Check if a value exists in a List of Dictionaries in Python
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- Check if a value exists in a List of Dictionaries in Python
- Check if a value doesn't exist in a list of dictionaries
- Get a list of all of the values for a given key
- Check if a value exists in a List of Dictionaries using a for loop
- Get the index of the matching dictionary in the list
- Check if a value exists in a List of Dictionaries using filter
- Check if a value exists in a List of Dictionaries using map
# Check if a value exists in a List of Dictionaries in Python
To check if a value exists in a list of dictionaries:
- Use a generator expression to iterate over the list.
- Access the given key in each dictionary and compare it to the value.
- Pass the result to the
any()function.
list_of_dicts = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice', 'salary': 100}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl', 'salary': 102}, ] if any( dictionary.get('name') == 'bobby' for dictionary in list_of_dicts ): # 👇️ this runs print('A dictionary with the specified value exists')
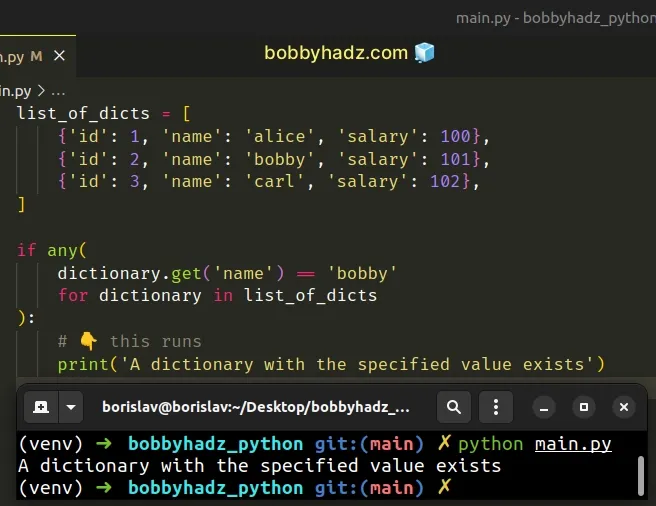
The first example checks if a value exists in a list of dictionaries.
The second checks if a value does not exist in a list of dictionaries.
We used a generator expression to iterate over the list.
list_of_dicts = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice', 'salary': 100}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl', 'salary': 102}, ] if any( dictionary['name'] == 'bobby' for dictionary in list_of_dicts ): # 👇️ this runs print('A dictionary with the specified value exists')
On each iteration, we access the name key and compare its value to a specific
string.
The any function
takes an iterable as an argument and returns True if any element in the
iterable is truthy.
any() function short-circuits and returns True.# Check if a value doesn't exist in a list of dictionaries
If you need to check if a value doesn't exist in a list of dictionaries, negate
the call to any().
list_of_dicts = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice', 'salary': 100}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl', 'salary': 102}, ] if not any(dictionary.get('name') == 'bobby' for dictionary in list_of_dicts): print('None of the dictionaries contain the specified value')
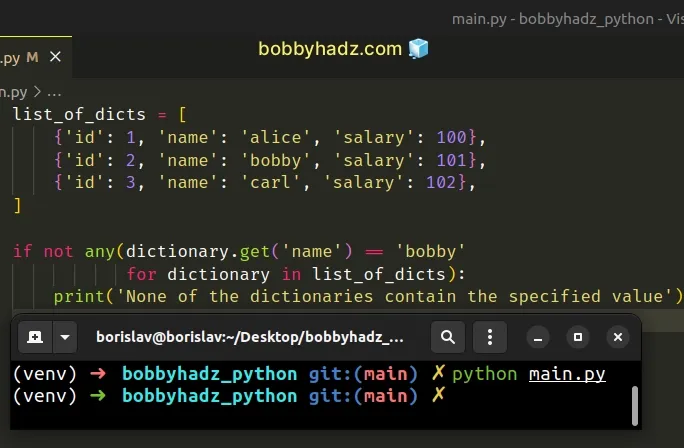
The not operator flips the result, so the if block is only run if the value
doesn't exist in any of the dictionaries in the list.
dict.get() method to avoid getting a KeyError exception if not all of the dictionaries in the list contain the given key.The dict.get() method returns the value for the given key if the key is in the dictionary, otherwise a default value is returned.
The method takes the following 2 parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| key | The key for which to return the value |
| default | The default value to be returned if the provided key is not present in the dictionary (optional) |
default parameter is not provided, it defaults to None, so the get() method never raises a KeyError.# Get a list of all of the values for a given key
If you need to get a list of all of the values for a given key, use a list comprehension.
list_of_dicts = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice', 'salary': 100}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl', 'salary': 102}, ] name_values = [ dictionary['name'] for dictionary in list_of_dicts ] print(name_values) # 👉️ ['alice', 'bobby', 'carl'] print('bobby' in name_values) # 👉️ True print('another' in name_values) # 👉️ False
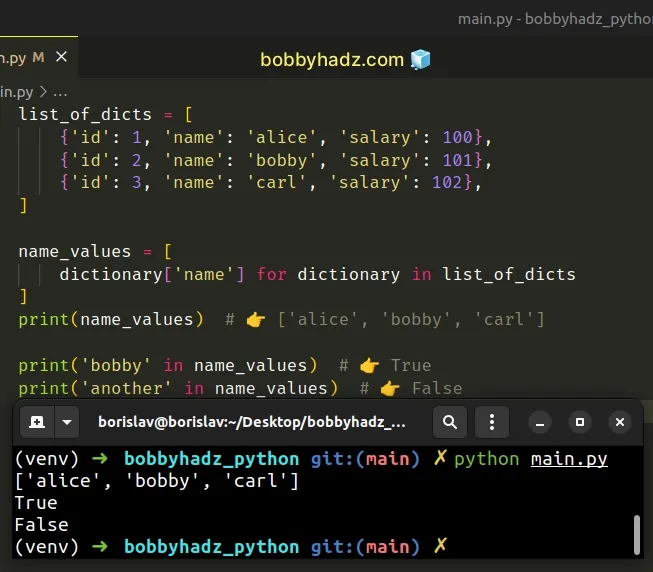
We use a list comprehension to iterate over the list.
