How to Convert a Map to JSON in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
# Convert a Map to JSON in JavaScript
To convert a Map to JSON:
- Use the
Object.fromEntries()method to convert theMapto an object. - Pass the object to the
JSON.stringify()method. - The
JSON.stringify()method will convert the supplied value to JSON.
const map = new Map([ ['name', 'bobby hadz'], ['country', 'Chile'], ]); // ✅ Convert to JSON string const json = JSON.stringify(Object.fromEntries(map)); // 👇️ '{"name":"bobby hadz","country":"Chile"}' console.log(json);
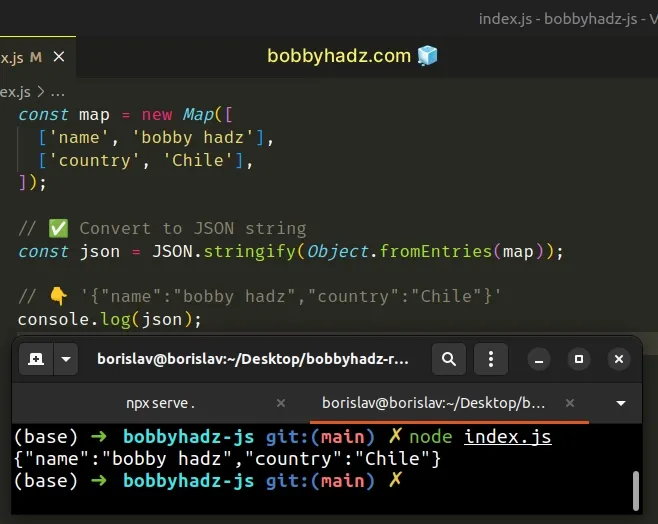
We used the Object.fromEntries()
method to convert a Map to an object.
const map = new Map([ ['name', 'bobby hadz'], ['country', 'Chile'], ]); const obj = Object.fromEntries(map); console.log(obj); // 👉️ { name: 'bobby hadz', country: 'Chile' }
This is necessary because Map objects don't have native support for
serialization or parsing.
The next step is to pass the object to the JSON.stringify() method.
The JSON.stringify() method converts the object to a JSON string and returns
the result.
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
function mapToJSON(map) { return JSON.stringify(Object.fromEntries(map)); } const map = new Map([ ['name', 'bobby hadz'], ['country', 'Chile'], ]); const json = mapToJSON(map); // 👇️ {"name":"bobby hadz","country":"Chile"} console.log(json); // 👇️ string console.log(typeof json);
The mapToJSON function takes a Map as a parameter and converts the Map to
a JSON string.
# Convert a JSON string to a Map object in JavaScript
If you need to convert the JSON string back to a Map, you have to:
- Use the
JSON.parse()method to parse the JSON string into an object. - Use the
Object.entries()method to get an array of key-value pairs. - Call the
Map()constructor with the array of key-value pairs.
const map = new Map([ ['name', 'bobby hadz'], ['country', 'Chile'], ]); const json = JSON.stringify(Object.fromEntries(map)); const obj = JSON.parse(json); const mapAgain = new Map(Object.entries(obj)); // 👇️ Map(2) { 'name' => 'bobby hadz', 'country' => 'Chile' } console.log(mapAgain);
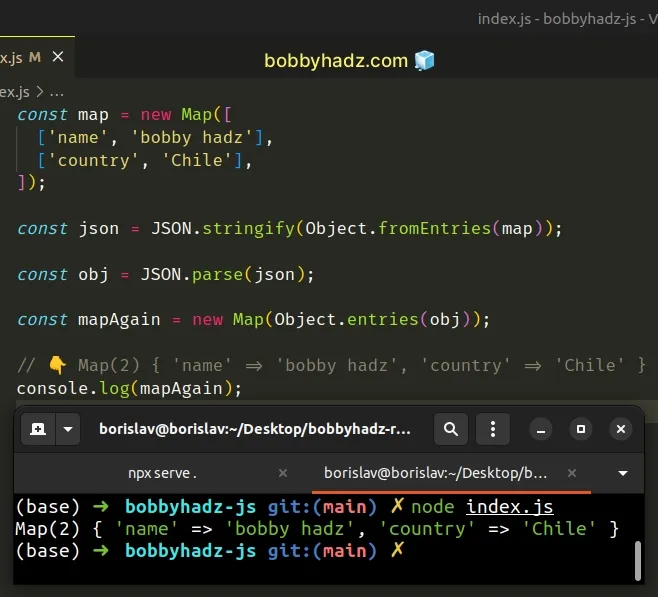
The Object.entries() method returns an array of the given object's key-value pairs.
