Hide/Show an Element using TypeScript
Last updated: Feb 29, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Hide/Show an Element using TypeScript
To hide/show an element in TypeScript, use the style.display property to
determine if the element is shown or hidden.
If its display property is set to none, show the element by setting it to
block, otherwise, hide the element by setting its display property to
none.
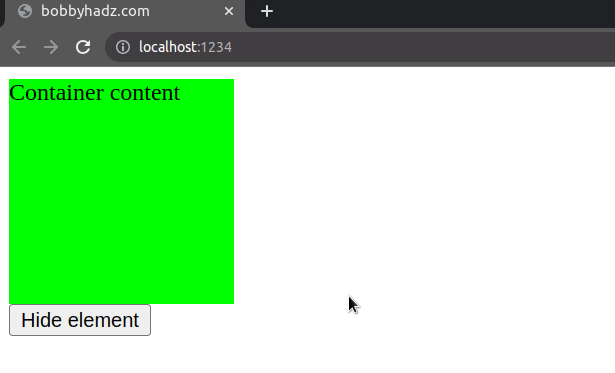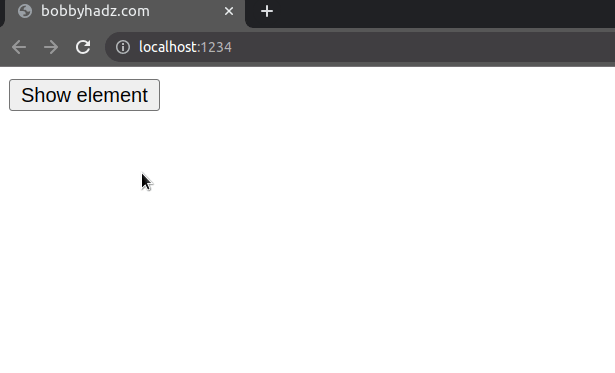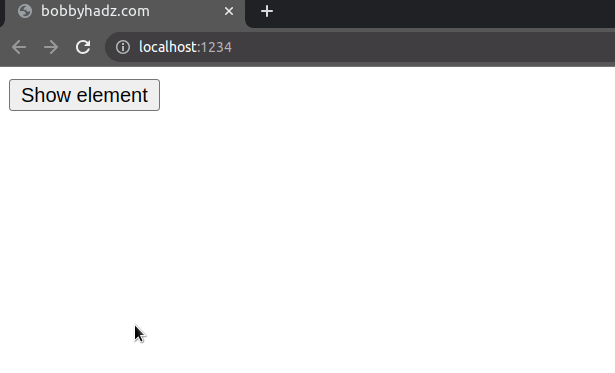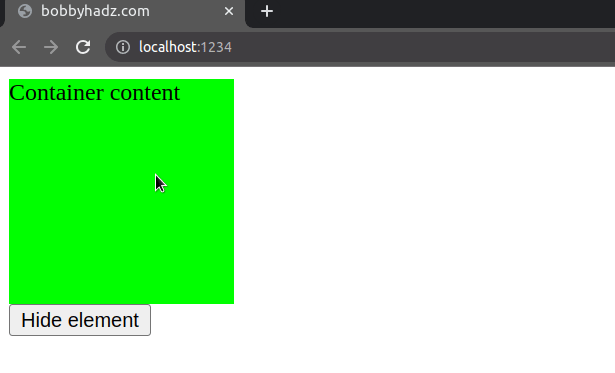
Here is the HTML for the examples.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <style> #container { background-color: lime; width: 150px; height: 150px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="container">Container content</div> <button id="btn">Hide element</button> <script src="./src/index.ts"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related TypeScript code.
const el = document.getElementById('container'); const btn = document.getElementById('btn'); if (el != null && btn != null) { btn.addEventListener('click', function handleClick() { if (el.style.display === 'none') { // ✅ Shows element if hidden el.style.display = 'block'; btn.textContent = 'Hide element'; } else { // ✅ Hides element if shown el.style.display = 'none'; btn.textContent = 'Show element'; } }); }
We used an if statement as a
type guard because the
document.getElementById method
returns null if no element with the provided id is found in the DOM.
The if statement helps us
remove null from the type
of the el and btn variables, so we can safely access their properties.
We
added a click event listener to a button.
Every time the button is clicked, the handleClick function is invoked.
