Read a text file into an Array using Node.js
Last updated: Apr 5, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Read a text file into an Array asynchronously in Node.js
To read a text file into an array:
- Use the
fsPromises.readFile()method to read the file's contents. - Await the promise that the method returns.
- Use the
String.split()method to split the string into an array of substrings.
// 👇️ if using ES6 Imports uncomment line below // import {readFileSync, promises as fsPromises} from 'fs'; const {promises: fsPromises} = require('fs'); // ✅ read file ASYNCHRONOUSLY async function asyncReadFile(filename) { try { const contents = await fsPromises.readFile(filename, 'utf-8'); const arr = contents.split(/\r?\n/); console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['One', 'Two', 'Three', 'Four'] return arr; } catch (err) { console.log(err); } } asyncReadFile('./example.txt');
Note: if you use the ES6 import/export syntax, use the following import statement instead.
import {readFileSync, promises as fsPromises} from 'fs';
example.txt file located in the same directory. Make sure to also open your terminal in that same directory.One Two Three Four
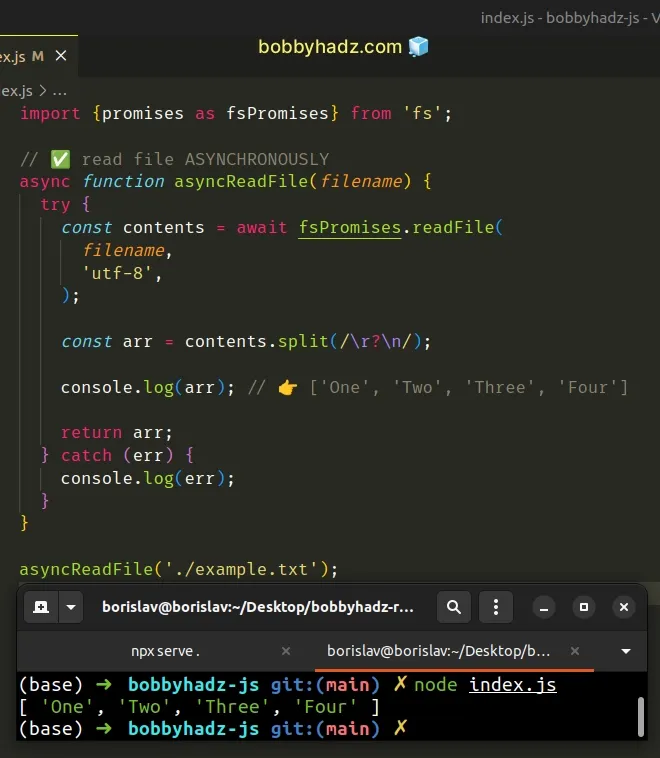
The directory structure in the example assumes that the index.js file and the
example.txt file are located in the same folder and our terminal is also in
that folder.
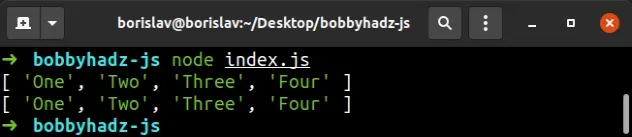
The fsPromises.readFile() method asynchronously reads the contents of the provided file.
encoding parameter, the method returns a buffer, otherwise, a string is returned.The method returns a promise that resolves with the contents of the file, so we
either have to await it or use the .then() method on it to get the resolved
string.
We used the String.split() method to split the contents on each newline character.
We passed a regular expression to the split() method.
const arr = contents.split(/\r?\n/);
The forward slashes / / mark the beginning and end of the regular expression.
\r and \n because the line breaks vary depending on the operating system.For example, Windows uses \r\n as an end-of-line character, whereas \n is
the default in Unix.
The question mark ? matches the preceding item (\r) 0 or 1 times. In other
words, the \r might or might not be there.
The split() method returns an array containing the substrings (each line) as
elements.
Alternatively, you can read the file synchronously.
# Read a text file into an Array synchronously using Node.js
Use the fs.readFileSync method to read a text file into an array
synchronously.
The method will return the contents of the file, which we can split on each newline character to get an array of strings.
