How to sum a List of Strings in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Sum a List of Strings in Python
- Sum a List of Strings using try/except
- Sum a List of Strings using str.join(
- Convert all values to strings before calling join()
- Concatenate to a string in a for loop in Python
- Sum the digits in a string in Python
# Sum a List of Strings in Python
To sum a list of strings:
- Use a
forloop to iterate over the list. - Check if each value is a valid number.
- Convert the valid numbers to integers or floats and sum them.
a_list = ['1', 'a', '2', 'c', '3', 4, 5] total = 0 for item in a_list: if isinstance(item, int) or ( hasattr(item, 'isdigit') and item.isdigit() ): total += int(item) print(total) # 👉️ 15
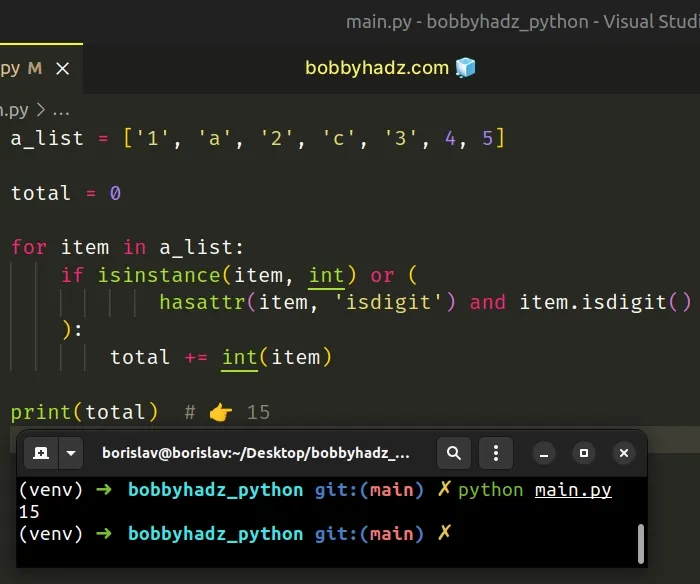
We used a for loop to iterate over the list of strings.
On each iteration, we check if the current item is an integer or an integer wrapped in a string.
If the condition is met, we add the value to the total variable.
# Sum a List of Strings using try/except
You can also use a try/except statement to sum a list of strings.
a_list = ['1', 'a', '2', 'c', '3', 4, 5] total = 0 for item in a_list: try: total += int(item) except ValueError: pass print(total) # 👉️ 15
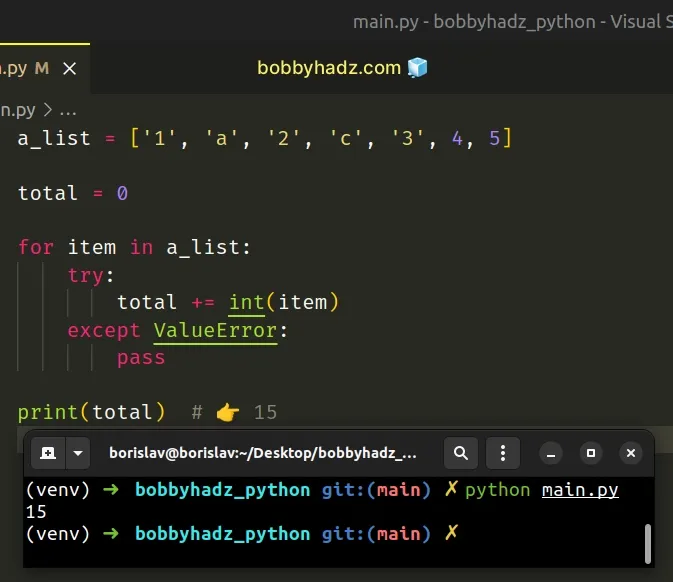
On each iteration, we try to convert the current item to an integer.
If a ValueError exception is raised, the except block runs.
Otherwise, the number gets added to the total.
# Sum a List of Strings using str.join()
This is a three-step process:
- Call the
str.join()method on an empty string. - Pass the iterable (e.g. a list of strings) to the
join()method. - The result will be a string containing the items of the iterable.