In the function, we check if the element's display property is set to none.
if (el.style.display === 'none') {}
display property set to none, then it is hidden, in which case, we set its display property to block to show the element.Otherwise, the element is shown, so we set its display property to none to
hide it.
We also used the textContent property, to update the button's text when the
element is hidden/shown.
# Hide/Show an Element in TypeScript using visibility
We used the display property in the examples, however, you might need to use the visibility property depending on your use case.
display property is set to none, the element is removed from the DOM and doesn't affect the layout. The document is rendered as though the element doesn't exist.On the other hand, when an element's visibility property is set to hidden, it
still takes up space on the page, however, the element is invisible (not drawn).
The element still affects the layout on your page as normal.
Here is an example that uses the visibility property to hide/show an element
by its id.
const el = document.getElementById('container'); const btn = document.getElementById('btn'); if (el != null && btn != null) { btn.addEventListener('click', function handleClick() { if (el.style.visibility === 'hidden') { // ✅ Shows element if hidden el.style.visibility = 'visible'; btn.textContent = 'Hide div'; } else { // ✅ Hides element if shown el.style.visibility = 'hidden'; btn.textContent = 'Show div'; } }); }
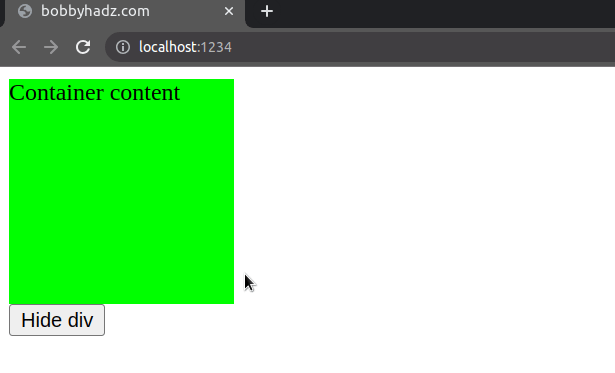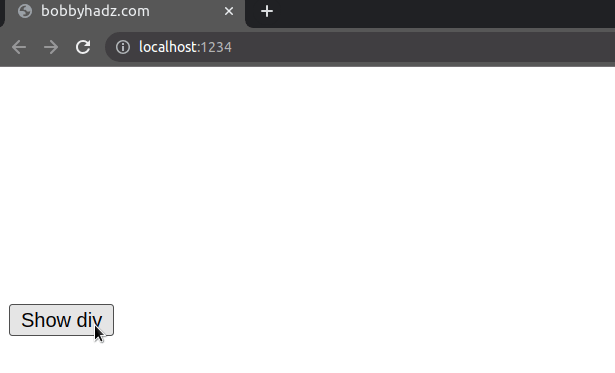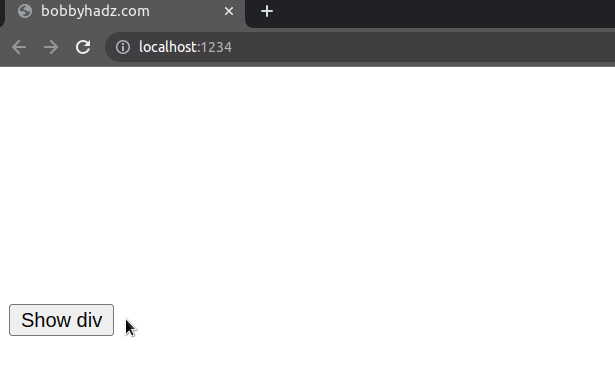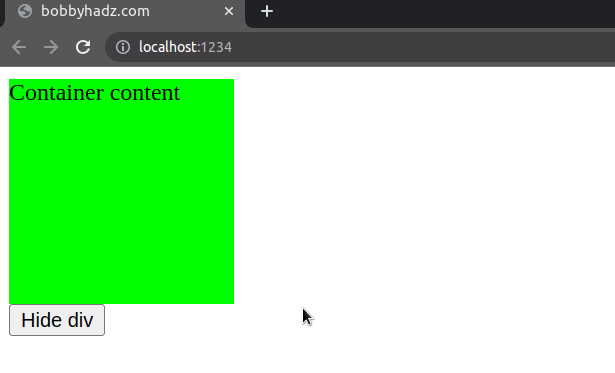
Even though the element is not rendered, it still affects the layout of the page as normal.
When we used the display property to hide the element, the button would take
its place in the DOM as the div element got completely removed from the
document.
I've also written articles on:

