Pandas: Reorder DataFrame rows based on Index List
Last updated: Apr 13, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
- Pandas: Reorder DataFrame rows based on Index List
- Sorting the DataFrame rows with sort_index()
- Pandas: Reorder DataFrame rows based on Index List using DataFrame.loc
# Pandas: Reorder DataFrame rows based on Index List
Use the DataFrame.reindex() method to reorder the rows of a Pandas
DataFrame based on an index list.
The DataFrame.reindex() method takes a labels argument that is used to
determine the row order.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan', 'Ethan'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5], }, index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']) print(df) print('-' * 50) index_list = ['C', 'D', 'E', 'B', 'A'] new_df = df.reindex(labels=index_list) print(new_df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary A Alice 1 175.1 B Bobby 1 180.2 C Carl 5 190.3 D Dan 7 205.4 E Ethan 7 210.5 -------------------------------------------------- name experience salary C Carl 5 190.3 D Dan 7 205.4 E Ethan 7 210.5 B Bobby 1 180.2 A Alice 1 175.1
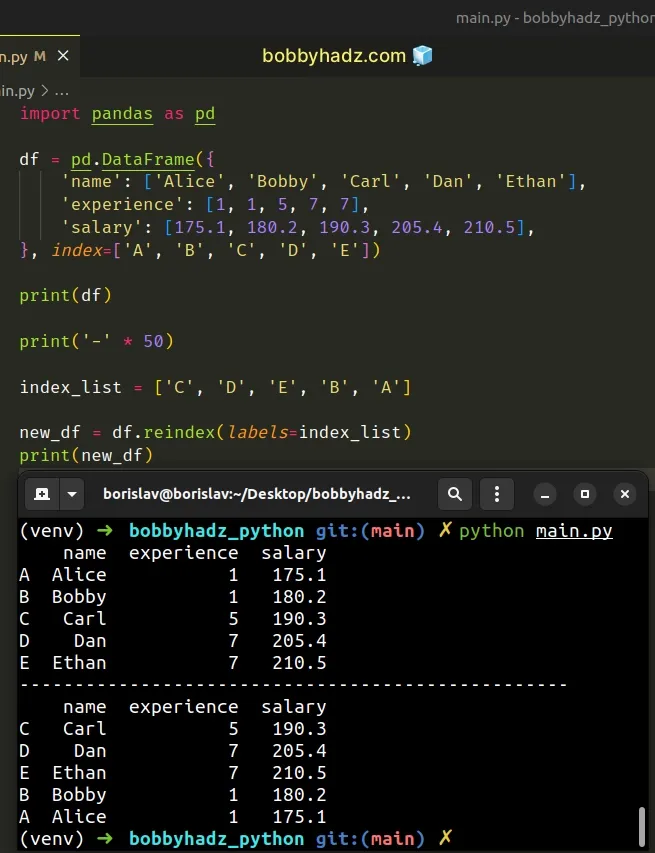
The index_list variable stores a list with the indices in which we want to
sort the DataFrame rows.
index_list = ['C', 'D', 'E', 'B', 'A'] new_df = df.reindex(labels=index_list)
The
DataFrame.reindex()
method conforms a DataFrame to a new index with optional filling logic.
The only argument we passed to the method is labels - the new index to conform
the row axis to.
