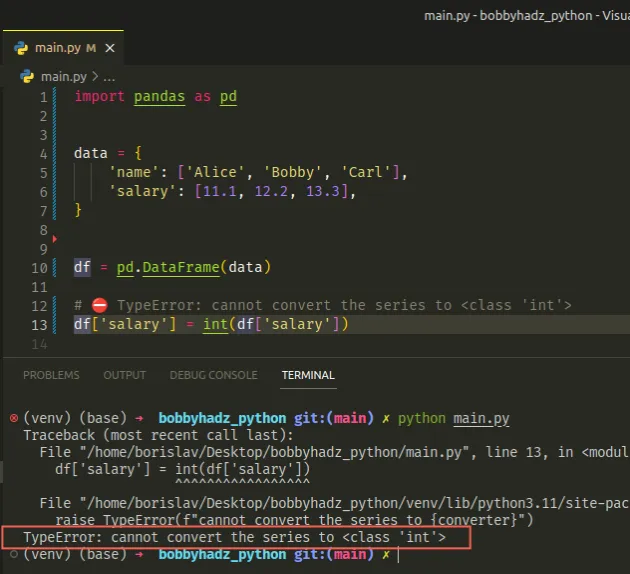
TypeError: cannot convert the series to <class 'int'>
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- TypeError: cannot convert the series to <class 'int'>
- TypeError: cannot convert the series to <class 'float'>
# TypeError: cannot convert the series to <class 'int'>
The Python "TypeError: cannot convert the series to <class 'int'>" occurs when
we try to convert a Series object to an integer.
To solve the error, use the astype() method to convert the values in the
Series object to integers.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [11.1, 12.2, 13.3], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) # ⛔️ TypeError: cannot convert the series to <class 'int'> df['salary'] = int(df['salary'])
The Series object is a one-dimensional array.
The values of the name and salary keys in the example are Series objects.
We tried to pass the Series to the
int() class to convert its
values to integers which caused the error.
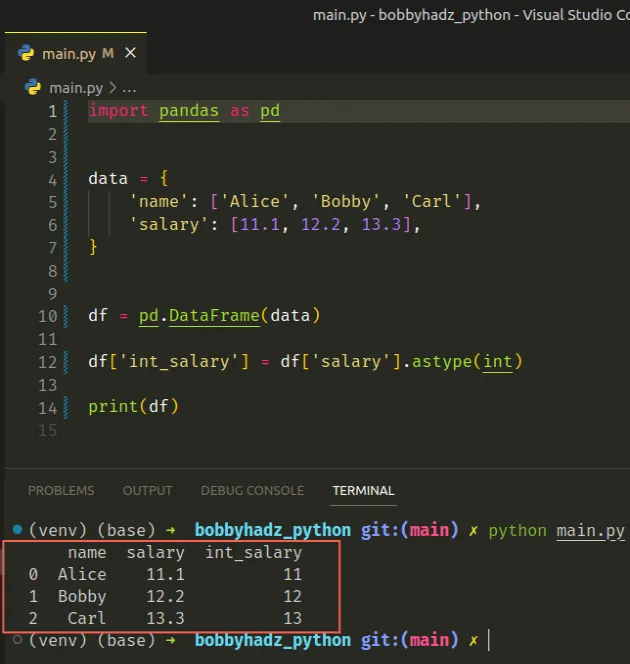
# Use the astype() method to convert the Series to integers
One way to solve the error is to use the
pandas.DataFrame.astype
method to convert the Series object to integers.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [11.1, 12.2, 13.3], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['int_salary'] = df['salary'].astype(int) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
name salary int_salary 0 Alice 11.1 11 1 Bobby 12.2 12 2 Carl 13.3 13
If you got the error: "TypeError: cannot convert the series to <class 'float'>",
pass the float class to the
astype()
method.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': ['11.1', '12.2', '13.3'], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['int_salary'] = df['salary'].astype(float) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
name salary int_salary 0 Alice 11.1 11.1 1 Bobby 12.2 12.2 2 Carl 13.3 13.3
# Converting a specific value in the Series to an integer
If you meant to access a specific value in the Series object and convert the
value to an integer, access it at an index.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [11.1, 12.2, 13.3], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) value = int(df['salary'][0]) print(value) # 👉️ 11
We accessed the first element in the salary Series object and used the int()
class to convert it to an integer.
# Use the apply() method to convert the Series to integers
You can also use the pandas.DataFrame.apply method to solve the error.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [11.1, 12.2, 13.3], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['int_salary'] = df['salary'].apply(int) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
name salary int_salary 0 Alice 11.1 11 1 Bobby 12.2 12 2 Carl 13.3 13
The apply() method applies a function along an axis of the DataFrame.
If you got the error "TypeError: cannot convert the series to <class
'float'>", you should pass the float class to apply().
