Array.find() possibly undefined in TypeScript [Solved]
Last updated: Feb 27, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Array.find() possibly undefined in TypeScript [Solved]
The Array.find() method returns an undefined value if the condition
implemented in the callback function is never met or you haven't returned a
value from the callback function.
To resolve the issue, use a type guard to check if find returned a value
before accessing properties or methods.
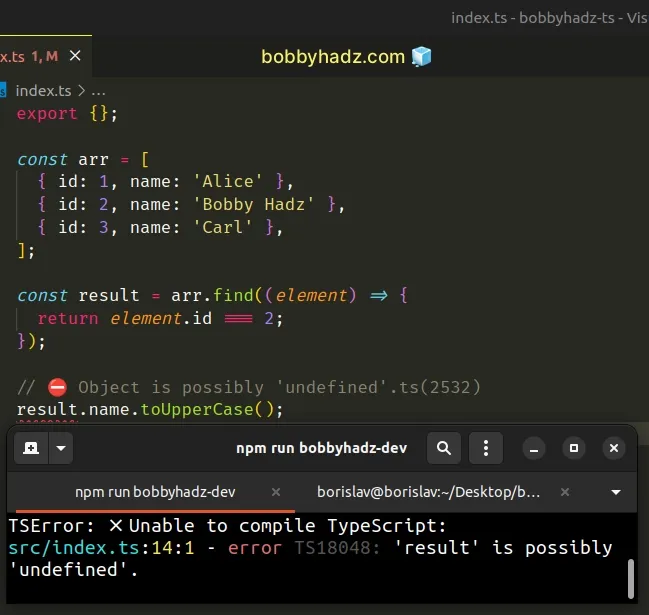
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
const arr = [ { id: 1, name: 'Alice' }, { id: 2, name: 'Bobby Hadz' }, { id: 3, name: 'Carl' }, ]; const result = arr.find((element) => { return element.id === 2; }); // ⛔️ Object is possibly 'undefined'.ts(2532) result.name.toUpperCase();
# Use a type guard to solve the error
Here is how you would get around the "Object is possibly undefined" error.
const arr = [ { id: 1, name: 'Alice' }, { id: 2, name: 'Bobby Hadz' }, { id: 3, name: 'Carl' }, ]; const result = arr.find((element) => { return element.id === 2; }); // 👇️ result is object or undefined here if (result !== undefined) { // 👇️ result is an object here console.log(result.name.toUpperCase()); // 👉️ BOBBY HADZ }
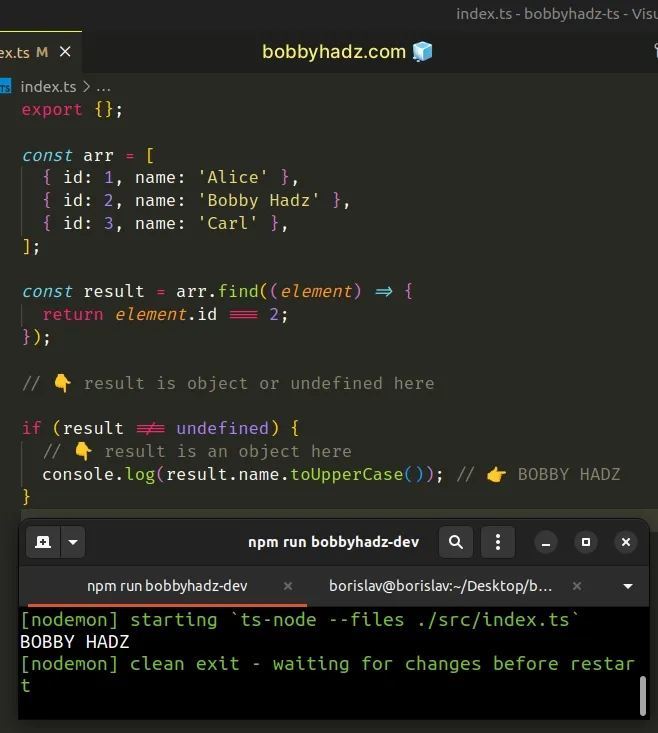
The if statement serves as a simple
type guard.
find() method returns the first value in the array for which the condition was met or undefined if the condition is never met.If we exclude undefined from the possible values, the compiler knows that the
variable is an object.
The function we passed to the Array.find method gets called for each element in the array until it returns a truthy value or iterates over the entire array.
If the callback function never returns a truthy value, the find() method
returns undefined.
