Remove non-ASCII characters from a string in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Remove non-ASCII characters from a string in Python
- Remove non-ASCII characters from a string using ord()
- Remove non-ASCII characters from a string using encode() and decode()
# Remove non-ASCII characters from a string in Python
To remove the non-ASCII characters from a string:
- Use the
string.printableattribute to get a string of the ASCII characters. - Use the
filter()method to remove the non-ASCII characters. - Use the
join()method to join the result into a string.
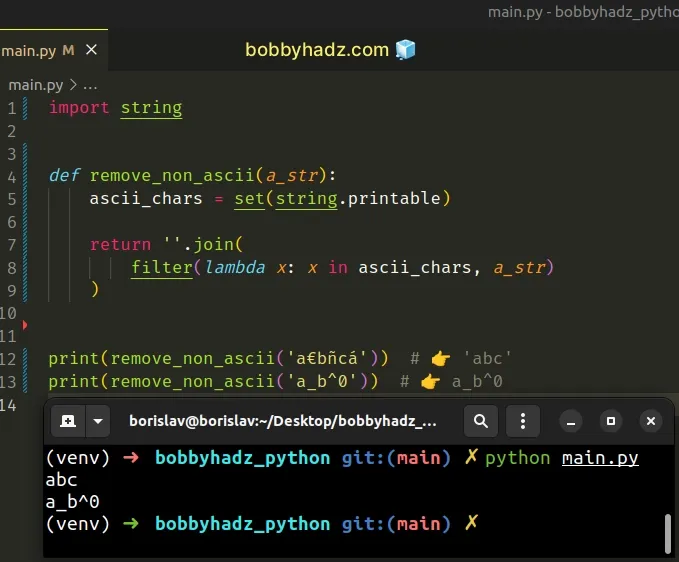
import string def remove_non_ascii(a_str): ascii_chars = set(string.printable) return ''.join( filter(lambda x: x in ascii_chars, a_str) ) print(remove_non_ascii('a€bñcá')) # 👉️ 'abc' print(remove_non_ascii('a_b^0')) # 👉️ a_b^0
The string.printable() method returns a string of the ASCII characters that are considered printable.
import string # 0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP # QRSTUVWXYZ!"#$%&'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~ jk print(string.printable)
The string is a combination of digits, ASCII letters, punctuation and whitespace.
The filter function takes a function and an iterable as arguments and constructs an iterator from the elements of the iterable for which the function returns a truthy value.
The lambda function we passed to filter() gets called with each character in
the string and filters out the non-ASCII characters.
import string def remove_non_ascii(a_str): ascii_chars = set(string.printable) return ''.join( filter(lambda x: x in ascii_chars, a_str) )
Alternatively, you can use the ord() function.
# Remove non-ASCII characters from a string using ord()
This is a three-step process:
- Check if each character in the string has a Unicode code point of less than 128.
- The first 128 Unicode code points represent the ASCII characters.
- Use the
join()method to join the matching characters into a string.
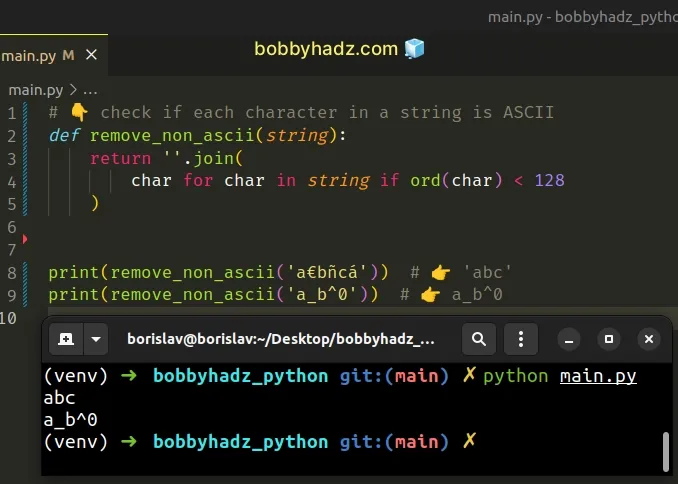
# 👇️ check if each character in a string is ASCII def remove_non_ascii(string): return ''.join( char for char in string if ord(char) < 128 ) print(remove_non_ascii('a€bñcá')) # 👉️ 'abc' print(remove_non_ascii('a_b^0')) # 👉️ a_b^0
The first function uses a generator expression to iterate over the string.
