React not reading .env file Environment Variables [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 7, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- React not reading .env file environment variables
- Create a .env file in the root directory of your project
- Make sure all environment variables start with
REACT_APP_ - Restart your development server after making changes to your .env file
- Access the environment variables on the process.env object
- The NODE_ENV environment variable
- Accessing your environment variables in the public/index.html file
- Defining temporary environment variables
- Using multiple .env files based on the environment
# React not reading .env file environment variables [Solved]
There are multiple reasons why React might not be picking up your environment
variables from a .env file.
When using a .env file in Create React App, make sure:
- Your
.envfile is located in the root directory of your project (right next to yourpackage.jsonfile). - All environment variables start with the
REACT_APP_prefix, e.g.REACT_APP_ENV=development. - To restart your server every time you make changes to your
.envfile.
process.env object returns undefined.# Create a .env file in the root directory of your project
Make sure you have a .env file in the root directory of your project (where
your package.json file is).
Your .env file should NOT be placed in the src/ directory, it should be in
the root directory.
# Make sure all environment variables start with REACT_APP_
All environment variables you define in your .env file must start with the
REACT_APP_ prefix.
By default, the NODE_ENV environment variable is defined and all other
environment variables that start with REACT_APP_.
React uses the REACT_APP_ prefix to make it clear that you shouldn't store
secrets (such as API keys or passwords) in React environment variables.
The syntax for environment variables in your .env file is REACT_APP_FOO=bar.
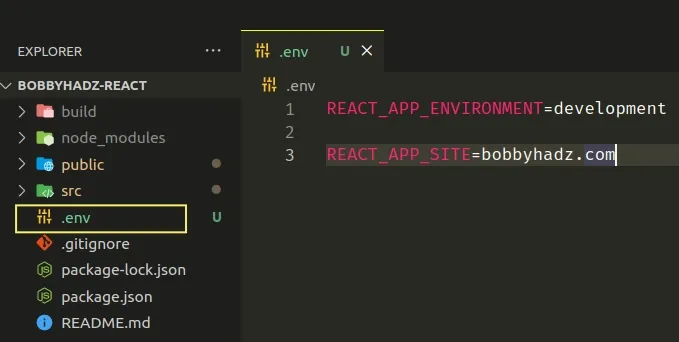
Here are the two environment variables I've defined for the example.
REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT=development REACT_APP_SITE=bobbyhadz.com
Make sure your .env file is formatted as REACT_APP_FOO=bar as shown in the
example.
Create React App won't be able to read your .env file if you have syntactical
errors.
If your values contain spaces, wrap them in quotes.
REACT_APP_FOO='hello world'
Make sure to not add semicolons after the key-value pairs.
# ⛔️ Incorrect (has semicolon at the end) REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT=development; # ✅ Correct (does NOT have a semicolon) REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT=development
# Restart your development server after making changes to your .env file
Create React App reads your .env file at build time.
In other words, the only way for React to pick up the changes you've made in
your .env file is to restart your server.
Once you make changes to your .env file:
- Save the file.
- Stop your development server by focusing your terminal and pressing
Ctrl+C.
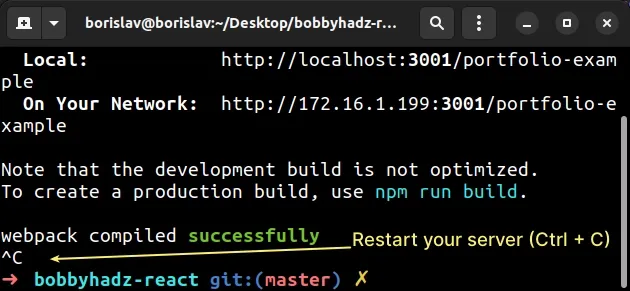
- Start your development server with the
npm startcommand.
npm start
# Access the environment variables on the process.env object
After you've set up your .env file and restarted your server, you can access
the environment variables on the process.env object.
Here is my .env file.
REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT=development REACT_APP_SITE=bobbyhadz.com
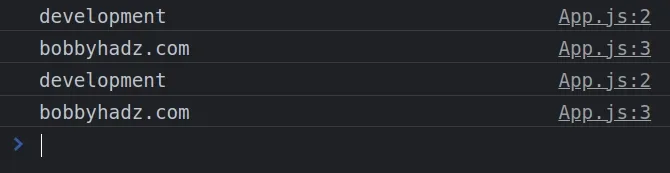
And here is my App.js file in which I access the 2 environment variables.
function App() { console.log(process.env.REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT); console.log(process.env.REACT_APP_SITE); return ( <div style={{margin: 50}}> <h2>bobbyhadz.com</h2> </div> ); } export default App;
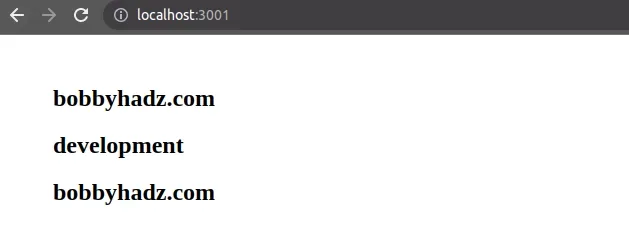
If I open my developer tools and click on the Console tab, I can see that the
values of the environment variables have been logged.
