TypeError: write() argument must be str, not X in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·11 min

# Table of Contents
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not BYTES
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not LIST
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not DICT
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not TUPLE
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not NONE
# TypeError: write() argument must be str, not bytes
The Python "TypeError: write() argument must be str, not bytes" occurs when we
try to write bytes to a file without opening the file in wb mode.
To solve the error, open the file in wb mode to write bytes or decode the
bytes object into a string.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
with open('example.txt', 'w') as my_file: # ⛔️ TypeError: write() argument must be str, not bytes my_file.write(b'bobbyhadz.com')
We opened the file in w mode and tried writing bytes to it which caused the
error.
The string literal in the example is prefixed with b, so it is a bytes object.
# Open the file in wb (write binary) mode to write bytes
If you need to write bytes to a file, open it in wb (write binary) mode rather
than w (write text) mode.
# ✅ Open file in `wb` mode with open('example.txt', 'wb') as my_file: my_file.write(b'bobbyhadz.com')
We opened the file in wb (binary) mode to write bytes to it.
Note that you shouldn't specify the encoding keyword argument when you open a file in binary mode.
If you need to also read from the file, use the rb (read binary) mode.
# ✅ Writing to the file with open('example.txt', 'wb') as my_file: my_file.write(b'bobbyhadz.com') # ✅ Reading from the file with open('example.txt', 'rb') as my_file: lines = my_file.readlines() print(lines) # 👉️ [b'bobbyhadz.com'] first_line = lines[0].decode('utf-8') print(first_line) # 👉️ bobbyhadz.com
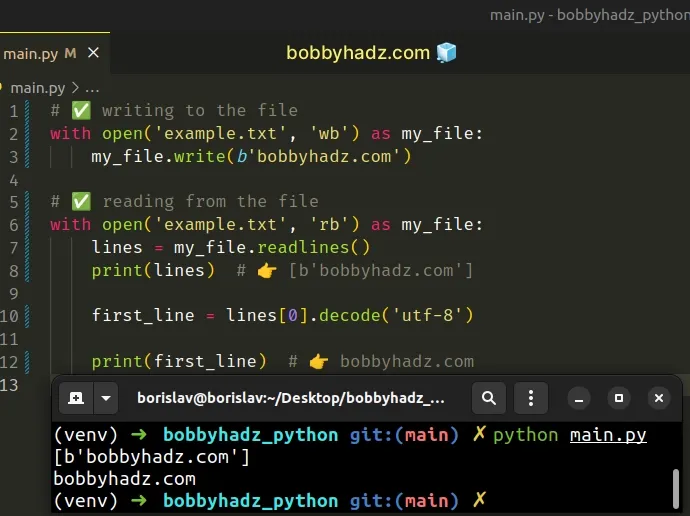
The readlines() method returns a list of bytes objects, so we used the
decode() method to convert the first item in the list to a string.
You can use a list comprehension to convert all lines in the file to strings.
with open('example.txt', 'wb') as my_file: my_file.write(b'bobbyhadz.com\n') my_file.write(b'bobbyhadz.com\n') with open('example.txt', 'rb') as my_file: lines = [l.decode('utf-8') for l in my_file.readlines()] # 👇️ ['bobbyhadz.com\n', 'bobbyhadz.com\n'] print(lines)
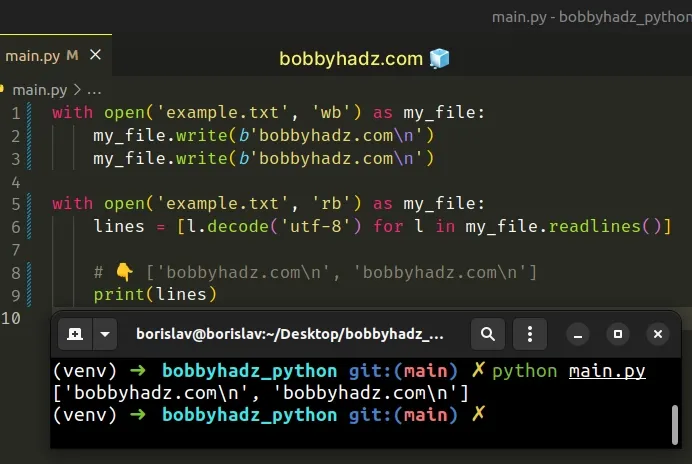
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
# Open the file in w (write text) mode to write text
Alternatively, you can decode the bytes object into a string.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_file.write(b'bobbyhadz.com'.decode('utf-8'))
Notice that we used the bytes.decode() method to decode the bytes object into
a string.
my_bytes = 'apple'.encode() print(my_bytes) # 👉️ b'apple' my_str = my_bytes.decode('utf-8') print(my_str) # 👉️ 'apple'
We opened the JSON file in w (write text) mode.
When a file is opened in text mode, we read and write strings from and to the file.
If you need to read from the file, open it in r (read text) mode.
