TypeError: 'bool' object is not iterable in Python [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- TypeError: 'bool' object is not iterable in Python
- TypeError: argument of type 'bool' is not iterable in Python
# TypeError: 'bool' object is not iterable in Python
The Python "TypeError: 'bool' object is not iterable" occurs when we try to
iterate over a boolean value (True or False) instead of an iterable (e.g. a
list).
To solve the error, track down where the variable got assigned a boolean and correct the assignment.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
my_bool = True # ⛔️ TypeError: 'bool' object is not iterable for i in my_bool: print(i)
We are trying to iterate over a boolean (True or False), but booleans are
not iterable.
Instead, you should iterate over iterable values, such as a list, a tuple or a string.
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com'] for item in my_list: # bobby # hadz # com print(item)
# Track down where the variable got assigned a boolean value
You have to figure out how the value got assigned a boolean and correct the assignment to an iterable such as a list, string, tuple, etc.
Make sure you aren't reassigning an iterable to a boolean somewhere by mistake.
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] # 👇️ Reassigned to boolean value by mistake my_list = True # ⛔️ TypeError: 'bool' object is not iterable for i in my_list: print(i)
We initially set the my_list variable to a list but later reassigned it to a
boolean which caused the error.
A common source of boolean values is comparisons and checking for conditions.
result = 5 == 5 print(result) # 👉️ True result = 5 > 15 print(result) # 👉️ False
# Passing a boolean value to the built-in constructors causes the error
Another common cause of the error is passing a boolean to the built-in
constructors, e.g. list(), dict(),
tuple() and
set().
The following 4 calls to the built-in constructors cause the error.
my_bool = False # ⛔️ TypeError: 'bool' object is not iterable list(my_bool) dict(my_bool) tuple(my_bool) set(my_bool)
To solve the error, we have to correct the assignment and figure out where the boolean value is coming from.
Here are working examples of using the 4 built-ins.
l = list(['a', 'b', 'c']) print(l) # 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c'] d = dict(name='Bobby Hadz', age=30) print(d) # 👉️ {'name': 'Bobby Hadz', 'age': 30} t = tuple([1, 2, 3]) print(t) # 👉️ (1, 2, 3) s = set(['a', 'b', 'a']) print(s) # 👉️ {'a', 'b'}
You have to figure out where the boolean value came from and correct the assignment.
# Providing a fallback value if the variable stores a boolean
You can use an if statement to check if the variable stores a boolean.
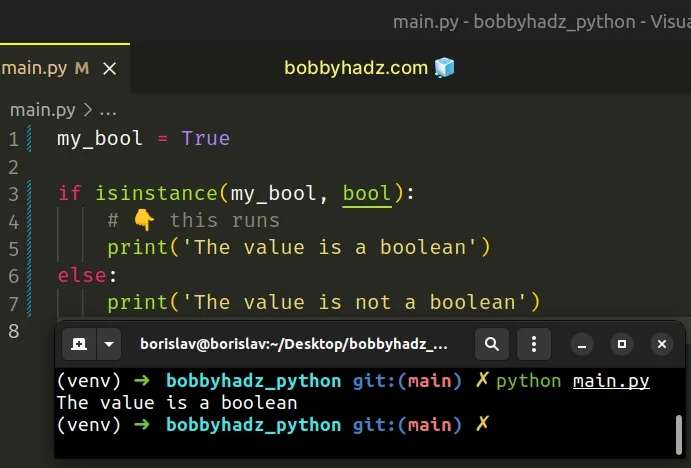
my_bool = True if isinstance(my_bool, bool): # 👇️ this runs print('The value is a boolean') else: print('The value is not a boolean')
Alternatively, you can check if the variable doesn't store a boolean.
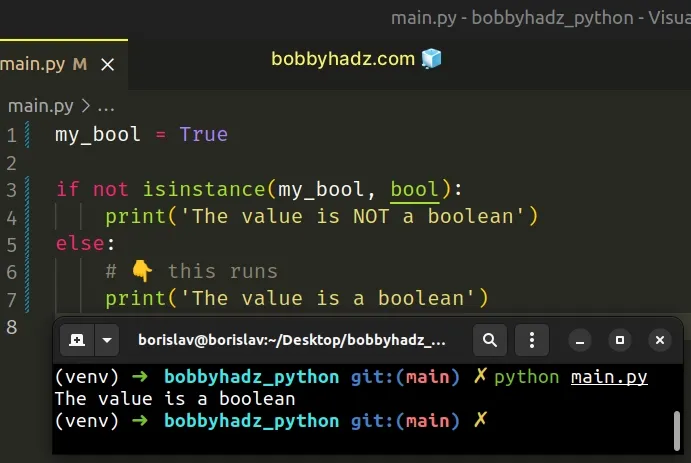
my_bool = True if not isinstance(my_bool, bool): print('The value is NOT a boolean') else: # 👇️ this runs print('The value is a boolean')
You can check if the variable stores a boolean and set it to an iterable, such as an empty list or an empty string to avoid the error.
a_list = True if isinstance(a_list, bool): a_list = [] else: for item in a_list: print(item) print(a_list) # 👉️ []
If the variable stores a boolean, we set it to an empty list, otherwise, the
else block runs where we iterate over it.
