Count the decimal places of a Float in Python
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Count the decimal places of a Float in Python
- Count the decimal places of a Decimal object in Python
- Count the decimal places of a Float using split()
- Count the decimal places of a Float using re.sub()
# Count the decimal places of a Float in Python
To get the number of digits after the decimal point:
- Use the
str()class to convert the number to a string. - Use string slicing to reverse the string.
- Use the
str.find()method to find the index of the period.
my_float = 3.14567 # ✅ Count decimal places in a float count_after_decimal = str(my_float)[::-1].find('.') print(count_after_decimal) # 👉️ 5
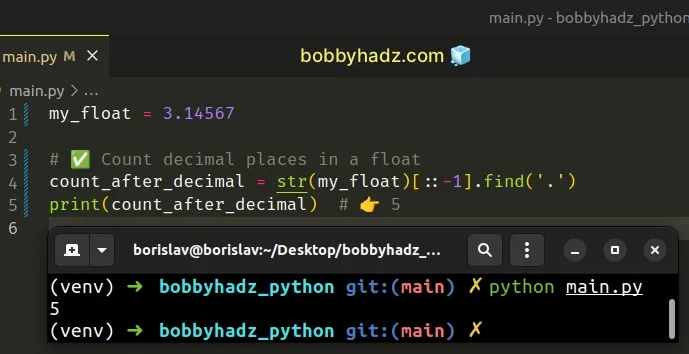
The example counts the number of digits after the decimal in a floating-point number.
str() class to convert the float to a string and reversed the string using string slicing.my_float = 3.14567 print(str(my_float)[::-1]) # 👉️ 76541.3
The syntax for string slicing
is my_str[start:stop:step].
We specified a value for the step of -1 to reverse the string.
The last step is to use the str.find() method to get the index of the period.
my_float = 3.14567 count_after_decimal = str(my_float)[::-1].find('.') print(count_after_decimal) # 👉️ 5
0, and the last character has an index of -1 or len(my_str) - 1.Since indexes are zero-based, the index of the period is equal to the number of decimal places in the number.
Note that you might run into unexpected rounding issues when using floating-point numbers.
my_float = 3.14567834 - 1.3123 print(my_float) # 👉️ 1.8333783399999999 count_after_decimal = str(my_float)[::-1].find('.') print(count_after_decimal) # 👉️ 16
# Count the decimal places of a Decimal object in Python
You can use the exponent attribute to get the number of digits after the
decimal point if you use the Decimal class.
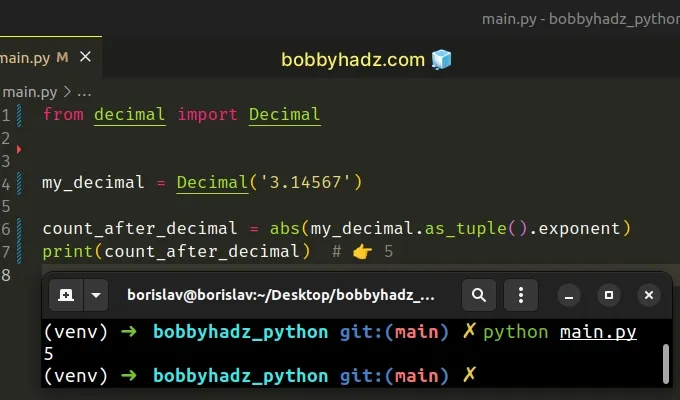
from decimal import Decimal my_decimal = Decimal('3.14567') count_after_decimal = abs(my_decimal.as_tuple().exponent) print(count_after_decimal) # 👉️ 5
The as_tuple() method returns a named tuple representation of the number.
my_decimal = Decimal('3.14567') print(my_decimal.as_tuple()) print(my_decimal.as_tuple().sign) # 👉️ 0 print(my_decimal.as_tuple().digits) # 👉️ (3, 1, 4, 5, 6, 7) print(my_decimal.as_tuple().exponent) # 👉️ -5
The named tuple has sign, digits and exponent attributes.