# ✅ Writing to the file with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_file.write(b'bobbyhadz.com'.decode('utf-8')) # ✅ Reading from the file with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: lines = my_file.readlines() print(lines) # 👉️ ['bobbyhadz.com']
Those strings are encoded using a specific encoding (utf-8 in the example).
encoding keyword argument, the default is platform-dependent.If you want to both read from and write to the file, use the r+ mode when
opening it.
b to the mode (like in the first code sample), the file is opened in binary mode.Note that you cannot specify encoding when opening a file in binary mode.
When a file is opened in binary mode, data is read and written as bytes
objects.
The bytes.decode() method returns a
string decoded from the given bytes. The default encoding is utf-8.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_file.write(b'hello world'.decode('utf-8'))
You can decode your bytes object to a string if you want to write strings to the file.
Conversely, the str.encode() method
returns an encoded version of the string as a bytes object. The default encoding
is utf-8.
with open('example.txt', 'wb') as my_file: my_file.write('hello world'.encode('utf-8'))
The example shows how to encode a string to a bytes object and write the bytes to a file.
string to a bytes object and decoding is the process of converting a bytes object to a string.# Table of Contents
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not LIST
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not DICT
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not TUPLE
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not NONE
# TypeError: write() argument must be str, not list
The Python "TypeError: write() argument must be str, not list" occurs when we
try to write a list object to a file using the write() method.
To solve the error, use the join() method to join the list into a string.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_list = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl'] # ⛔️ TypeError: write() argument must be str, not list my_file.write(my_list)
write() method, but the method can only be called with a string argument.# Use the str.join() method to join the list into a string
One way to solve the error is to use the str.join() method to join the list
into a string.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_list = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl'] my_file.write(','.join(my_list)) # 👉️ "Alice,Bob,Carl"
We used a comma as the separator between the items of the list, but you can use any other separator.
my_list = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl'] print(' '.join(my_list)) # 👉️ Alice Bob Carl print('-'.join(my_list)) # 👉️ Alice-Bob-Carl print(''.join(my_list)) # 👉️ AliceBobCarl
You can also use an empty string if you don't need a separator between the elements.
The str.join() method takes an iterable as an argument and returns a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the iterable.
TypeError if there are any non-string values in the iterable.# All values in the collection must be strings
If your list contains numbers or other types, convert all of the values to
string before calling join().
my_list = ['a', 'b', 1, 2] all_strings = list(map(str, my_list)) print(all_strings) # 👉️ ['a', 'b', '1', '2'] result = ''.join(all_strings) print(result) # 👉️ "ab12"
The string the method is called on is used as the separator between elements.
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] my_str = '-'.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ "a-b-c"
If you don't need a separator and just want to join the iterable's elements into
a string, call the join() method on an empty string.
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] my_str = ''.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ "abc"
# Converting a list to a string before writing it to the file
Alternatively, you can pass the list to the str() class to convert it to a string before writing it to the file.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_list = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl'] my_file.write(str(my_list)) # 👉️ "['Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl']"
The str() class converts the supplied value to a string and returns the
result.
You can also convert the list to a JSON string before writing it to the file.
import json with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_list = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl'] my_file.write(json.dumps(my_list)) # 👉️ ["Alice", "Bob", "Carl"]
The json.dumps() method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
# Table of Contents
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not DICT
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not TUPLE
- TypeError: write() argument must be str, not NONE
# TypeError: write() argument must be str, not dict
The Python "TypeError: write() argument must be str, not dict" occurs when we
pass a dictionary to the write() method.
To solve the error, convert the dictionary to a string or access a specific key in the dictionary that has a string value.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_dict = {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} # ⛔️ TypeError: write() argument must be str, not dict my_file.write(my_dict)
dict object to the write() method, but the method can only be called with a string argument.# Convert the dictionary to a string before writing it to the file
One way to solve the error is to convert the dictionary to a string.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_dict = {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} my_file.write(str(my_dict)) # 👉️ {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30}
The str() class converts the given value to a string and returns the result.
You can also convert the dictionary to a JSON string by using the json.dumps
method.
import json with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_dict = {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} my_file.write(json.dumps(my_dict)) # 👉️ {"name": "Alice", "age": 30}
The json.dumps() method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
# Writing a specific dictionary value to the file
If you meant to access a specific key in the dictionary, use square brackets.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_dict = {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} my_file.write(my_dict['name']) # 👉️ Alice
write() method can only get called with a string argument.# Checking what type a variable stores
If you aren't sure what type a variable stores, use the built-in type() class.
my_dict = {'name': 'Bobby Hadz'} print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'> print(isinstance(my_dict, dict)) # 👉️ True my_str = 'hello' print(type(my_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'> print(isinstance(my_str, str)) # 👉️ True
The type class returns the type of an object.
The isinstance() function
returns True if the passed-in object is an instance or a subclass of the
passed in class.