Alternatively, you can check for a specific type.
a_list = True if not isinstance(a_list, list): a_list = [] else: print('The variable is a list') for item in a_list: print(item) print(a_list) # 👉️ []
If the variable is not a list, we set it to an empty list, otherwise, the else
block runs where we know that the variable is a list.
# Checking if an object is iterable
If you need to check if an object is iterable, use a try/except statement.
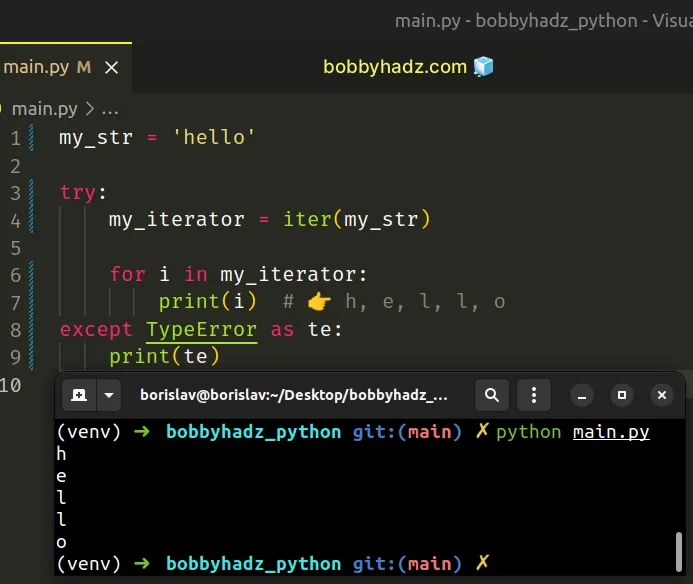
my_str = 'hello' try: my_iterator = iter(my_str) for i in my_iterator: print(i) # 👉️ h, e, l, l, o except TypeError as te: print(te)
The iter() function raises a
TypeError if the passed-in value doesn't support the __iter__() method or
the sequence protocol (the __getitem__() method).
If we pass a non-iterable object like a boolean to the iter() function, the
except block is run.
my_bool = False try: my_iterator = iter(my_bool) for i in my_iterator: print(i) except TypeError as te: print(te) # 👉️ 'bool' object is not iterable
Examples of iterables include all sequence types (list, str, tuple) and
some non-sequence types like dict, file objects and other objects that define
an __iter__() or a __getitem__() method.
# TypeError: argument of type 'bool' is not iterable (Python)
The Python "TypeError: argument of type 'bool' is not iterable" occurs when we
use the membership test operators (in and not in) with a boolean (True or
False) value.
To solve the error, correct the assignment before using the in operators.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
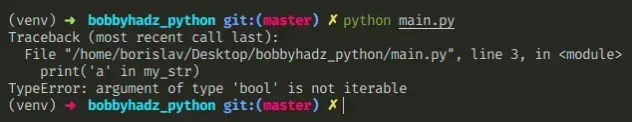
my_str = True # ⛔️ TypeError: argument of type 'bool' is not iterable print('a' in my_str)
We tried to use a
membership test operator
with a boolean (True or False) value and got the error.
Chances are you meant to use the operator with an iterable, e.g. a string or a list.
# Track down where the variable got assigned a boolean
The best way to solve the error is to track down where the variable was assigned a boolean and correct the assignment.
For example, you can reassign the variable if it stores a value of an unexpected type.
my_list = True if not isinstance(my_list, list): my_list = [] else: print('The variable is a list') print('a' in my_list) # 👉️ False
We check if the my_list variable doesn't store a list, and if it doesn't, we
set it to an empty list before using the in operator.
You can use this approach with any other object, e.g. str, dict, tuple,
etc.
my_str = True if not isinstance(my_str, str): my_str = '' else: print('The variable is a string') print('a' in my_str) # 👉️ False
Alternatively, you can check if the value is not a bool before using the in
or not in operators.
my_str = False if not isinstance(my_str, bool): print('a' in my_str) else: # 👇️ this runs print('value is a boolean')
We check if the value is not an instance of the bool class, and if it isn't,
we use the in operator to test for membership.
However, it's safer to check if the value is of the expected type, e.g. a str,
a list, or a dict.
if isinstance(my_list, list): print('a' in my_list) else: print('value is not a list')
Our if statement checks if the value is an instance of the list class, and
if it is, we use the in operator.
The in operator tests
for membership. For example, x in s evaluates to True if x is a member of
s, otherwise it evaluates to False.
my_str = 'bobby hadz' print('bobby' in my_str) # 👉️ True print('another' in my_str) # 👉️ False
x not in s returns the negation of x in s.
All built-in sequences and set types support the in and not in operators.
When used with a dictionary, the operators check for the existence of the
specified key in the dict object.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

