How to filter a List of Dictionaries in Python
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- How to filter a List of Dictionaries in Python
- Filter a List of Dictionaries by unique values
- Filter a List of Dictionaries based on a key
# How to filter a List of Dictionaries in Python
To filter a list of dictionaries based on one or multiple values:
- Store the acceptable values in a list.
- Use a list comprehension to iterate over the list of dictionaries.
- Check if the specific key in each dictionary is equal to one of the acceptable values.
list_of_dictionaries = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby'}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl'}, ] list_of_values = [1, 3] filtered_list_of_dicts = [ dictionary for dictionary in list_of_dictionaries if dictionary['id'] in list_of_values ] # 👇️ [{'id': 1, 'name': 'alice'}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl'}] print(filtered_list_of_dicts)
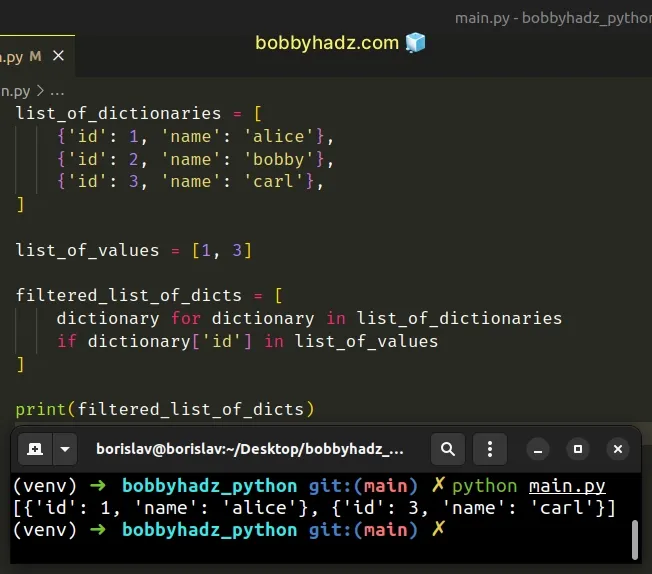
We stored the acceptable values in a list and used a list comprehension to iterate over the list of dictionaries.
On each iteration, we check if the current dictionary has an id key with one
of the values in the list.
The in operator tests
for membership. For example, x in l evaluates to True if x is a member of
l, otherwise, it evaluates to False.
# Checking for a single value
If you only want to check for a single value, use the equality operator.
list_of_dictionaries = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby'}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl'}, {'id': 4, 'name': 'bobby'}, ] filtered_list_of_dicts = [ dictionary for dictionary in list_of_dictionaries if dictionary['name'] == 'bobby' ] # 👇️ [{'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby'}, {'id': 4, 'name': 'bobby'}] print(filtered_list_of_dicts)
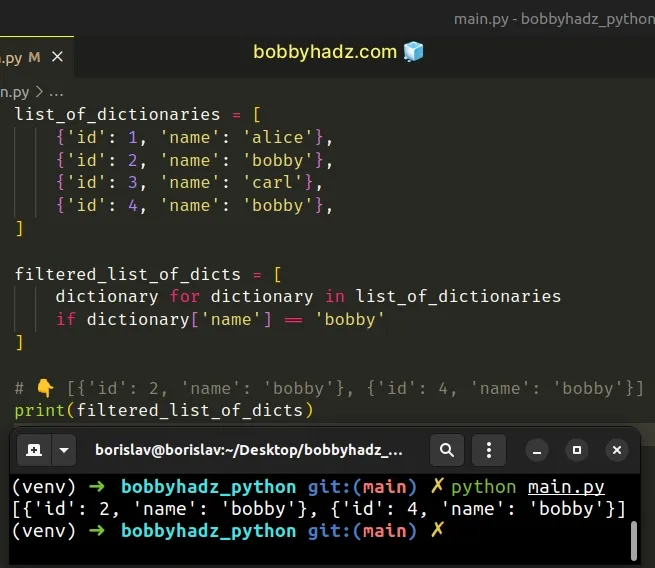
The example checks if each dictionary has a name key with a value equal to
bobby and returns the result.
The new list only contains the matching dictionaries.
# Filter a list of dictionaries using a for loop
You could also use a for loop to filter a list of dictionaries.