# Table of Contents
# TypeError: write() argument must be str, not tuple
The Python "TypeError: write() argument must be str, not tuple" occurs when we
try to write a tuple object to a file using the write() method.
To solve the error, use the join() method to join the tuple into a string,
e.g. my_file.write(','.join(my_tuple)).
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_tuple = ('Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl') # ⛔️ TypeError: write() argument must be str, not dict my_file.write(my_tuple)
write() method, but the method can only be called with a string argument.# Join the tuple's elements into a string before writing to the file
One way to solve the error is to use the str.join() method to join the tuple
into a string.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_tuple = ('Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl') my_file.write(','.join(my_tuple)) # 👉️ Alice,Bob,Carl
We used a comma as the separator between the items of the tuple, but you can use any other separator or an empty string if you don't need a separator between the elements.
The str.join method takes an iterable as an argument and returns a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the iterable.
TypeError if there are any non-string values in the iterable.# Convert all values in the tuple to strings
If your tuple contains numbers or other types, convert all of the values to
string before calling join().
my_tuple = ('a', 'b', 1, 2) all_strings = tuple(map(str, my_tuple)) print(all_strings) # 👉️ ('a', 'b', '1', '2') result = ''.join(all_strings) print(result) # 👉️ 'ab12'
The string the method is called on is used as the separator between elements.
my_tuple = ('a', 'b', 'c') result = '-'.join(my_tuple) print(result) # 👉️ 'a-b-c'
If you don't need a separator and just want to join the iterable's elements into
a string, call the join() method on an empty string.
my_tuple = ('a', 'b', 'c') result = ''.join(my_tuple) print(result) # 👉️ 'abc'
# Converting the tuple to a string or a JSON string
Alternatively, you can pass the tuple to the str() class to convert it to a
string before writing it to the file.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_tuple = ('Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl') my_file.write(str(my_tuple)) # 👉️ ('Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl')
You can also convert the tuple to a JSON string before writing it to the file.
import json with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_tuple = ('Alice', 'Bob', 'Carl') my_file.write(json.dumps(my_tuple)) # 👉️ ["Alice", "Bob", "Carl"]
The json.dumps() method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
Since JSON doesn't support tuples, the tuple gets converted to a list.
# How tuples are constructedin Python
In case you declared a tuple by mistake, tuples are constructed in multiple ways:
- Using a pair of parentheses
()creates an empty tuple - Using a trailing comma -
a,or(a,) - Separating items with commas -
a, bor(a, b) - Using the
tuple()constructor
If you aren't sure what type of object a variable stores, use the type()
class.
my_tuple = 'bobby', 'hadz' print(type(my_tuple)) # 👉️ <class 'tuple'> print(isinstance(my_tuple, tuple)) # 👉️ True my_str = 'bobby hadz' print(type(my_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'> print(isinstance(my_str, str)) # 👉️ True
The type class returns the type of an object.
The isinstance() function
returns True if the passed-in object is an instance or a subclass of the
passed-in class.
# TypeError: write() argument must be str, not None
The Python "TypeError: write() argument must be str, not None" occurs when we
pass a None value to the write() method.
To solve the error, correct the assignment and pass a string to the write()
method.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_str = None my_file.write(my_str)
We passed a None value to the write method which caused the error.
The method takes a string and writes it to the file.
None value comes from and correct the assignment.# Common sources of None values in Python
The most common sources of None values are:
- Having a function that doesn't return anything (returns
Noneimplicitly). - Explicitly setting a variable to
None. - Assigning a variable to the result of calling a built-in function that doesn't return anything.
- Having a function that only returns a value if a certain condition is met.
# A function that doesn't return a value returns None
Functions that don't explicitly return a value return None.
# 👇️ this function returns None def get_str(): print('hello world') with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_str = get_str() print(my_str) # 👉️ None # ⛔️ TypeError: write() argument must be str, not None my_file.write(my_str)
You can use a return statement to return a value from a function.
def get_str(): return 'hello world' with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_str = get_str() print(my_str) # 👉️ "hello world" my_file.write(my_str)
# Checking if the variable is not None before writing to the file
Use an if statement if you need to check whether a
variable doesn't store a None value before
writing it to the file.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_str = None if my_str is not None: my_file.write(my_str)
Alternatively, you can provide an empty string as a fallback.
with open('example.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_str = None if my_str is None: my_str = '' my_file.write(my_str)
# Having a function that returns a value only if a condition is met
Another common cause of the error is having a function that returns a value only if a condition is met.
def get_string(a): if len(a) > 3: return a my_string = get_string('hi') print(my_string) # 👉️ None
The if statement in the get_string function is only run if the passed in
string has a length greater than 3.
None.To solve the error in this scenario, you either have to check if the function
didn't return None or return a default value if the condition is not met.
def get_string(a): if len(a) > 3: return a return '' my_string = get_string('hi') print(my_string) # 👉️ ""
Now the function is guaranteed to return a string regardless of whether the condition is met.