You can also read the environment variables in your JSX code.
function App() { return ( <div style={{margin: 50}}> <h2>bobbyhadz.com</h2> <h2>{process.env.REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT}</h2> <h2>{process.env.REACT_APP_SITE}</h2> </div> ); } export default App;
If you get undefined when you try to access an environment variable, make
sure:
- The environment variable starts with
REACT_APP_(this is a must when using Create React App). - You have restarted your server after making changes to your
.envfile. - You haven't misspelled the environment variable when accessing it on the
process.envobject.
You must always restart your server after making changes to your .env file.
Otherwise, the build step isn't run and your environment variables will be stale
or undefined.
If your environment variable is named REACT_APP_FOO, access it as
process.env.REACT_APP_FOO in your code.
# The NODE_ENV environment variable
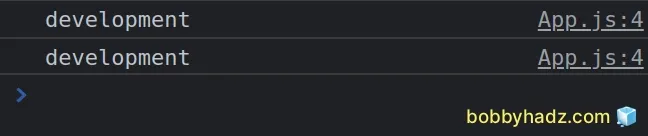
Create React App automatically sets the NODE_ENV environment variable.
The built-in environment variable can be accessed as process.env.NODE_ENV.
function App() { console.log(process.env.NODE_ENV); return ( <div style={{margin: 50}}> <h2>bobbyhadz.com</h2> </div> ); } export default App;
Here is a table that shows the value of the NODE_ENV environment variable
depending on the command you run.
| Command | NODE_ENV value |
|---|---|
| npm start | development |
| npm test | test |
| npm run build | production |
The NODE_ENV environment variable is read-only and cannot be overwritten.
You can use the environment variable to check if your application is running in development or production mode.
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { console.log('App is not in production mode'); }
# Accessing your environment variables in the public/index.html file
You can also access your environment variables in the public/index.html file.
For example, assuming I have the following .env file.
REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT=development REACT_APP_SITE=bobbyhadz.com
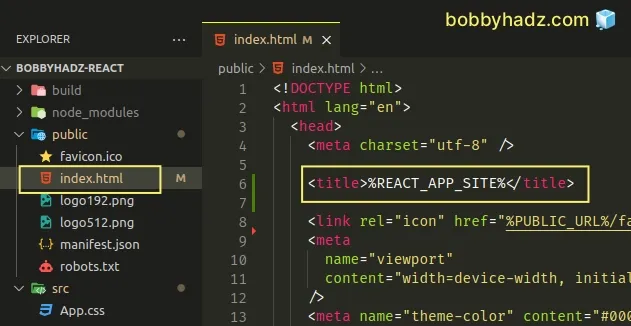
I can read the REACT_APP_SITE environment variable in my index.html file as
follows.
<title>%REACT_APP_SITE%</title>
Notice that we don't use the process.env object when reading environment
variables in the index.html file.
Instead, we wrap the environment variable name in percent signs %.
If you aren't able to access the environment variable, try restarting your development server and make sure you don't have any typos.
You can access the built-in NODE_ENV and PUBLIC_URL variables in your
index.html file and all user-defined variables that start with REACT_APP_.
As previously noted, the environment variables are injected at build time.
If you need to inject them at run time, check out this section of the Create React Docs.
# Defining temporary environment variables
You can also define temporary environment variables that last for the life of the shell session.
If you are on macOS or Linux, use the following syntax.
# For macOS and Linux REACT_APP_DOMAIN="bobbyhadz.com" npm start
If you are on Windows and use CMD, use the following syntax instead.
# For Windows (CMD.exe) set "REACT_APP_DOMAIN=bobbyhadz.com" && npm start
If you are on Windows and use PowerShell, use the following syntax.
# For Windows (PowerShell) ($env:REACT_APP_DOMAIN = "bobbyhadz.com") -and (npm start)
If you'd rather have an operating system agnostic way to manage your temporary environment variables, use the cross-env package.
First, install the package by running the following command.
# 👇️ with NPM npm install cross-env # 👇️ with YARN yarn add cross-env
Now, update the start script in your package.json file to set the
environment variable right before issuing the react-scripts start command.
{ "scripts": { "start": "cross-env REACT_APP_DOMAIN_ABC=bobbyhadz.com react-scripts start", } }
# Using multiple .env files based on the environment
As shown in
this section
of the Create React App, you can use multiply .env files based on the
environment.
.env- the default file..env.local- local overrides (loaded for all environments excepttest)..env.development,.env.test,.env.production- environment-specific files..env.development.local,.env.test.local,.env.production.local- local overrides for environment-specific files.
The following commands look for the following .env files in this order.
| command | Description |
|---|---|
| npm start | .env.development.local, .env.local, .env.development, .env |
| npm run build | .env.production.local, .env.local, .env.production, .env. |
| npm test | .env.test.local, .env.test, .env |
The commands look for the environment variable files in the specified order (from left to right).
.env files into source control except for the .env*.local files which are your local overrides.Note that the .env*.local files are not loaded when running the npm test
command.
When using a .env file in Create React App, make sure:
- Your
.envfiles are located in the root directory of your project (right next to yourpackage.jsonfile). - All environment variables start with the
REACT_APP_prefix, e.g.REACT_APP_ENV=development. - To restart your server every time you make changes to your
.envfiles.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to add Comments to a .env file - Complete Guide
- Using .env files in Node.js with the dotenv module
- Using .env files in Python with the dotenv module
- error:0308010C:digital envelope routines::unsupported
- React: Could not find a required file. Name: index.html
- Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'map') in React
- ReferenceError: process is not defined error [Solved]
- How to set the PUBLIC_URL variable in Create-React-App
- process.env.NODE_ENV is undefined issue [Solved]