# Sorting the DataFrame rows with sort_index()
If you need to sort the DataFrame rows by the index in ascending order, use
the
DataFrame.sort_index()
method.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan', 'Ethan'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5], }, index=['C', 'D', 'E', 'B', 'A']) print(df) print('-' * 50) df = df.sort_index(ascending=True) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary C Alice 1 175.1 D Bobby 1 180.2 E Carl 5 190.3 B Dan 7 205.4 A Ethan 7 210.5 -------------------------------------------------- name experience salary A Ethan 7 210.5 B Dan 7 205.4 C Alice 1 175.1 D Bobby 1 180.2 E Carl 5 190.3
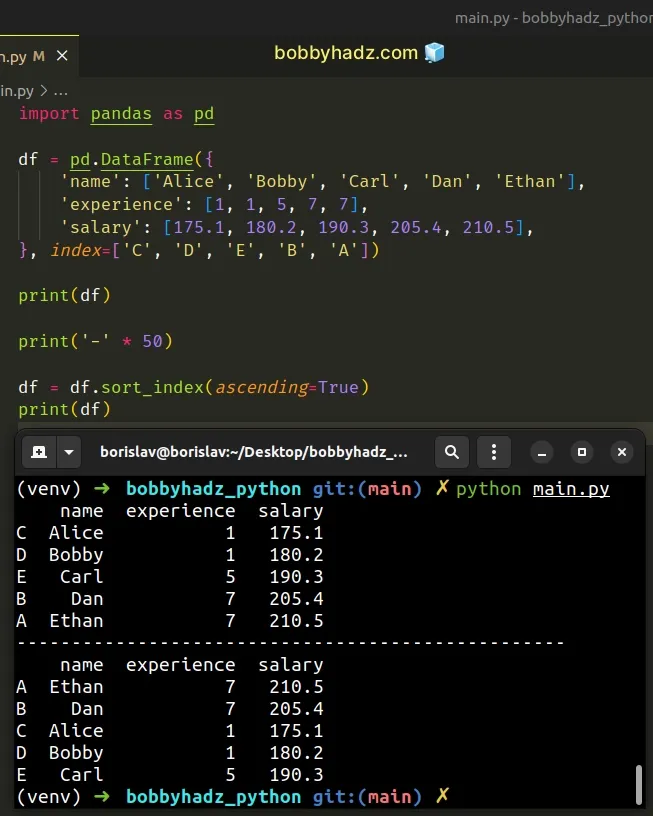
If you want to sort the DataFrame rows by the index in descending order, set
the ascending argument to False.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan', 'Ethan'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5], }, index=['C', 'D', 'E', 'B', 'A']) print(df) print('-' * 50) df = df.sort_index(ascending=False) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary C Alice 1 175.1 D Bobby 1 180.2 E Carl 5 190.3 B Dan 7 205.4 A Ethan 7 210.5 -------------------------------------------------- name experience salary E Carl 5 190.3 D Bobby 1 180.2 C Alice 1 175.1 B Dan 7 205.4 A Ethan 7 210.5
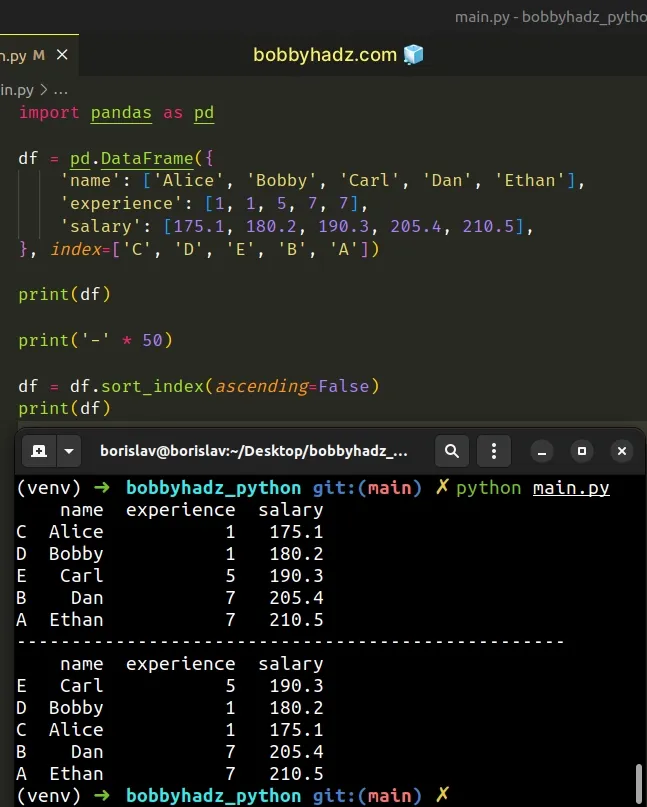
The DataFrame.sort_index() method sorts the DataFrame by its index.
