Get a list of all routes defined in a Flask application
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Get a list of all routes defined in a Flask application
- Get a list of all routes defined in a Flask application by using
url_mapin your Python Interpreter - Get a list of all routes in a Flask app using the command line
# Get a list of all routes defined in a Flask application
To get a list of all routes defined in a Flask application:
- Use the
app.url_mapclass to get an object that stores all URL rules for the app. - Iterate over the rules and filter out the ones that require parameters and ones you can't visit in the browser.
from flask import Flask, url_for app = Flask(__name__) @app.route("/") def home_route(): return "<p>Home: bobbyhadz.com</p>" @app.route("/about") def about_route(): return "<p>About: bobbyhadz.com</p>" def has_no_empty_params(rule): defaults = rule.defaults if rule.defaults is not None else () arguments = rule.arguments if rule.arguments is not None else () return len(defaults) >= len(arguments) @app.route("/site-map") def site_map_route(): routes = [] for rule in app.url_map.iter_rules(): # Exclude rules that require parameters and rules you can't open in a browser if "GET" in rule.methods and has_no_empty_params(rule): url = url_for(rule.endpoint, **(rule.defaults or {})) routes.append((url, rule.endpoint)) print(routes) return routes if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=True, host='localhost', port=8000)
I can start the Flask application by running python app.py.
python app.py python3 app.py
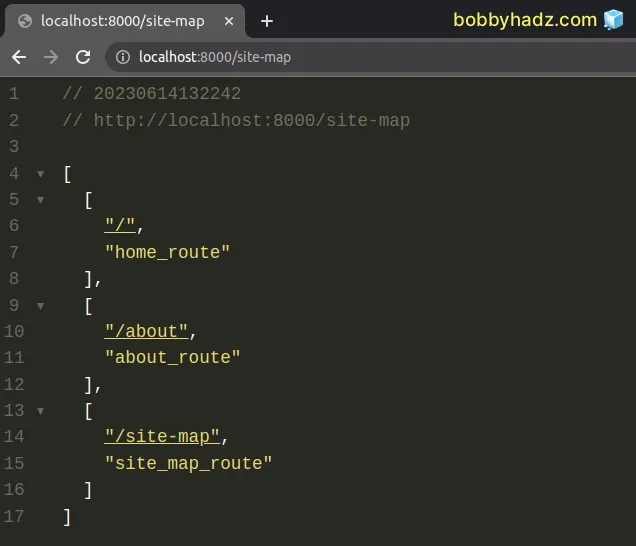
If I now open the http://localhost:8000/site-map route, I can see that all
routes of the Flask app are displayed in a list.
Here is the part of the code that sets up the /site-map route.
from flask import Flask, url_for app = Flask(__name__) def has_no_empty_params(rule): defaults = rule.defaults if rule.defaults is not None else () arguments = rule.arguments if rule.arguments is not None else () return len(defaults) >= len(arguments) @app.route("/site-map") def site_map_route(): routes = [] # print(app.url_map) for rule in app.url_map.iter_rules(): # Exclude rules that require parameters and rules you can't open in a browser if "GET" in rule.methods and has_no_empty_params(rule): url = url_for(rule.endpoint, **(rule.defaults or {})) routes.append((url, rule.endpoint)) print(routes) return routes
The app.url_map property returns a werkzeug.routing.Map instance that stores
all the URL rules and some configuration parameters of the Flask application.
for rule in app.url_map.iter_rules():
The Map object might look something like this:
Map([<Rule '/static/<filename>' (GET, HEAD, OPTIONS) -> static>, <Rule '/' (GET, HEAD, OPTIONS) -> home_route>, <Rule '/about' (GET, HEAD, OPTIONS) -> about_route>, <Rule '/site-map' (GET, HEAD, OPTIONS) -> site_map_route> ])
We used the iter_rules method to iterate over all URL rules.
On each iteration, we check if the GET string is contained in the
rule.methods sequence.
# Exclude rules that require parameters and rules you can't open in a browser if "GET" in rule.methods and has_no_empty_params(rule): url = url_for(rule.endpoint, **(rule.defaults or {})) routes.append((url, rule.endpoint))
The methods attribute returns a sequence of HTTP methods this rule applies to.
The next step is to exclude the rules that require parameters and rules you can't open in a browser.
The url_for method generates a URL to the given endpoint with the given
values.
The last step is to use the
list.append method to add a
tuple containing the URL and the endpoint to the routes list.
Your routes list may look something like this:
[ [ "/", "home_route" ], [ "/about", "about_route" ], [ "/site-map", "site_map_route" ] ]
The first element in each sublist is the URL path and the second argument is the endpoint.
Visiting the /site-map path in your browser renders the list of routes.

# Get a list of all routes defined in a Flask application by using url_map in your Python Interpreter
You can also list all routes that are defined in a Flask application by using
url_map in your Python interpreter.
Suppose we have the following app.py file.
from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) @app.route("/") def home_route(): return "<p>Home: bobbyhadz.com</p>" @app.route("/about") def about_route(): return "<p>About: bobbyhadz.com</p>" if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=True, host='localhost', port=8000)
- Open your terminal in the root directory of your Flask project.
- Start the Python interpreter.
python # Or with python3 python3
Import your app and access the url_map attribute.
from app import app app.url_map
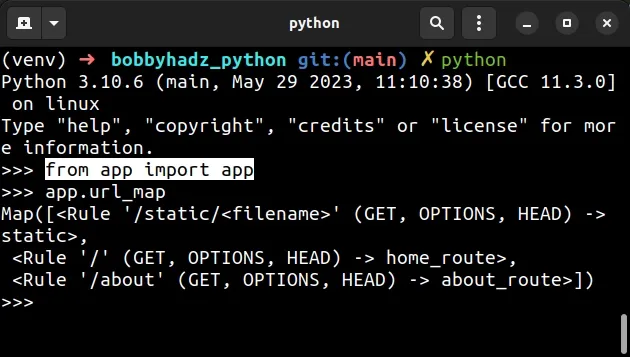
The url_map attribute will return a Map object that contains the routes in
your Flask application.
# Get a list of all routes in a Flask app using the command line
You can also use the command line to get a list of all routes in a Flask application.
- Open your terminal in the root directory of your project.
- Run the
flask routescommand.
flask routes
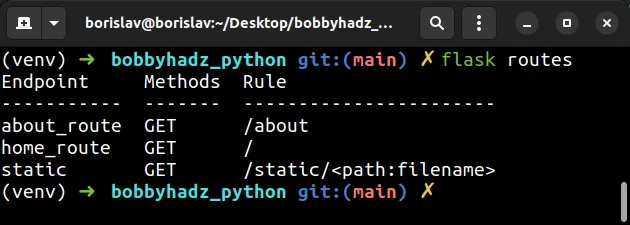
The flask routes command displays the endpoint, methods and path of each URL.
You can also view a short description of the supported commands by issuing
flask --help.
flask --help
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment
- How to change the Port and Host in a Flask application
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'flask' in Python
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'flask_cors' in Python
- How to access the HTTP request Headers in a Flask app
- AssertionError: View function mapping is overwriting an existing endpoint function
- How to auto-reload a Flask app when code changes
- RuntimeError: Either 'SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI' or 'SQLALCHEMY_BINDS' must be set