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': ['11.1', '12.2', '13.3'], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['int_salary'] = df['salary'].apply(float) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
name salary int_salary 0 Alice 11.1 11.1 1 Bobby 12.2 12.2 2 Carl 13.3 13.3
We passed the int class to the apply() method, but you can also pass a
custom function to the method.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [11.1, 12.2, 13.3], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['int_salary'] = df['salary'].apply( lambda x: int(x + 500) ) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
name salary int_salary 0 Alice 11.1 511 1 Bobby 12.2 512 2 Carl 13.3 513
We passed a lambda function to the apply() method, but you can also use a
named function in the same way.
The function gets called with each of the elements in the Series object.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [11.1, 12.2, 13.3], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) def process_data(x): return int(x + 500) df['int_salary'] = df['salary'].apply(process_data) print(df)
We used a named process_data function instead of an inline lambda.
The output of the code sample is the same.
name salary int_salary 0 Alice 11.1 511 1 Bobby 12.2 512 2 Carl 13.3 513
# Use the to_numeric method to solve the error
There is also a pandas.to_numeric() method that you can use to solve the error.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': ['11.1', '12.2', '13.3'], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['salary'] = pd.to_numeric(df['salary']) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
name salary 0 Alice 11.1 1 Bobby 12.2 2 Carl 13.3
The to_numeric method converts the supplied argument to a numeric type.
The default return
dtype is
float64 or int64 depending on the supplied data.
You can use the downcast argument to convert the data to other types.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [11.0, 12.0, 13.0], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['salary'] = pd.to_numeric( df['salary'], downcast='unsigned' ) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
# name salary # 0 Alice 11 # 1 Bobby 12 # 2 Carl 13
# Using the map() method to solve the error
The
pandas.Series.map()
method maps the values of a Series according to an input mapping or function.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [11.0, 12.0, 13.0], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['salary_int'] = df['salary'].map(int) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
name salary salary_int 0 Alice 11.0 11 1 Bobby 12.0 12 2 Carl 13.0 13
We passed the int class to the map() method, but we could have also passed
it a custom function.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [11.0, 12.0, 13.0], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) def custom_map_fn(x): return int(x + 500) df['salary_int'] = df['salary'].map(custom_map_fn) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
name salary salary_int 0 Alice 11.0 511 1 Bobby 12.0 512 2 Carl 13.0 513
The custom function gets called with each value from the salary Series object.
# TypeError: cannot convert the series to <class 'float'>
The error "TypeError: cannot convert the series to <class 'float'>" commonly
occurs when using methods from the math module instead of using NumPy-specific
methods when processing data in a Series object.
Here is an example.
import pandas as pd import math data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [100, 200, 300], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) # ⛔️ TypeError: cannot convert the series to <class 'float'> df['salary'] = math.sqrt(df['salary'])
Methods from the math module cannot directly be used to process Series
objects.
Instead, you should use the equivalent method from the NumPy module.
First, make sure you have NumPy installed by running the following command.
pip install numpy # 👇️ or with pip3 pip3 install numpy
We tried using the math.sqrt method in the example, so the equivalent method
from the numpy module is np.sqrt().
import pandas as pd import numpy as np data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [100, 200, 300], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['salary'] = np.sqrt(df['salary']) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
name salary 0 Alice 10.000000 1 Bobby 14.142136 2 Carl 17.320508
The numpy module exposes math functions that can be used to directly process
a Series object, e.g. np.log, np.ceil, np.floor, np.sqrt, etc.
These methods should be used over the methods from the built-in math module
when working with Series objects.
# Converting the elements of a Series object to float using astype()
If you got the error when converting the elements of a Series object to float,
use the astype method.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [100, 200, 300], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['salary'] = df['salary'].astype(float) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
name salary 0 Alice 100.0 1 Bobby 200.0 2 Carl 300.0
# Converting the elements of a Series object to float using apply()
If you need to convert the elements of a Series object to float and process them
in a way, use the apply() method.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [100, 200, 300], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['salary'] = df['salary'].apply(float) print(df)
The code sample produces the following output.
name salary 0 Alice 100.0 1 Bobby 200.0 2 Carl 300.0
You can also pass a custom function to the apply() method.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [100, 200, 300], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) df['salary'] = df['salary'].apply(lambda x: x / 50) print(df)
Output:
name salary 0 Alice 2.0 1 Bobby 4.0 2 Carl 6.0
The lambda function from the example gets called with each element from the
Series object, divides the value by 50 and returns the result.
You can also extract the logic into a reusable function.
import pandas as pd data = { 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [100, 200, 300], } df = pd.DataFrame(data) def process_data(x): return x / 50 df['salary'] = df['salary'].apply(process_data) print(df)
The output is the same.
name salary 0 Alice 2.0 1 Bobby 4.0 2 Carl 6.0
The process_data function gets called with each value from the Series
object, divides it by 50 and returns the result.

