Python: Process finished with exit code 137 in PyCharm
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Python: Process finished with exit code 137 in PyCharm
- Make sure you aren't running into permission issues
- Try to clear variables that store large objects
- If you got the error in PyCharm, try to close it before running your script
- Try to process the data in smaller chunks
- Make sure the correct Python interpreter is selected
- Increasing the swap space
- Run the script on a machine that has more RAM
# Python: Process finished with exit code 137 in PyCharm
The Python error "Process finished with exit code 137 (interrupted by signal 9: SIGKILL)" occurs for 3 main reasons (usually when using PyCharm):
- Manually stopping the script, e.g. by pressing
Ctrl+Cor stopping it via System Monitor or Task Manager. - The process is stopped due to excessive memory usage.
- The process is stopped due to permission issues.
If you didn't manually stop the process, then you're most likely running out of memory.
If you run out of memory while running the script, your operating system will stop the process with an exit code of 137 (signal 9) SIGKILL.
This is often an issue when training machine learning models with sklearn.
If your dataset is large, try to train the ML model with a smaller dataset.
Note that you can't handle the error in a try/except block because it is not a
Python exception. It is an operating system exception.
# Make sure you aren't running into permission issues
If your script is located somewhere in your home directory, e.g. /home/ubuntu
or /home/your_user, try to move the script to a different directory, e.g.
/home/your_user/Desktop/your_project.
You might be getting the error because the script is located in a directory to which you don't have the necessary permissions.
# Try to clear variables that store large objects
If your error is caused due to excessive memory usage, you can try to clear (or delete) variables that store large objects.
large_object = {'first': 'bobby', 'last': 'hadz'} # After you're done large_object = None
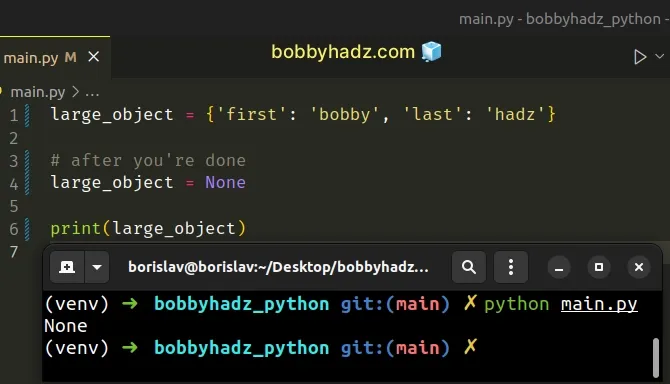
You can set variables that store large objects to None after you are done
working with them.
You can also use the del statement to completely delete a variable after you
are done working with it.
large_object = {'first': 'bobby', 'last': 'hadz'} del large_object
However, make sure to not reference the variable after using the del statement.
Otherwise, you'd get the error NameError: name 'X' is not defined in Python.
# If you got the error in PyCharm, try to close it before running your script
If you got the error in PyCharm, try to close it before running your script.
PyCharm and Visual Studio Code take large amounts of memory (1.5 GiB or more).
Instead, you can open your terminal in your project's root directory and run
your script with the python command without opening your IDE.
python your_script.py # Or with python3 python3 your_script.py # Or with py alias (Windows) py your_script.py
You can also try to close browser tabs you don't need to try to reduce your memory consumption before running the script.
# Try to process the data in smaller chunks
Another thing you can try is to process the data in smaller chunks.
For example, if you are reading a file, don't read the entire file in memory, instead, use a for loop to iterate over the file and read each line separately.
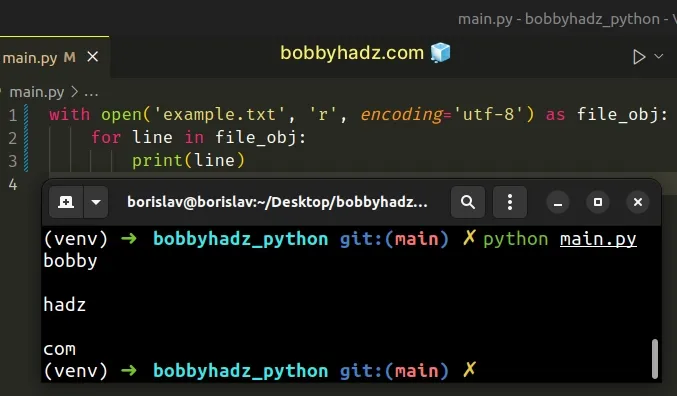
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file_obj: for line in file_obj: print(line)
The code sample assumes that you have an example.txt file in the same
directory as your main.py script.
bobby hadz com
If you get the error when training ML models with a large dataset, try using a smaller dataset instead.
# Make sure the correct Python interpreter is selected
Another thing you can try is to make sure the correct Python interpreter is selected.
For example, if you use PyCharm:
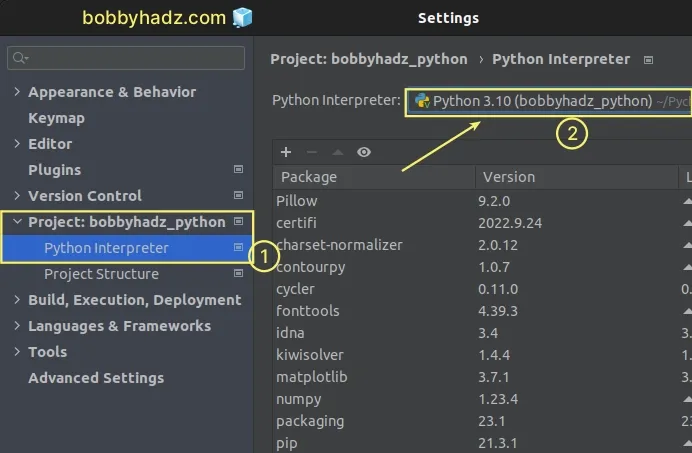
- Click on File in the top menu and then select Settings.
- Click on Project: YOUR_PROJECT in the left sidebar.
- Select Python interpreter.
- Make sure the correct Python interpreter is selected in the dropdown menu at the top.
If you use VS Code for your IDE, follow the instructions in this article on how to select the correct Python interpreter.
Try to rerun your script after making the change.
# Increasing the swap space
If you got the error on Ubuntu, you can also try to increase the swap space.
The following forum post has step-by-step instructions on how to increase the swap space by creating a swap file.
# Run the script on a machine that has more RAM
If none of the suggestions helped, you have to run the script on a machine that has more RAM.
For example, you can provision an Amazon EC2 instance with X GiB of RAM, run the script and stop the instance.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