The method returns a new DataFrame sorted by the index.
The sort_index() method takes an optional axis argument which determines the
axis along which to sort.
By default, the axis argument is set to 0 (the rows axis).
# Pandas: Reorder DataFrame rows based on Index List using DataFrame.loc
You can also use the
DataFrame.loc label-based
indexer to reorder the rows of a DataFrame based on an index list.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan', 'Ethan'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5], }, index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']) print(df) print('-' * 50) index_list = ['C', 'D', 'E', 'B', 'A'] df = df.loc[index_list] print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary A Alice 1 175.1 B Bobby 1 180.2 C Carl 5 190.3 D Dan 7 205.4 E Ethan 7 210.5 -------------------------------------------------- name experience salary C Carl 5 190.3 D Dan 7 205.4 E Ethan 7 210.5 B Bobby 1 180.2 A Alice 1 175.1
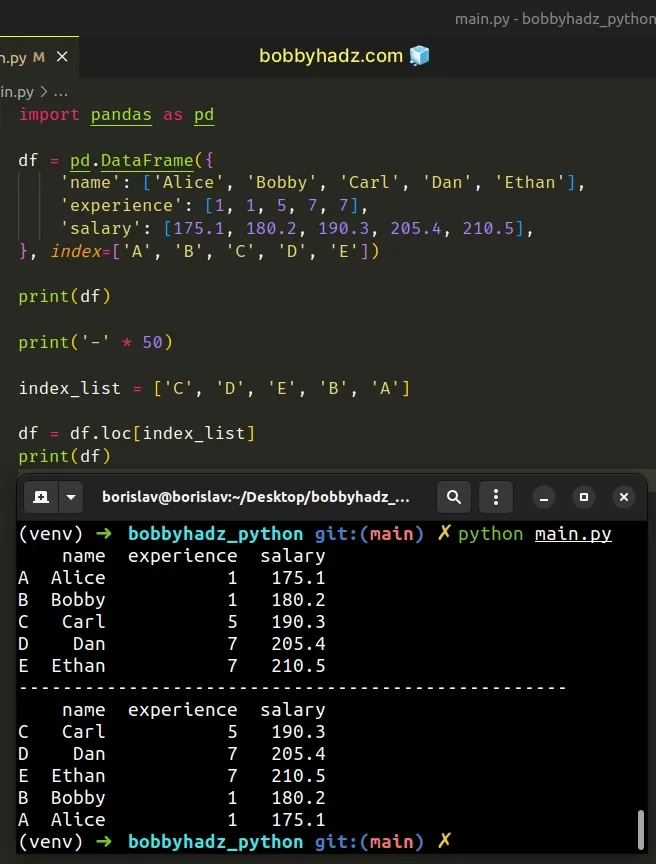
The DataFrame.loc indexer enables us to select the DataFrame rows in the
specified order.
index_list = ['C', 'D', 'E', 'B', 'A'] # name experience salary # C Carl 5 190.3 # D Dan 7 205.4 # E Ethan 7 210.5 # B Bobby 1 180.2 # A Alice 1 175.1 print(df.loc[index_list])
However, make sure there aren't any indices in the index list that are not
present in the DataFrame, otherwise, you'd get a
KeyError exception.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Pandas: Setting column names when reading a CSV file
- Export a Pandas DataFrame to Excel without the Index
- Pandas: How to Convert a Pivot Table to a DataFrame
- Pandas: Count the unique combinations of two Columns
- Pandas: How to Query a Column name with Spaces
- Pandas: Find the closest value to a Number in a Column

