Get closest Parent element by Class or Tag in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 5, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Get the closest Parent element by Class using JavaScript
- Get the closest Parent element by Tag using JavaScript
- Check if a Parent has a specific Class using JavaScript
- Check if the direct parent of an element has a specific class
# Get the closest Parent element by Class using JavaScript
Use the closest() method to get the closest parent element by class, e.g.
child.closest('.parent').
The closest() method traverses the Element and its parents until it finds
a node that matches the provided selector.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>bobbyhadz.com</title> </head> <body> <div class="parent"> <div id="child">Child 1</div> </div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
const child = document.getElementById('child'); const parentWithClass = child.closest('.parent'); console.log(parentWithClass); // 👉️ div.parent
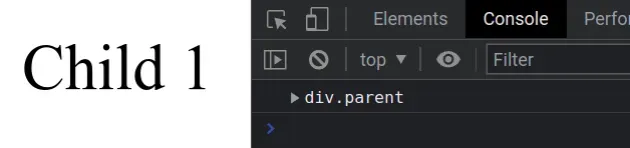
We got the child element by its id and called the
closest()
method on it.
closest() method traverses the Element and its parents until it finds a node that matches the provided selector.If the element itself matches the selector, the element is returned.
If no element matches the provided selector, the closest() method returns
null.
The method takes a string that contains a selector. The provided selector can be as specific as necessary.
const child = document.getElementById('child'); const parentWithClass = child.closest('div.parent'); console.log(parentWithClass); // 👉️ div.parent
The example matches only div elements that have the parent class.
The following example selects a div element that has a class of parent and
has the body element as the parent.
const child = document.getElementById('child'); const parentWithClass = child.closest('body > div.parent'); console.log(parentWithClass); // 👉️ div.parent
The following example returns the closest parent that has the parent class and
is not a span element.
const child = document.getElementById('child'); const parentWithClass = child.closest(':not(span).parent'); console.log(parentWithClass); // 👉️ div.parent
closest() method, a SyntaxError is thrown.# Get the closest Parent element by Tag using JavaScript
You can also use the closest() method to get the closest parent element by
tag.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>bobbyhadz.com</title> </head> <body> <div id="parent-1"> <span id="parent-2"> <div id="child">Child 1</div> </span> </div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
const child = document.getElementById('child'); // ✅ Gets immediate parent, regardless of which Tag const immediateParent = child.parentElement; console.log(immediateParent); // 👉️ span#parent-2 // ✅ Gets a parent that is a `div` element const parent = child.parentElement.closest('div'); console.log(parent); // 👉️ div#parent-1
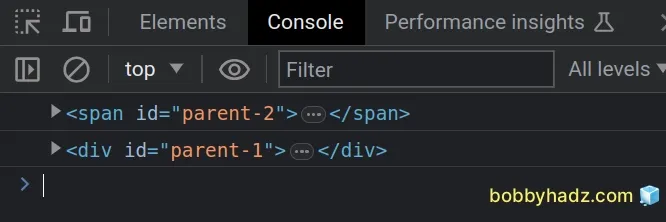
We used the Node.parentElement property to get the DOM node's immediate parent element.
However, the parentElement property doesn't allow us to filter the results as
it returns the parent element.
We used the closest method to get the closest parent element by tag.
parentElement property on the child before calling the closest() method is because the closest() method traverses the Element and its parents until it finds a node that matches the provided selector string.In our case, the child is a div element and the parent we want access to is a
div, so calling the closest() method and passing it a div selector returns
the child element.
parentElement property, we start traversing the DOM for an element that matches the selector from the parent element onwards.If no element matches the selector, the closest() method returns null.
The method takes a string that contains a selector. The provided selector can be as specific as necessary.
const child = document.getElementById('child'); // ✅ Gets a parent that is a `div` element const parent = child.parentElement.closest('body > div'); console.log(parent); // 👉️ div#parent-1
The example above selects a div element that has the body element as its
parent.
If an invalid selector string is provided to the closest() method, a
SyntaxError is thrown.
# Check if a Parent has a specific Class using JavaScript
To check if a parent element has a specific class:
- Pass the class selector as a parameter to the
closest()method. - If a parent with the specified class exists, the method returns the element.
- If no parent with the provided class exists, the method returns
null.
Here is the HTML for the examples.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <title>bobbyhadz.com</title> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div class="parent-1"> <div class="parent2"> <div id="child">Box 1</div> </div> </div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
// ✅ Check if any of the parent elements have class `parent-1` const child = document.getElementById('child'); const parentHasClass = child.closest('.parent-1') !== null; console.log(parentHasClass); // 👉️ true // ------------------------------------------------------------ // ✅ Check if the DIRECT parent element has class `parent-1`. const directParentHasClass = child.parentElement?.classList.contains('parent-1'); console.log(directParentHasClass); // 👉️ false
We used the
Element.closest()
method to select a parent element with the class of parent-1.
closest() method traverses the element and its parents until it finds a node that matches the provided selector.If the element itself matches the selector, the element is returned.
If no element that matches the provided selector exists, the closest() method
returns null.
The parentHasClass variable stores a boolean value:
trueif there is a parent element of thedivwithidofchildthat contains theparent-1class.falseif there isn't.
# Check if the direct parent of an element has a specific class
To check if the direct parent of the element has a specific class:
- Use the
parentElementproperty to select the parent of the element. - Use the
classList.contains()method to check if the parent contains the class. - The method returns
trueif the element's class list contains the class andfalseotherwise.
const child = document.getElementById('child'); // ✅ Check if the DIRECT parent element has class `parent-1`. const directParentHasClass = child.parentElement?.classList.contains('parent-1'); console.log(directParentHasClass); // 👉️ false
The
parentElement
property returns the DOM node's parent element or null if the node has no
parent or its parent is not a DOM element.
The
classList.contains()
method returns a boolean value - true if the class is contained in the
element's class list and false otherwise.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