// 👇️ if using ES6 Imports uncomment line below // import {readFileSync, promises as fsPromises} from 'fs'; const {readFileSync} = require('fs'); // ✅ read file SYNCHRONOUSLY function syncReadFile(filename) { const contents = readFileSync(filename, 'utf-8'); const arr = contents.split(/\r?\n/); console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['One', 'Two', 'Three', 'Four'] return arr; } syncReadFile('./example.txt');
Note: if you use the ES6 import/export syntax, use the following import statement instead.
import {readFileSync, promises as fsPromises} from 'fs';
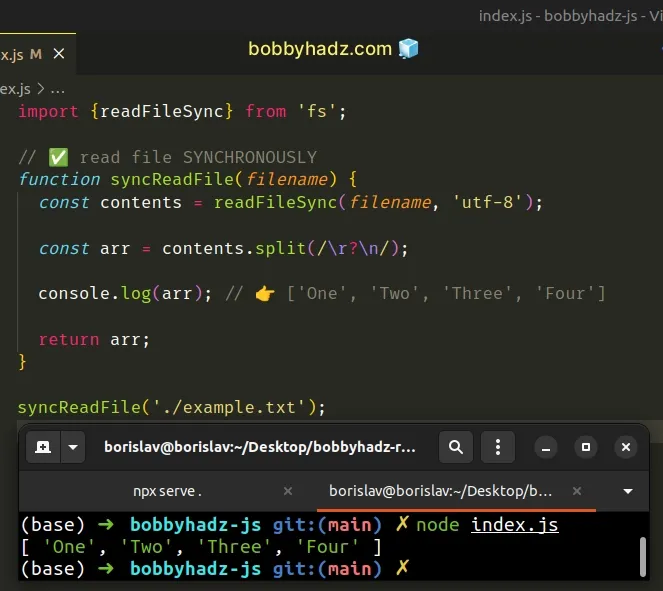
The function from the first example reads the contents of a file synchronously.
The
fs.readFileSync()
method takes the path to the file as the first parameter and the encoding as
the second.
The method returns the contents of the provided path.
If you omit the encoding parameter, the function will return a buffer,
otherwise, a string is returned.
# Read a text file into an Array asynchronously using .then()
The first code sample reads a text file into an array asynchronously using
async/await.
If you prefer using the .then() and .catch() syntax when handling Promises,
use the following code snippet instead.
// 👇️ if using ES6 Imports uncomment line below // import {readFileSync, promises as fsPromises} from 'fs'; const {promises: fsPromises} = require('fs'); // ✅ read file ASYNCHRONOUSLY function asyncReadFile(filename) { return fsPromises .readFile(filename, 'utf-8') .then(contents => { const arr = contents.split(/\r?\n/); console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['One', 'Two', 'Three', 'Four'] return arr; }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); }); } asyncReadFile('./example.txt');
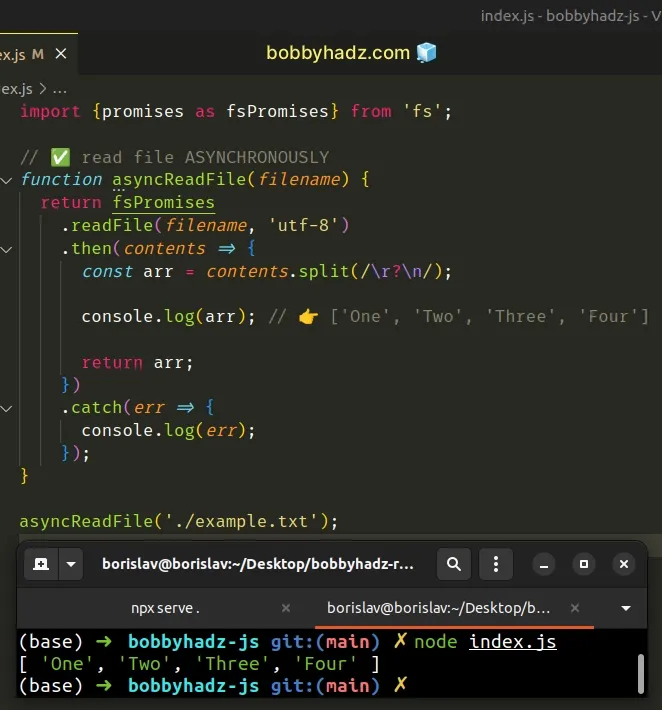
The code sample achieves the same result but makes use of the .then() and
.catch() syntax instead of a try/except block using async/await.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Remove file extension from a String using JavaScript
- Get the filename without the path using JavaScript
- Import all Exports from a File in JavaScript or TypeScript
- Import a JSON file in JavaScript and Node.js (ES6 Modules)
- How to delete a File in Node.js and JavaScript
- Import a JavaScript file into a TypeScript file
- TypeError: fs.readFileSync is not a Function in JS [Solved]

