How to Format a Date as DD/MM/YYYY in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·4 min
# Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Format a Date as DD/MM/YYYY in JavaScript
- Format a Date as DD/MM/YYYY using date-fns
- Format a Date as DD/MM/YYYY using moment.js
# Introduction
If you just need a quick and short solution instead of a solid, reusable function, use the following one-liner.
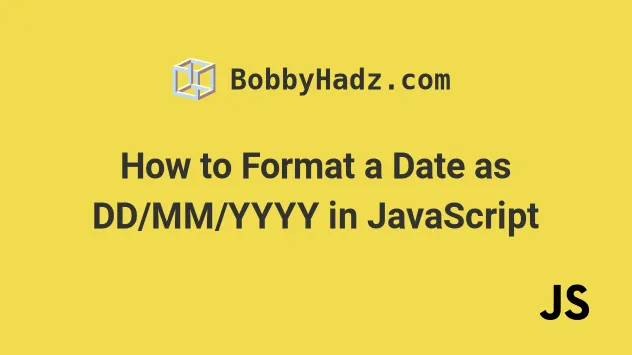
const date = new Date(); // ✅ DD/MM/YYYY const result1 = new Date().toLocaleDateString('en-GB'); console.log(result1); // 👉️ 24/07/2023
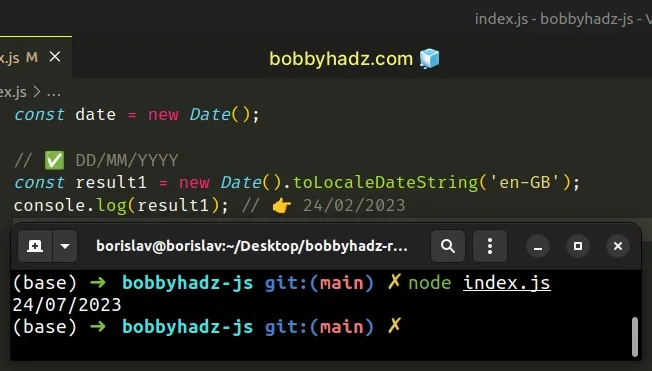
The code can also be tweaked to include the time.
const date = new Date(); const result2 = new Date().toLocaleString('en-GB', { hour12: false, }); console.log(result2); // 👉️ 24/07/2023, 11:47:44
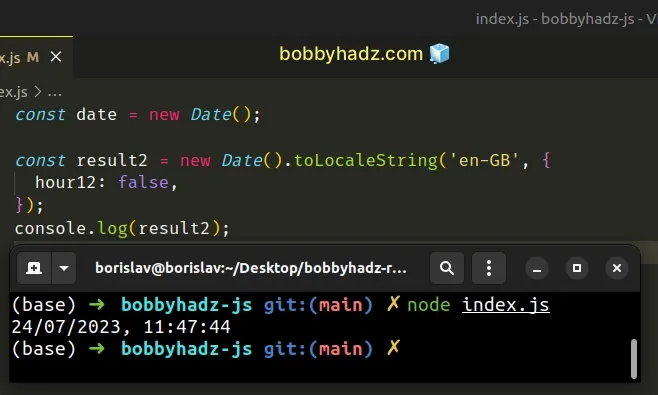
We used the en-GB locale in a hacky way to format the date as DD/MM/YYYY.
Alternatively, you can define a reusable function that works in a more predictable manner.
# Format a Date as DD/MM/YYYY in JavaScript
To format a date as DD/MM/YYYY:
- Use the
getDate(),getMonth()andgetFullYear()methods to get the day, month and year of the date. - Add a leading zero to the day and month digits if the value is less than
10. - Add the results to an array and join them with a forward slash separator.