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] # 👇️ without a separator my_str = ''.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'abc' # 👇️ with a space separator my_str = ' '.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'a b c'
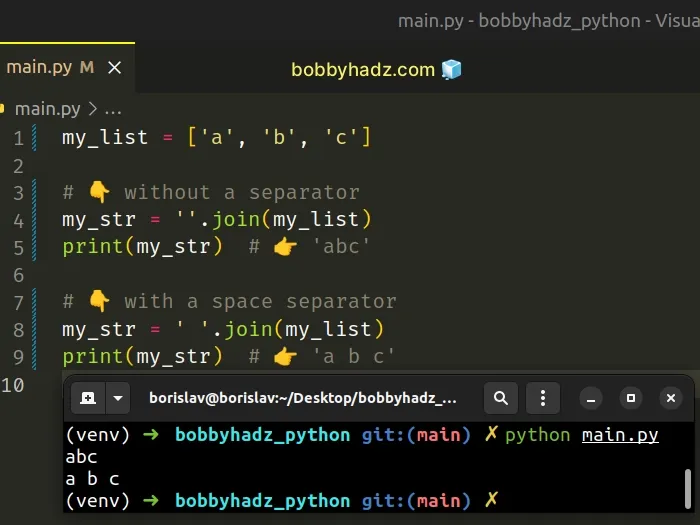
The str.join() method takes an iterable as an argument and returns a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the iterable.
TypeError if there are any non-string values in the iterable.# Convert all values to strings before calling join()
If your list contains numbers or other types, convert all of the values to
string before calling join().
my_list = ['a', 1, 'b', 2, 'c', 3] my_str = ''.join(map(str, my_list)) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'a1b2c3'
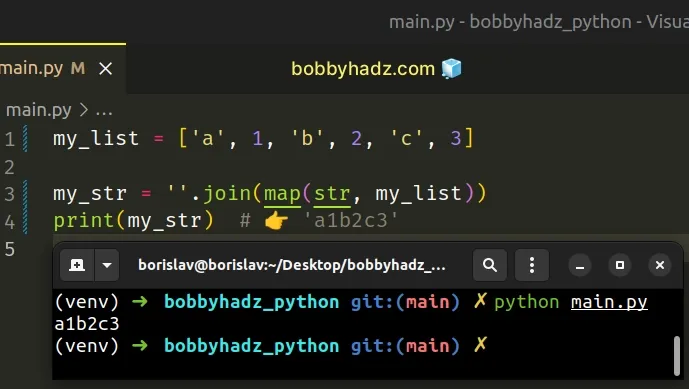
The map() function takes a function and an iterable as arguments and calls the function with each item of the iterable.
str.join() method.The string the join() method is called on is used as the separator between
elements.
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] my_str = '-'.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'a-b-c'
If you need to join the list of strings with spaces, call the method on a string that contains a space.
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] # 👇️ with a space separator my_str = ' '.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'a b c'
If you don't need a separator and just want to join the iterable's elements into
a string, call the join() method on an empty string.
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] my_str = ''.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'abc'
Alternatively, you can concatenate to a string in a for loop.
# Concatenate to a string in a for loop in Python
This is a three-step process:
- Declare a variable and initialize it to an empty string.
- Use a for loop to iterate over the sequence.
- Reassign the variable to its current value plus the current item.
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com'] my_str = '' for item in my_list: my_str += item print(my_str) # 👉️ 'bobbyhadzcom'
The first step is to declare a new variable and initialize it to an empty string.
On each iteration in the for loop, we reassign the variable to its current
value plus the value of the current list item.
+= operator is a shorthand for my_str = my_str + item.The following code sample achieves the same result.
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com'] my_str = '' for item in my_list: my_str = my_str + item print(my_str) # 👉️ 'bobbyhadzcom'
# Sum the digits in a string in Python
If you need to sum the digits in a string:
- Use a generator expression to iterate over the string.
- On each iteration, convert each character to an integer if it is a digit.
- Use the
sum()function to get the sum of the digits.
my_str = '1ab2c3' # ✅ Sum digits in a string that might contain non-digits total = sum(int(char) for char in my_str if char.isdigit()) print(total) # 👉️ 6 # ----------------------------------------------------------- # ✅ Sum digits in a string that contains only digits my_str = '246' total = sum(int(d) for d in my_str) print(total) # 👉️ 12
We used a generator expression to iterate over the string.
On each iteration, we check if the character is a digit.
The str.isdigit() method returns
True if all characters in the string are digits and there is at least 1
character, otherwise False is returned.
We convert all digits to integers and use the sum() function to get the total.
my_str = '1ab2c3' total = sum(int(char) for char in my_str if char.isdigit()) print(total) # 👉️ 6
The sum() function takes an iterable, sums its items from left to right and returns the total.
The sum function takes the following 2 arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| iterable | the iterable whose items to sum |
| start | sums the start value and the items of the iterable. sum defaults to 0 (optional) |
If your string is guaranteed to only contain digits, you don't have to use the
str.isdigit() method.
my_str = '246' total = sum(int(d) for d in my_str) print(total) # 👉️ 12
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

