How to find an Object in an Array in TypeScript
Last updated: Feb 27, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
- Find the first object in an Array that matches a condition in TS
- Find all Objects in an Array that match a condition in TS
# Find the first object in an array that matches a condition in TS
To find an object in an array:
- Use the
Array.find()method to iterate over the array. - Check if each object meets a condition.
- The
findmethod will return the first matching object.
const arr = [ { id: 1, country: 'Mexico' }, { id: 2, country: 'Germany' }, { id: 3, country: 'Mexico' }, ]; const found = arr.find((obj) => { return obj.id === 1; }); // 👇️ {id: 1, country: 'Mexico'} console.log(found);
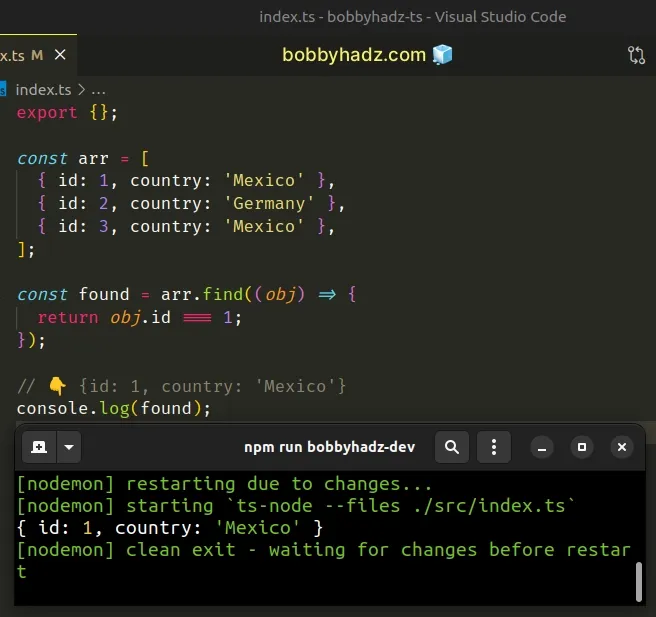
The function we passed to the Array.find method gets called with each element (object) in the array until it returns a truthy value or iterates over the entire array.
On each iteration, we check if the id property of the object is equal to 1.
find() method returns the corresponding object and short-circuits.This is very convenient when you only need to get the first object that matches the specific condition.
find() method short-circuits and returns the object.If the callback function we passed to the find() method never returns a
truthy value, the find() method returns undefined.
const arr = [ { id: 1, country: 'Mexico' }, { id: 2, country: 'Germany' }, { id: 3, country: 'Mexico' }, ]; // 👇️ const found: {id: number; country: string; } | undefined const found = arr.find((obj) => { return obj.id === 1; });
Notice that the type of the found variable is either an object or undefined.
You can use a type guard to narrow down the type to be able to access properties on the object.
const arr = [ { id: 1, country: 'Mexico' }, { id: 2, country: 'Germany' }, { id: 3, country: 'Mexico' }, ]; // 👇️ const found: {id: number; country: string; } | undefined const found = arr.find((obj) => { return obj.id === 1; }); if (found) { // ✅ TypeScript now knows that found is an object // and not undefined console.log(found.country); // 👉️ Mexico }
TypeScript can safely infer the type of the found variable to be an object in
the if block.
# Find all Objects in an Array that match a condition in TS
To find all objects in an array that match a condition:
- Use the
filter()method to iterate over the array. - Check if each object matches a condition.
- The
filtermethod will return a new array containing the objects that match the condition.
const arr = [ { id: 1, country: 'Mexico' }, { id: 2, country: 'Germany' }, { id: 3, country: 'Mexico' }, ]; const filtered = arr.filter((obj) => { return obj.country === 'Mexico'; }); // 👇️ [{id: 1, country: 'Mexico'}, {id: 3, country: 'Mexico'}] console.log(filtered);
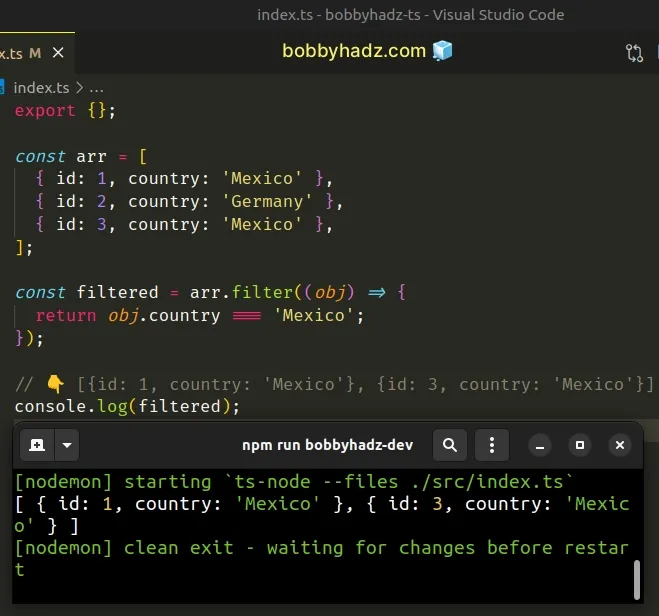
The function we passed to the Array.filter method gets called with each element (object) in the array.
The filter() method returns a new array that only contains the elements that
meet the condition.
Note that the filter() method will iterate over the entire array, regardless
of how many times the condition is met.
This way, we are able to get multiple objects that meet a specific condition from an array of objects.
If the callback function we passed to the filter method never returns a truthy
value, the filter method returns an empty array.