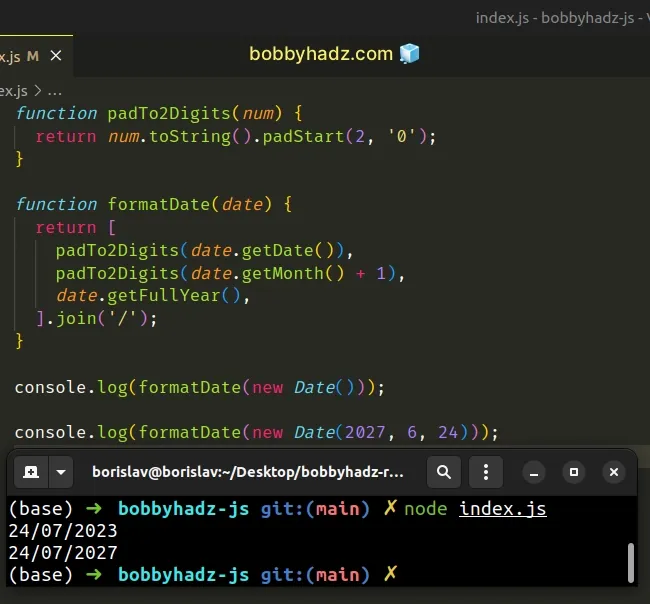
function padTo2Digits(num) { return num.toString().padStart(2, '0'); } function formatDate(date) { return [ padTo2Digits(date.getDate()), padTo2Digits(date.getMonth() + 1), date.getFullYear(), ].join('/'); } // 👇️ 24/07/2023 (DD/MM/YYYY) console.log(formatDate(new Date())); // 👇️️ 24/07/2027 (DD/MM/YYYY) console.log(formatDate(new Date(2027, 6, 24)));
The padTo2Digits function takes care of
adding a leading zero if the
month and day values only contain a single digit (are less than 10).
function padTo2Digits(num) { return num.toString().padStart(2, '0'); } console.log(padTo2Digits(2)); // 👉️ '02' console.log(padTo2Digits(6)); // 👉️ '06' console.log(padTo2Digits(10)); // 👉️ '10' console.log(padTo2Digits(24)); // 👉️ '24'
We want to make sure that the values for the month and day are always consistently formatted, so we used the String.padStart() method.
The arguments we passed to the padStart() method are:
- the total length of the string
- the pad character (
0in our case)
The next function we created is the one that formats a date as DD/MM/YYYY.
// ✅ format date as DD/MM/YYYY function formatDate(date) { return [ padTo2Digits(date.getDate()), padTo2Digits(date.getMonth() + 1), date.getFullYear(), ].join('/'); } function padTo2Digits(num) { return num.toString().padStart(2, '0'); }
The function uses the following 3 methods on the Date object:
Date.getDate() - returns an integer between
1and31representing the day of the month for a specific date.Date.getMonth() - returns an integer between
0(January) and11(December) and represents the month of the given date. Yes, unfortunately, thegetMonthmethod is off by1.Date.getFullYear() - returns a four-digit number that represents the year of the given date.
getMonth method returns a zero-based value where January is 0 and December is 11.// 👇️ May 19th 2025 console.log(new Date(2025, 4, 19)); // 👇️ June 19th 2025 console.log(new Date(2025, 5, 19)); // 👇️ July 19th 2025 console.log(new Date(2025, 6, 19));
The getMonth() method returns a zero-based value, so we have to add 1 to get
the expected result.
The last step is to group the day, month and year into an array and format them
as DD/MM/YYYY using Array.join().
console.log(['28', '06', '2027'].join('/')); // 👉️ '28/06/2027' console.log(['16', '09', '2026'].join('/')); // 👉️ '16/09/2026'
The Array.join() method concatenates all of the elements in an array using a
separator.
