvider> ) }
The QueryClientProvider component is used to connect a QueryClient to your
application.
useQuery hook have to be located somewhere under a QueryClientProvider.The QueryClientProvider component takes a client prop.
The clientProp is required and must be set to a QueryClient (the
QueryClient instance to provide).
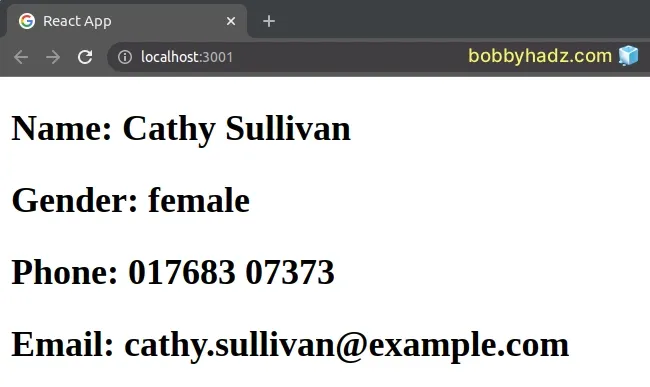
Here is a complete example that fetches data from a remote API using React query.
import React from 'react'; import { QueryClient, QueryClientProvider, useQuery, } from 'react-query'; const queryClient = new QueryClient(); export default function App() { // 👇️ Wrap with QueryClientProvider here return ( <QueryClientProvider client={queryClient}> <Users /> </QueryClientProvider> ); } function Users() { // 👇️ Can use the useQuery hook here const {isLoading, error, data} = useQuery({ queryKey: ['usersData'], queryFn: () => fetch('https://randomuser.me/api').then(res => res.json()), }); if (isLoading) return 'Loading...'; if (error) return 'An error has occurred: ' + error.message; console.log(data); return ( <div> {data.results.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> <h2>Gender: {user.gender}</h2> <h2>Phone: {user.phone}</h2> <h2>Email: {user.email}</h2> </div> ))} </div> ); }
Note: if you use React-Query v4, you have to import from
@tanstack/react-queryinstead.
import { QueryClient, QueryClientProvider, useQuery, } from '@tanstack/react-query';
# Wrapping your App component with a QueryClientProvider in index.js
An alternative approach is to wrap your App component with a
QueryClientProvider in your index.js file.
Your index.js file is the entry point of your React.js application, so all
components in your React app will be able to use the useQuery hook.
Here is the code for the index.js file.
import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'; import App from './App'; import {QueryClient, QueryClientProvider} from 'react-query'; const queryClient = new QueryClient(); const root = ReactDOM.createRoot( document.getElementById('root'), ); root.render( <React.StrictMode> <QueryClientProvider client={queryClient}> <App /> </QueryClientProvider> </React.StrictMode>, );
Note: If you use React-Query v4, you have to import from
@tanstack/react-queryinstead.
import { QueryClient, QueryClientProvider, useQuery, } from '@tanstack/react-query';
We wrapped the App component in a QueryClientProvider and rendered the
result.
Here is the code for the App component.
import React from 'react'; import {useQuery} from 'react-query'; export default function App() { return <Users />; } function Users() { const {isLoading, error, data} = useQuery({ queryKey: ['usersData'], queryFn: () => fetch('https://randomuser.me/api').then(res => res.json()), }); if (isLoading) return 'Loading...'; if (error) return 'An error has occurred: ' + error.message; console.log(data); return ( <div> {data.results.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> <h2>Gender: {user.gender}</h2> <h2>Phone: {user.phone}</h2> <h2>Email: {user.email}</h2> </div> ))} </div> ); }
Your App component and all of its descendants can now use React query as the
QueryClient instance is provided to all components in the chain.
# Setting the contextSharing prop to true
If the error persists, try setting the contextSharing prop to true in your
QueryClientProvider.
import React from 'react'; import { QueryClient, QueryClientProvider, useQuery, } from 'react-query'; const queryClient = new QueryClient(); export default function App() { // 👇️ Wrap with QueryClientProvider // and set the `contextSharing` prop to true return ( <QueryClientProvider client={queryClient} contextSharing={true} > <Users /> </QueryClientProvider> ); }
Notice that the contextSharing prop is set to true.
When set to true, the prop enables context sharing.
The first instance of the context is shared across the window to ensure that if React Query is used across different bundles or micro-frontends, they use the same instance of context, regardless of module scoping.
# Make sure your import statements are correct
The error is also raised if you import from react-query and
@tanstack/react-query in the same application.
Make sure to keep your import statements.
- If you use React Query v3, import from
react-query. - If you use React Query v4+, import from
@tanstack/react-query.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- React Hook useEffect has a missing dependency error [Fixed]
- useEffect must not return anything besides a function
- Can't perform a react state update on an unmounted component
- TypeError: Failed to fetch and CORS in JavaScript
- Fetch API cannot load localhost. URL scheme is not supported
- Cannot update a component while rendering a different component
- How to convert an Object to FormData in JavaScript
- Failed to parse source map from X error in React [Solved]
- How to decode URL and Form parameters in Python

