TypeError: getFullYear() is not a Function in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# TypeError: getFullYear() is not a Function in JavaScript
The "TypeError: getFullYear is not a function" error occurs for multiple reasons:
- Not using the
newoperator when instantiating aDateobject. - Calling the
getFullYear()method on an object that is not a valid Date. - Misspelling the
getFullYearmethod. - Placing a second set of parentheses when calling the method, e.g.
new Date().getFullYear()().
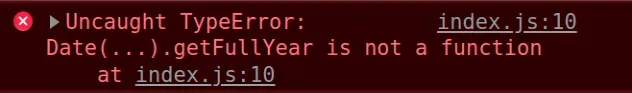
Here are some examples of how the error occurs:
// ⛔️ did not use `new` operator const d1 = Date('Sept 24, 22 13:20:18').getFullYear(); // ------------------------------------------------- // ⛔️ did not spell `getFullYear` correctly const d2 = new Date('Sept 24, 22 13:20:18').getFullyear(); // ------------------------------------------------- // ⛔️ added a second set of parentheses const d3 = new Date('Sept 24, 22 13:20:18').getFullYear()(); // ------------------------------------------------- // ⛔️ not calling getFullYear on a valid date object const d4 = {}.getFullYear();
In the first example, we didn't use the new operator to create the Date
object, which is what caused the error.
// ⛔️ did not use `new` operator const d1 = Date('Sept 24, 22 13:20:18').getFullYear(); // ----------------------------------------------- // ✅ Correct const d1 = new Date('Sept 24, 22 13:20:18').getFullYear(); console.log(d1); // 👉️ 2022
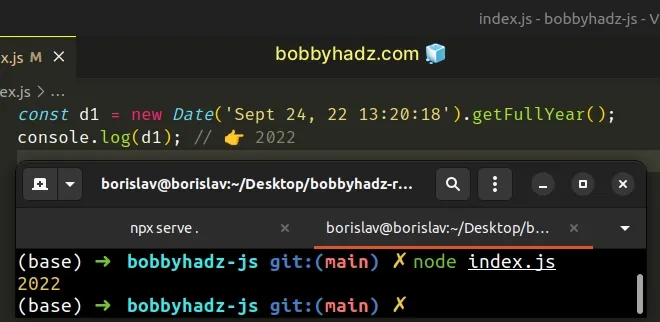
Make sure to use the new keyword when creating a Date object.
In the second example, we didn't capitalize the getFullYear() method correctly.
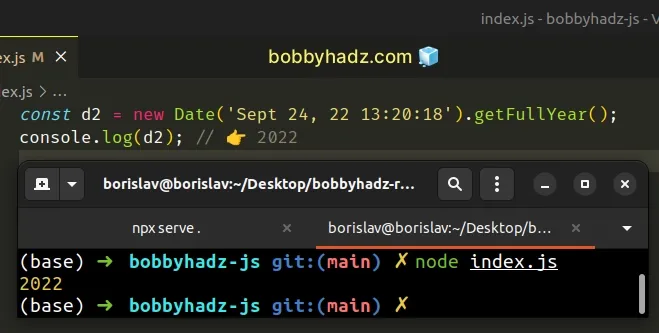
// ⛔️ did not spell `getFullYear` correctly const d2 = new Date('Sept 24, 22 13:20:18').getFullyear(); // -------------------------------------------------------- // ✅ correct const d2 = new Date('Sept 24, 22 13:20:18').getFullYear(); console.log(d2); // 👉️ 2022
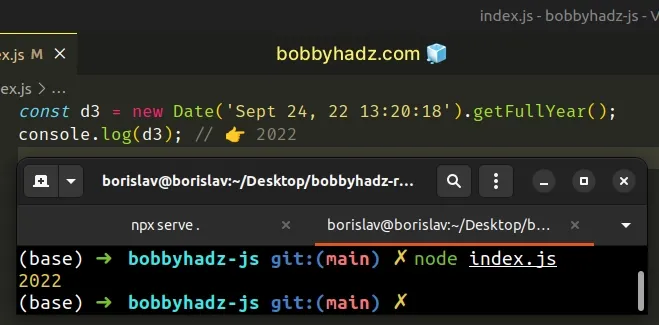
In the third example, we added an additional set of parentheses, which ended up trying to call the method on an integer.
// ⛔️ added a second set of parentheses const d3 = new Date('Sept 24, 22 13:20:18').getFullYear()(); // -------------------------------------------------------- // ✅ correct const d3 = new Date('Sept 24, 22 13:20:18').getFullYear(); console.log(d3); // 👉️ 2022
The fourth example calls the getFullYear method on an object that isn't a
valid Date object.
// ⛔️ not calling getFullYear on a valid date object const d4 = {}.getFullYear(); // -------------------------------------------------------- // ✅ correct const d4 = new Date().getFullYear(); console.log(d4); // 👉️ 2024
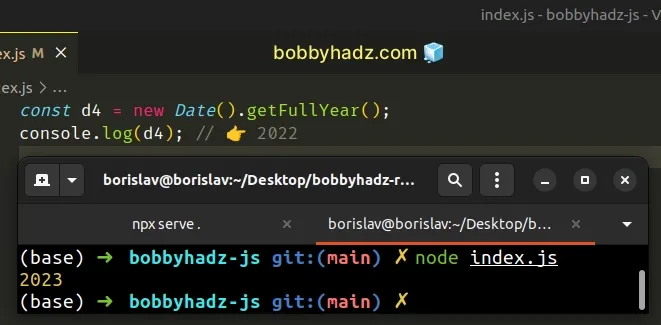
Make sure to only call the getFullYear() method on a valid Date object.
The getFullYear method returns the year of the date object the method was
called on.
const d1 = new Date('Sept 24, 22 13:20:18').getFullYear(); console.log(d1); // 👉️ 2022
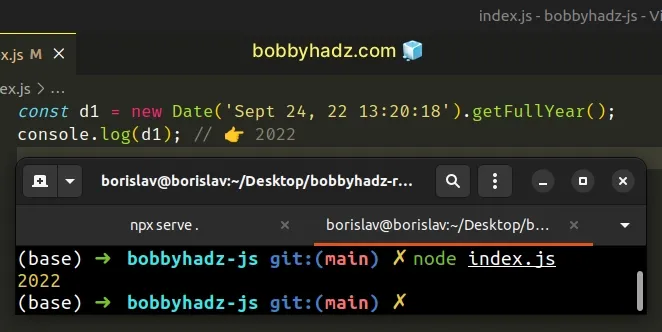
The getFullYear method can only be called on a valid Date object and returns
a four-digit number representing the year.
If you need to get the current year, you don't need to pass anything to the Date() constructor.
const current = new Date().getFullYear(); console.log(current); // 👉️ 2024
If you pass an invalid date to the Date() constructor, the getFullYear
method will return NaN (not a number).
const d1 = new Date('invalid').getFullYear(); console.log(d1); // 👉️ NaN
You can console.log the value you are calling the getFullYear method on and
see if it's a valid Date object.
You should call the getFullYear method on valid Date objects.
# Conclusion
To solve the "getFullYear is not a function" error, make sure to only call the
getFullYear() method on a valid Date object.
The getFullYear method returns the year of the date object the method was
called on.