list_of_dictionaries = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby'}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl'}, ] list_of_values = [1, 3] filtered_list_of_dicts = [] for dictionary in list_of_dictionaries: if dictionary['id'] in list_of_values: filtered_list_of_dicts.append(dictionary) # 👇️ [{'id': 1, 'name': 'alice'}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl'}] print(filtered_list_of_dicts)
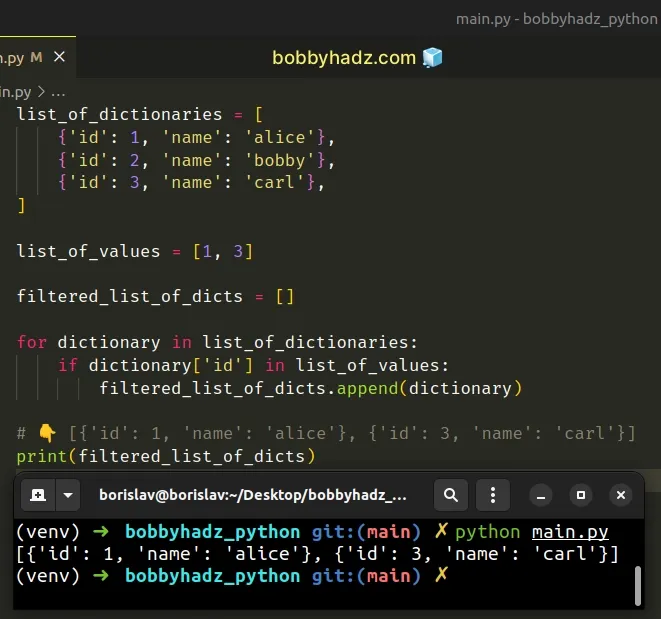
We used a for loop to iterate over the list of dictionaries.
On each iteration, we check if a certain condition is met.
If the condition is met, we append the current dictionary to a new list.
# Filter a List of Dictionaries by unique values
To filter a list of dictionaries by unique values:
- Use a dict comprehension to iterate over the list.
- Use the value of each
idproperty as a key and the dictionary as a value. - Use the
dict.values()method to only get the unique dictionaries. - Use the
list()class to convert the result to a list.
list_of_dictionaries = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby'}, {'id': 1, 'name': 'carl'}, ] list_of_unique_dictionaries = list( { dictionary['id']: dictionary for dictionary in list_of_dictionaries }.values() ) # 👇️ [{'id': 1, 'name': 'carl'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby'}] print(list_of_unique_dictionaries)
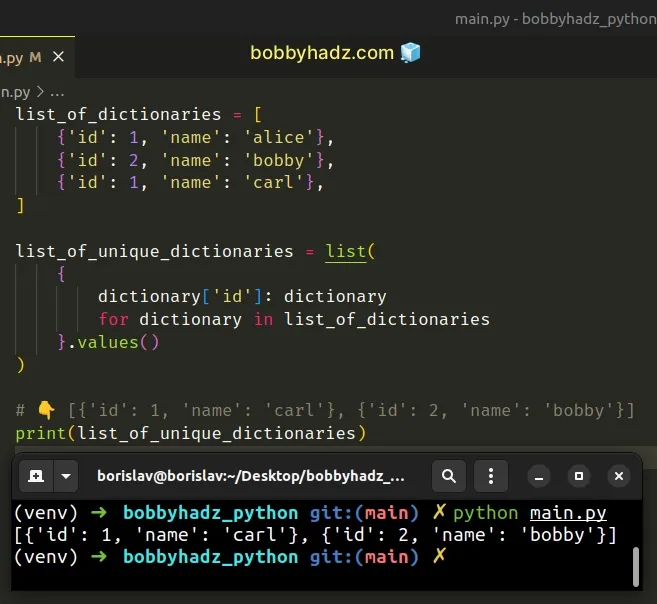
We used a dict comprehension to iterate over the list of dictionaries.
Dict comprehensions are very similar to list comprehensions.
On each iteration, we set the value of the current id as the key and the
actual dictionary as the value.
The keys in a dictionary are unique, so any duplicate values get filtered out.
We then use the dict.values() method to only return the unique dictionaries.
The dict.values() method returns a new view of the dictionary's values.
my_dict = {'id': 1, 'name': 'bobbyhadz'} print(my_dict.values()) # 👉️ dict_values([1, 'bobbyhadz'])
The last step is to use the list() class to convert the view object to a list containing unique dictionaries.
# Filter a list of dictionaries based on a key
To filter a list of dictionaries based on a key:
- Use a list comprehension to iterate over the list of dictionaries.
- Use the
dict.get()method to check if each dictionary contains the given key. - The new list will only contain the dictionaries that contain the key.
list_of_dictionaries = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby'}, {'id': 3, 'salary': 100}, ] filtered_list = [ dictionary for dictionary in list_of_dictionaries if dictionary.get('name') is not None ] # 👇️ [{'id': 1, 'name': 'alice'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby'}] print(filtered_list)
We used a list comprehension to iterate over the list of dictionaries.
dict.get() method to check if the current dictionary contains the name key.The dict.get() method returns the value for the given key if the key is in the dictionary, otherwise a default value is returned.
The method takes the following 2 parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| key | The key for which to return the value |
| default | The default value to be returned if the provided key is not present in the dictionary (optional) |
If a value for the default parameter is not provided, it defaults to None,
so the get() method never raises a KeyError.
The new list only contains the dictionaries that contain the given key.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