// 👇️ [['name', 'bobby'], ['country', 'Chile']] console.log(Object.entries({name: 'bobby', country: 'Chile'}));
The Map() constructor expects an
iterable whose elements are key-value pairs, so we can directly pass it the
result of calling the Object.entries() method.
To get around the fact that Map objects don't have native support for
serialization or parsing, we convert the Map to an object and serialize the
object.
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
function JSONtoMap(json) { const obj = JSON.parse(json); return new Map(Object.entries(obj)); } const json = JSON.stringify({name: 'bobby', age: 30}); const map = JSONtoMap(json); // 👇️ Map(2) { 'name' => 'bobby', 'age' => 30 } console.log(map);
The JSONtoMap function takes a JSON string as a parameter and converts the
given string to a Map object.
# Convert a Map to JSON using Map.forEach()
This is a two-step process:
- Use the
Map.forEach()method to convert theMapto an object. - Use the
JSON.stringify()method to convert the object to JSON.
function mapToJSON(map) { const obj = {}; map.forEach((value, key) => { obj[key] = value; }); return JSON.stringify(obj); } const map = new Map([ ['name', 'bobby hadz'], ['country', 'Chile'], ]); const json = mapToJSON(map); // 👇️ {"name":"bobby hadz","country":"Chile"} console.log(json); // 👇️ string console.log(typeof json);
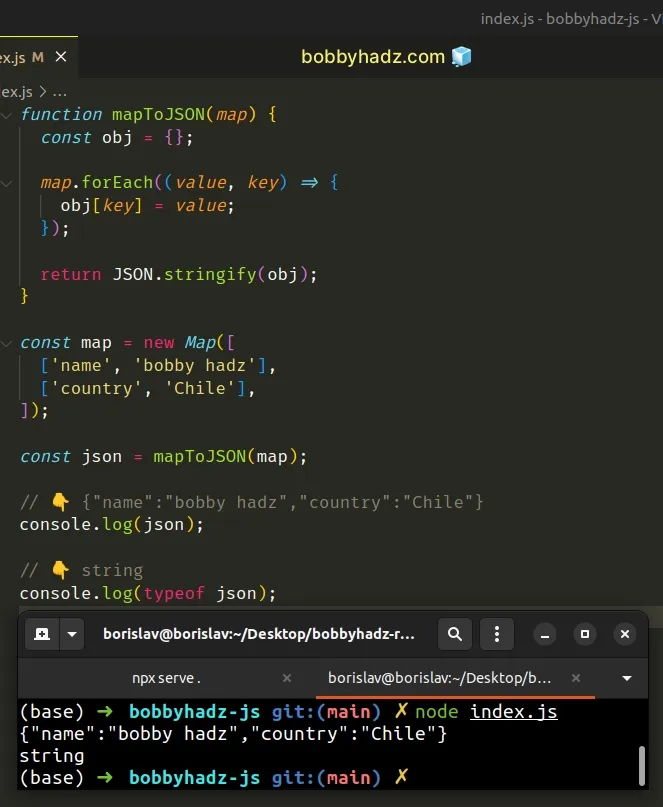
We used the Map.forEach() method to iterate over the key-value pairs of the
Map.
On each iteration, we assign the current key-value pair to an object.
The last step is to use the JSON.stringify() method to convert the object to a
Map.
This is a more manual approach than using the native Object.fromEntries()
method which takes care of converting the Map to an object.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