# Forgetting to return a value from the callback function
Another common cause of the find() method returning undefined is when we
forget to explicitly return a value from the callback function we passed to
find().
const arr = [ { id: 1, name: 'Alice' }, { id: 2, name: 'Bobby Hadz' }, { id: 3, name: 'Carl' }, ]; const result = arr.find((element) => { element.id === 2; }); console.log(result); // 👉️ undefined
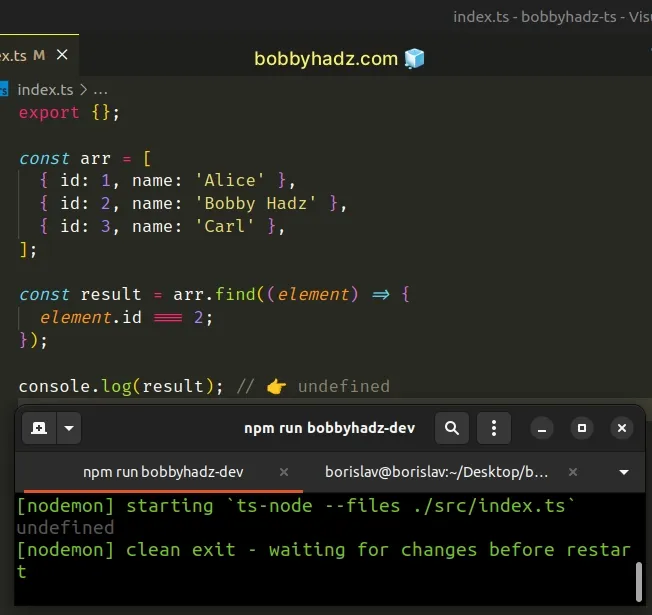
Notice that we didn't use an arrow function with implicit return and didn't use
the return statement.
undefined on each invocation and eventually find() also returns undefined.# Make sure to return a value from the callback function
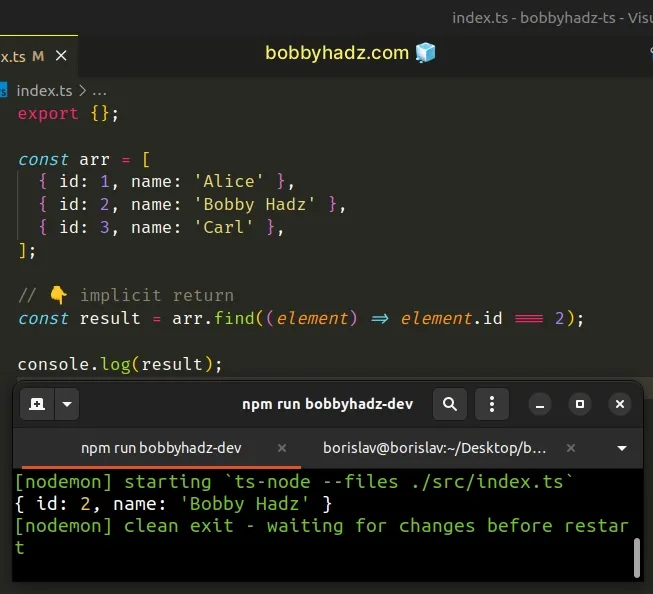
Make sure you return a value from the callback function, either by using an
implicit return in an arrow function or by explicitly using the return
statement.
const arr = [ { id: 1, name: 'Alice' }, { id: 2, name: 'Bobby Hadz' }, { id: 3, name: 'Carl' }, ]; // 👇️ implicit return const result = arr.find((element) => element.id === 2);
# Solve the error using the optional chaining operator
An alternative solution to the find() method returning undefined is to use
optional chaining (?.).
const arr = [ { id: 1, name: 'Alice' }, { id: 2, name: 'Bobby Hadz' }, { id: 3, name: 'Carl' }, ]; const result = arr.find((element) => element.id === 2); // 👇️ "BOBBY HADZ" console.log(result?.name.toUpperCase());
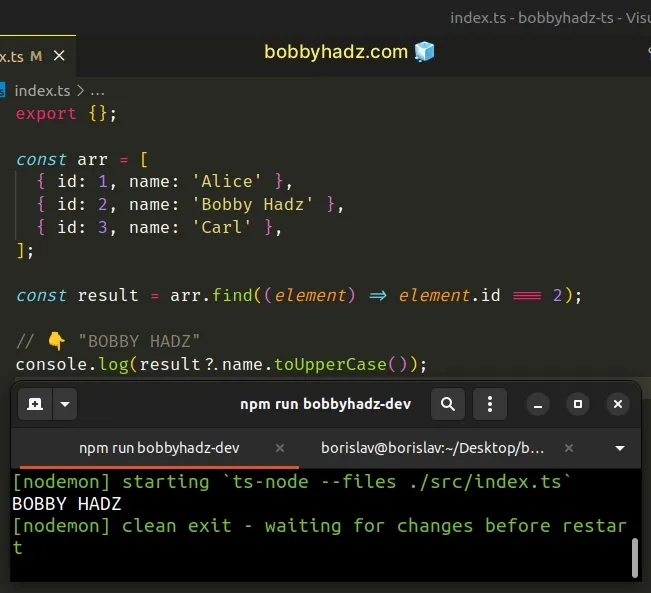
The optional chaining (?.) operator short-circuits, instead of throwing an
error, if the reference is equal to undefined or null.
result variable has a value of undefined or null, the operator will short-circuit and return undefined.You can use this approach to access deeply nested properties that may have an
undefined or a null value without getting an error.
I've also written a detailed guide on how to find an object in an array.

