How to get the Current Year in JavaScript [for copyright]
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Get the Current Year in JavaScript
- Get the Last 2 Digits of the current Year
- Get the current Year for Copyright using JavaScript
# Get the Current Year in JavaScript
To get the current year:
- Use the
new Date()constructor to get aDateobject. - Call the
getFullYear()method on theDateobject. - The
getFullYearmethod will return the current year.
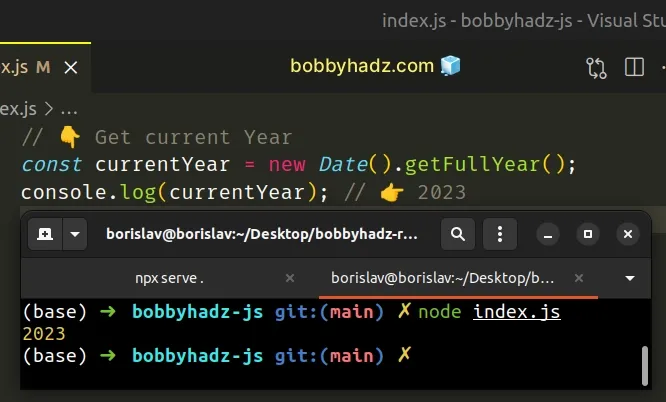
// 👇️ Get current Year const currentYear = new Date().getFullYear(); console.log(currentYear); // 👉️ 2024
We used the Date() to get a
Date object, on which we can call various methods.
const date = new Date(); console.log(date); // 👉️ 2024-01-04T05:21:48.504Z console.log(date.getFullYear()); // 👉️ 2024
The last step is to use the Date.getFullYear() method to get the current year.
The method returns the year of the specified date according to local time.
new Date() constructor.If you call the method on a Date object that stores a different date and time,
the output is reflected.
All you have to do is pass the specific date into the Date constructor on
which you call the methods.
const date = new Date('January 04, 2025 05:24:07'); const yearOfDate = date.getFullYear(); console.log(yearOfDate); // 👉️ 2025
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
function getCurrentYear() { return new Date().getFullYear(); } const currentYear = getCurrentYear(); console.log(currentYear); // 👉️ 2024
The getCurrentYear function takes no parameters and returns the current year.
If you only need the last 2 digits of the current year, use the slice()
method.
function getCurrentYear() { return String(new Date().getUTCFullYear()).slice(-2); } const currentYear = getCurrentYear(); console.log(currentYear); // 👉️ 24
We used the String.slice() method to get the last 2 digits of the current
year.
# Get the Last 2 Digits of the current Year
If you need to get the last 2 digits of the current year, use the slice()
method.
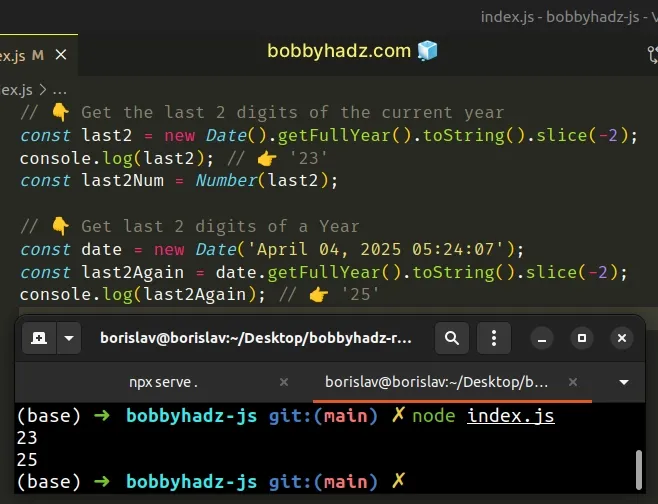
// 👇️ Get the last 2 digits of the current year const last2 = new Date().getFullYear().toString().slice(-2); console.log(last2); // 👉️ '24' const last2Num = Number(last2); // 👇️ Get last 2 digits of a Year const date = new Date('April 04, 2025 05:24:07'); const last2Again = date.getFullYear().toString().slice(-2); console.log(last2Again); // 👉️ '25'
The only argument we passed to the slice method is the start index - the
index at which we start extraction of characters from the string.
We used a negative index of -2 to get the last 2 digits of the year.
# Get the current Year for Copyright using JavaScript
Use the getFullYear() method to get the current year for copyright, e.g.
new Date().getFullYear().
The getFullYear method returns the current year when called on the current
date.
const currentYear = new Date().getFullYear(); console.log(currentYear); // 👉️ 2024
Here is an example that injects the current year into an HTML element directly on the page.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div>Content here</div> <div id="copyright"></div> <script> const paragraph = ` <p> Copyright © ${new Date().getFullYear()} John Doe </p> `; document.getElementById('copyright').innerHTML = paragraph; </script> </body> </html>
And here is an example that displays the current date for copyright in a React.js component using JSX.
export const Footer = () => ( <div> <p> Copyright © {new Date().getFullYear()} John Doe </p> </div> );
The Date() constructor creates
a new Date object.
Date, so it created a Date object that stores the current date.The Date.getFullYear method returns a number that represents the year of the given date.
Placing the script tag before declaring the DOM elements would run it before the elements exist on the page and cause an error.
In the HTML example, we used the
innerHTML
property to set the inner HTML of the element with id set to copyright.
The paragraph variable uses backticks (not single quotes) to create a template
string that stores a p element that contains the copyright message.
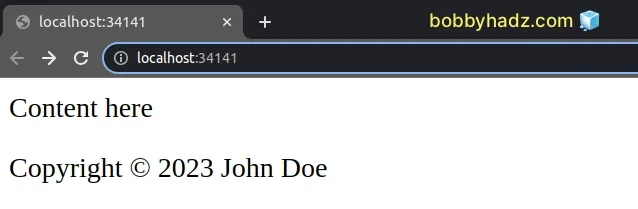
Here is how the p element looks on the page.

My blog uses the same approach to display the current year at the footer.
You could change the structure or the style of the element by editing the HTML code in the template string.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