Array.join() method takes is a separator - the string used to separate the elements of the array.You can extract the logic into a reusable function to not have to remember that
the getMonth method returns a zero-based value.
function padTo2Digits(num) { return num.toString().padStart(2, '0'); } function formatDate(date) { return [ padTo2Digits(date.getDate()), padTo2Digits(date.getMonth() + 1), date.getFullYear(), ].join('/'); } // 👇️ 24/10/2021 (dd/mm/yyyy) console.log(formatDate(new Date())); // 👇️️ 24/07/2027 (dd/mm/yyyy) console.log(formatDate(new Date(2027, 6, 24)));
The function takes a Date object as a parameter, formats the date as
dd/mm/yyyy and returns the result.
This approach can be used to format a date in any other way. All you have to do
is reorder the elements in the array and change the separator (e.g. to a hyphen
-).
If you also need to include the time components, check out my other article: Format a Date as YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss in JavaScript.
# Format a Date as DD/MM/YYYY using date-fns
You can also use the date-fns module to format a date as DD/MM/YYYY.
First, make sure you have the module installed.
Open your terminal in your project's root directory (where your package.json
file is) and run the following command to install date-fns.
# 👇️ if you need to create a package.json file npm init -y # 👇️ with NPM npm install date-fns # 👇️ with YARN yarn add date-fns
Now you can import and use the format() function to format a date as
DD/MM/YYYY.
import {format} from 'date-fns'; const date = new Date(); const result = format(date, 'dd/MM/yyyy'); console.log(result); // 👉️ 24/07/2023
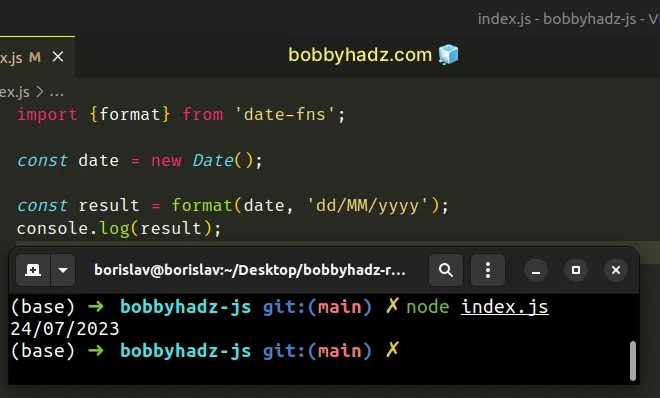
The format function takes a date and a format string and returns the formatted date string in the specified format.
You can view all of the possible tokens that can be used in the second argument of the method in this table of the official docs.
# Format a Date as DD/MM/YYYY using moment.js
You can also use the moment.js library to format a date as DD/MM/YYYY.
However, note that the date-fns package is a better option because it is more
modern and quite a bit faster than moment.
You can install the moment library by running the following command.
# 👇️ with NPM npm install moment # 👇️ with YARN yarn add moment
Now you can import and use the moment module to format the date as DD/MM/YYYY.
import moment from 'moment'; const result = moment().format('DD/MM/YYYY'); console.log(result); // 👉️ 24/07/2023
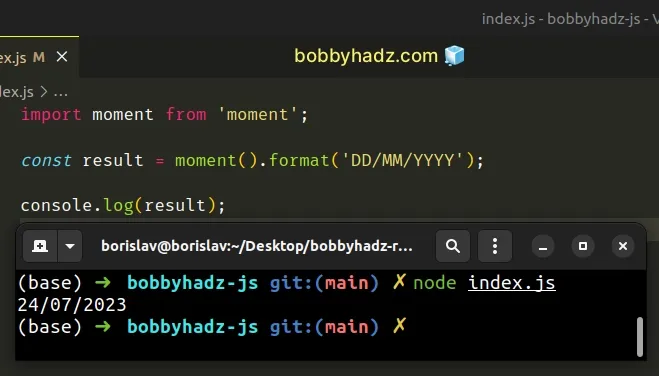
However, as previously noted, you probably shouldn't use the moment module
unless your project already makes use of it.
The module is quite a bit slower than the more modern date-fns package.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