def remove_non_ascii(string): return ''.join(char for char in string if ord(char) < 128) print(remove_non_ascii('a€bñcá')) # 👉️ 'abc' print(remove_non_ascii('a_b^0')) # 👉️ a_b^0
On each iteration, we check if the Unicode code point of the character is less than 128.
The ord function takes a string that represents 1 Unicode character and returns an integer representing the Unicode code point of the given character.
The last step is to join the characters that satisfy the condition.
The str.join method takes an iterable as an argument and returns a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the iterable.
The string the method is called on is used as the separator between the elements.
Alternatively, you can use the str.encode() and bytes.decode() methods.
# Remove non-ASCII characters from a string using encode() and decode()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
str.encode()method to encode the string using the ASCII encoding. - Set the
errors argument to
ignore, so all non-ASCII characters are dropped. - Use the
bytes.decode()method to convert the bytes object to a string.
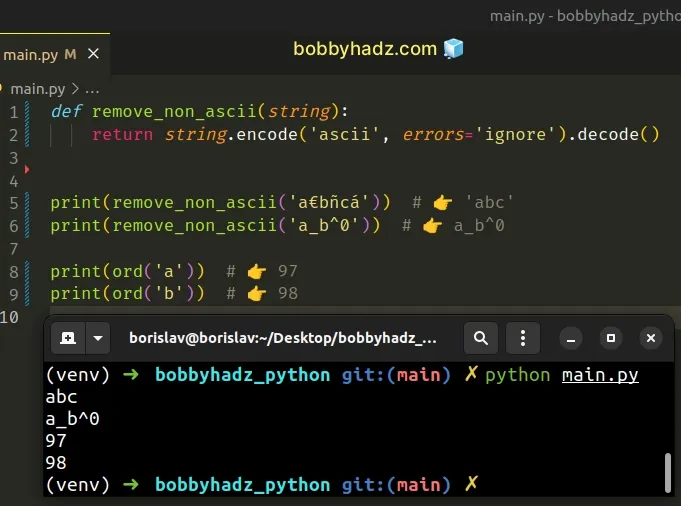
def remove_non_ascii(string): return string.encode('ascii', errors='ignore').decode() print(remove_non_ascii('a€bñcá')) # 👉️ 'abc' print(remove_non_ascii('a_b^0')) # 👉️ a_b^0 print(ord('a')) # 👉️ 97 print(ord('b')) # 👉️ 98
The str.encode() method returns an
encoded version of the string as a bytes object. The default encoding is
utf-8.
We set the encoding to ascii and the errors argument to ignore.
errors keyword argument is set to ignore, characters that cannot be encoded are dropped.All characters that cannot be encoded using the ASCII encoding will get dropped from the string.
The last step is to use the bytes.decode() method to decode the bytes object
to a string.
string to a bytes object and decoding is the process of converting a bytes object to a string.The bytes.decode() method returns a
string decoded from the given bytes. The default encoding is utf-8.
The result is a string that doesn't contain any non-ASCII characters.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Remove Newline characters from a List or a String in Python
- Remove non-alphanumeric characters from a Python string
- Remove the non utf-8 characters from a String in Python
- Remove punctuation from a List of strings in Python
- How to remove Quotes from a List of Strings in Python
- Remove characters matching Regex from a String in Python
- Remove special characters except Space from String in Python
- Remove square brackets from a List or a String in Python
- How to Remove the Tabs from a String in Python

