How to Push an Object to an Array in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 1, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Push an Object to an Array in JavaScript
- Pushing multiple objects to an array with Array.push()
- Pushing an object to the beginning of an array with unshift()
- Pushing multiple objects to the beginning of an array
- Pushing an Object to an Array using spread syntax
- Pushing an Object to an Array using Array.splice()
- Pushing an Object to an Array using Array.concat()
# Push an Object to an Array in JavaScript
Use the Array.push() method to push an object to an array, e.g.
arr.push(object);.
The Array.push() method will push the supplied object to the end of the
array.
const arr = []; const obj = {name: 'Tom'}; arr.push(obj); console.log(arr); // 👉️ [{name: 'Tom'}]
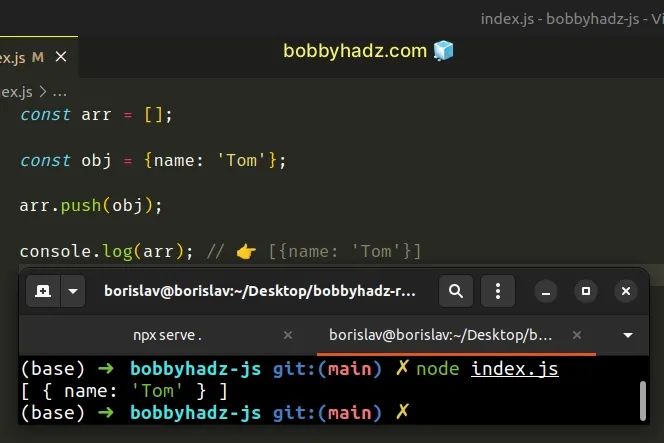
We used the Array.push() method to push an object to an array.
The object gets pushed to the end of the array.
If you only have the values that the object should contain, create the object before pushing it into the array.
const arr = []; const obj = {}; const name = 'Tom'; obj['name'] = name; arr.push(obj); console.log(arr); // 👉️ [{name: 'Tom'}]
We can use bracket notation to add one or more key-value pairs to the object.
Array.push() method to add the object to the end of the array.# Adding the object to the array upon declaration
If you haven't declared the array, you can add the objects to the array when declaring the variable.
const obj1 = {name: 'Tom'}; const obj2 = {name: 'Alice'}; const arr = [obj1]; console.log(arr); // [ { name: 'Tom' } ] const arr2 = [obj1, obj2]; console.log(arr2); // [ { name: 'Tom' }, { name: 'Alice' } ]
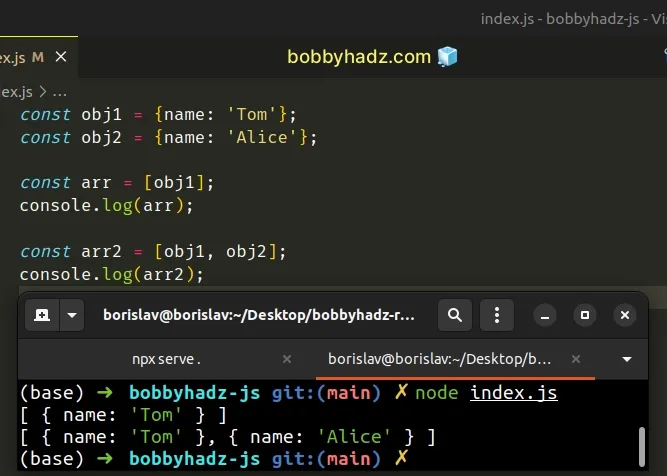
We added the objects between the square brackets to declare an array of objects.
# Pushing multiple objects to an array with Array.push()
The same approach can be used to push multiple objects to an array.
const arr = []; const obj1 = {name: 'Alice'}; const obj2 = {name: 'Bob'}; const obj3 = {name: 'Carl'}; arr.push(obj1, obj2, obj3); // 👇️ [{name: 'Alice'}, {name: 'Bob'}, {name: 'Carl'}] console.log(arr);
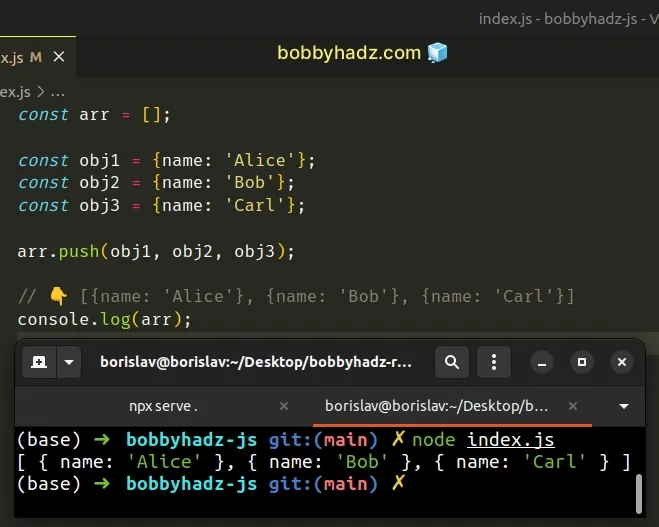
We used the Array.push() method to push 3 objects to an array in a single
statement.