On each iteration, we access a specific key in the current dictionary and return the corresponding value.
Alternatively, you can use a for loop.
# Check if a value exists in a List of Dictionaries using a for loop
This is a three-step process:
- Use a
forloop to iterate over the list. - Access the given key in each dictionary and compare it to the value.
- If you find a matching dictionary, exit the
forloop.
list_of_dicts = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice', 'salary': 100}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl', 'salary': 102}, ] value_exists = False for dictionary in list_of_dicts: if dictionary.get('name') == 'bobby': value_exists = True # 👇️ {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101} print(dictionary) break
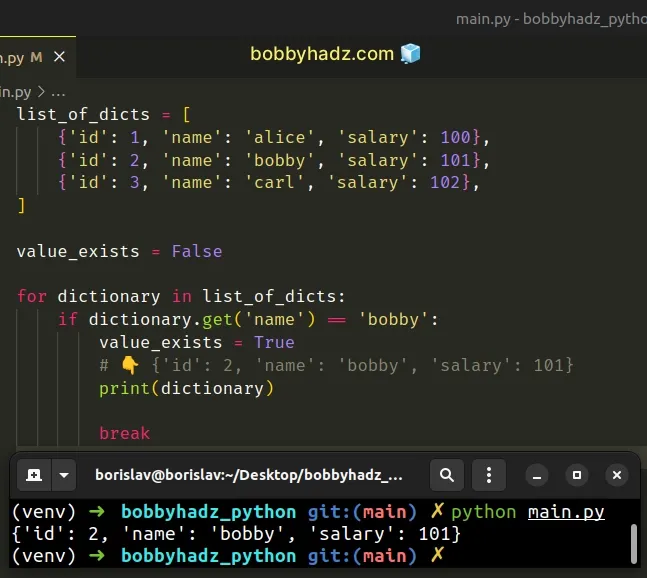
We used a for loop to iterate over the list.
On each iteration, we check if the current dictionary has a name key with a
specific value.
If the condition is met, we set the value_exists variable to True and exit
the for loop.
The break statement breaks out of the
innermost enclosing for or while loop.
# Get the index of the matching dictionary in the list
If you need to get the index of the matching dictionary in the list, use the
enumerate() function.
list_of_dicts = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice', 'salary': 100}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl', 'salary': 102}, ] value_exists = False for index, dictionary in enumerate(list_of_dicts): if dictionary.get('name') == 'bobby': value_exists = True # 👇️ {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101} print(dictionary) print(index) # 👉️ 1 break
We used the enumerate() function to get access to the index of the current
iteration.
The enumerate() function takes an iterable and returns an enumerate object containing tuples where the first element is the index and the second is the corresponding item.
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com'] for index, item in enumerate(my_list): print(index, item) # 👉️ 0 bobby, 1 hadz, 2 com
# Check if a value exists in a List of Dictionaries using filter
You can also use the filter() function to check if a value exists in a list of
dictionaries.
list_of_dicts = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice', 'salary': 100}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl', 'salary': 102}, ] matching_dicts = list( filter( lambda x: x.get('name') == 'bobby', list_of_dicts ) ) # [{'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101}] print(matching_dicts) if len(matching_dicts) > 0: print('The value exists in the list of dictionaries')
The filter() function takes a function and an iterable as arguments and constructs an iterator from the elements of the iterable for which the function returns a truthy value.
The lambda function we passed to filter() gets called with each dictionary
from the list.
The function gets the name attribute of the dictionary and compares it to the
given value.
If the condition is met, the dictionary is included in the filter object.
The last step is to check if the length of the variable is greater than 0.
If it is, then at least one dictionary has the specified value.
# Check if a value exists in a List of Dictionaries using map
You can also use the map() function to check if a value exists in a list of
dictionaries.
from operator import itemgetter list_of_dicts = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice', 'salary': 100}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl', 'salary': 102}, ] if 'bobby' in map(itemgetter('name'), list_of_dicts): # 👇️ this runs print('The value is in the dictionary') else: print('The value is NOT in the dictionary')
The map() function takes a function and an iterable as arguments and calls the function with each item of the iterable.
The operator.itemgetter() class returns a callable object that fetches the items at the specified indices or keys.
For example, x = itemgetter('name') and then calling x(my_dict), returns
my_dict['name'].
from operator import itemgetter list_of_dicts = [ {'id': 1, 'name': 'alice', 'salary': 100}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'bobby', 'salary': 101}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'carl', 'salary': 102}, ] # 👇️ ['alice', 'bobby', 'carl'] print(list(map(itemgetter('name'), list_of_dicts)))
The last step is to use the in operator to check if the given value is
contained in the list.
I've also written an article on how to filter a list of dictionaries.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Remove a Dictionary from a List of Dictionaries in Python
- Remove duplicates from a List of Dictionaries in Python
- Check if a Value exists in a Two-dimensional List in Python
- Check if multiple Values are in a List in Python
- How to merge two JSON objects in Python
- How to destructure Dictionaries and Lists in Python