To get the number of digits after the decimal, we have to change the sign of the
exponent value, so we passed the result to the abs() function.
from decimal import Decimal my_decimal = Decimal('3.14567') count_after_decimal = abs(my_decimal.as_tuple().exponent) print(count_after_decimal) # 👉️ 5
The abs function returns the absolute value of a number. In other words, if the number is positive, the number is returned, and if the number is negative, the negation of the number is returned.
print(abs(-50)) # 👉️ 50 print(abs(50)) # 👉️ 50
# Count the decimal places of a Float using split()
You can also use the split() method to count the decimal places of a
floating-point number.
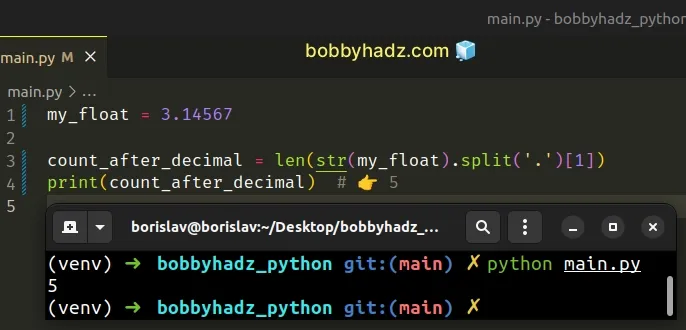
my_float = 3.14567 count_after_decimal = len(str(my_float).split('.')[1]) print(count_after_decimal) # 👉️ 5
We used the str() class to convert the float to a string and split the string on the period.
my_float = 3.14567 print(str(my_float).split('.')) # 👉️ ['3', '14567']
The second element in the list is the decimal part.
0, and the last item has an index of -1 or len(a_list) - 1.We accessed the list at index 1 and used the len() function to get the count
of the decimal places.
The len() function returns the length (the number of items) of an object.
# Count the decimal places of a Float using re.sub()
You can also use the re.sub() method to count the decimal places in a float.
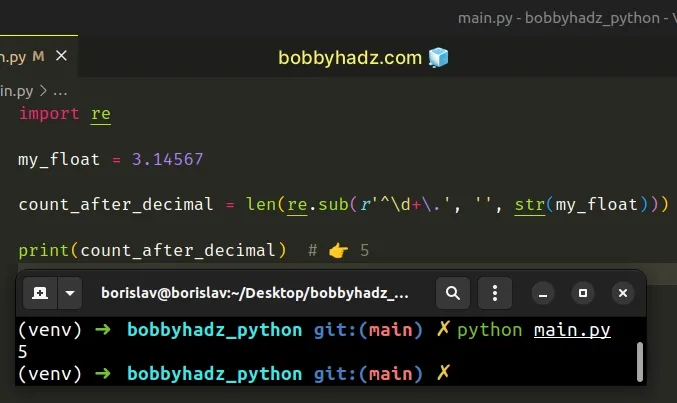
import re my_float = 3.14567 count_after_decimal = len(re.sub(r'^\d+\.', '', str(my_float))) print(count_after_decimal) # 👉️ 5
The re.sub() method returns a new string that is obtained by replacing the occurrences of the pattern with the provided replacement.
The first argument we passed to the method is a regular expression.
The \d character matches the digits [0-9] (and many other digit characters).
+ causes the regular expression to match 1 or more repetitions of the preceding character (the digit).We used a backslash to escape the period because periods have a special meaning in regular expressions.
In its entirety, the regular expression matches one or more digits at the start of the string followed by a period and removes the characters by replacing them with an empty string.
The last step is to use the len() function to count the number of digits after
the decimal.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Add zeros to a Float after the Decimal in Python
- Remove the Decimal part from a Float in Python
- How to Remove the trailing Zeros from a Decimal in Python
- Round a Float to 1, 2 or 3 Decimal places in Python
- Split a Float into Integer and Decimal parts in Python
- Format number with comma as thousands separator in Python
- SyntaxError: invalid decimal literal in Python [Solved]
- SyntaxError: leading zeros in decimal integer literals are not permitted
- Pandas: Make new Column from string Slice of another Column