The Array.push() method takes one or more values and pushes them to the array.
push() method.# Pushing an object to the beginning of an array with unshift()
If you want to push an object to the beginning of an array, use the
Array.prototype.unshift() method.
const arr = [{id: 2, name: 'Bobby'}]; const obj = {id: 1, name: 'Alice'}; arr.unshift(obj); // 👇️ [ { id: 1, name: 'Alice' }, { id: 2, name: 'Bobby' } ] console.log(arr);
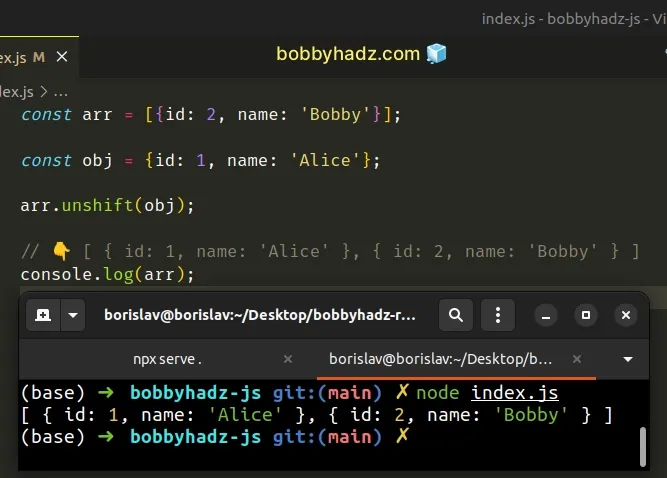
The Array.unshift() method adds one or more elements to the beginning of an array.
# Pushing multiple objects to the beginning of an array
The Array.unshift() method can also be called with multiple objects.
const arr = [{id: 3, name: 'Carl'}]; const obj1 = {id: 1, name: 'Alice'}; const obj2 = {id: 2, name: 'Bobby'}; arr.unshift(obj1, obj2); // [ // { id: 1, name: 'Alice' }, // { id: 2, name: 'Bobby' }, // { id: 3, name: 'Carl' } // ] console.log(arr);
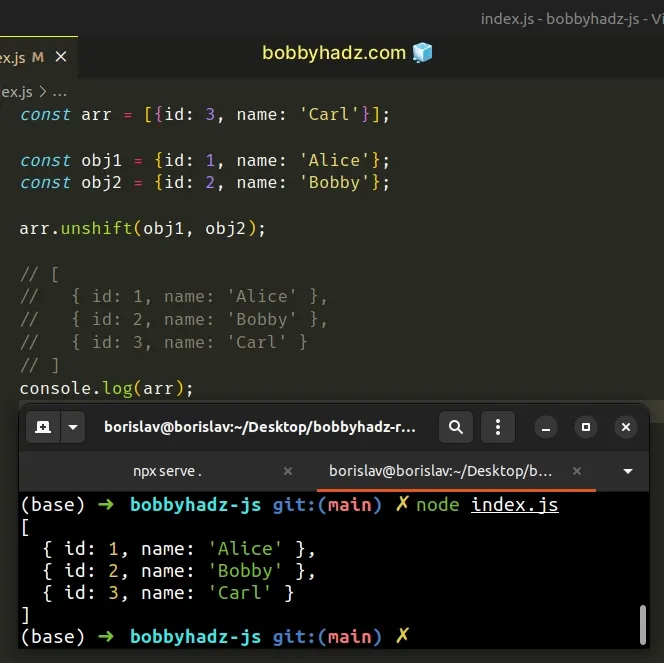
The statement adds the 2 supplied objects to the beginning of the array.
You can also use dot notation to add key-value pairs to an object. You just have to make sure the names of the keys don't contain spaces and don't start with special characters.
let arr = []; const obj = {}; obj.name = 'Tom'; obj.age = 30; console.log(obj); // 👉️ { name: 'Tom', age: 30 } arr.push(obj); console.log(arr); // 👉️ [ { name: 'Tom', age: 30 } ]
Using dot notation to add properties to an object is much more concise and elegant.
However, make sure to use bracket notation if the name of the key contains spaces.
Alternatively, you can use the spread syntax (...).
# Push an Object into an Array using spread syntax
This is a three-step process:
- Declare the array using the
letkeyword. - Use the spread syntax (...) to unpack the array and add the object.
- Reassign the value of the array variable to the result.
let arr = [{id: 1, name: 'Alice'}]; const obj = {id: 2, name: 'Bobby'}; arr = [...arr, obj]; // 👇️ [ { id: 1, name: 'Alice' }, { id: 2, name: 'Bobby' } ] console.log(arr);
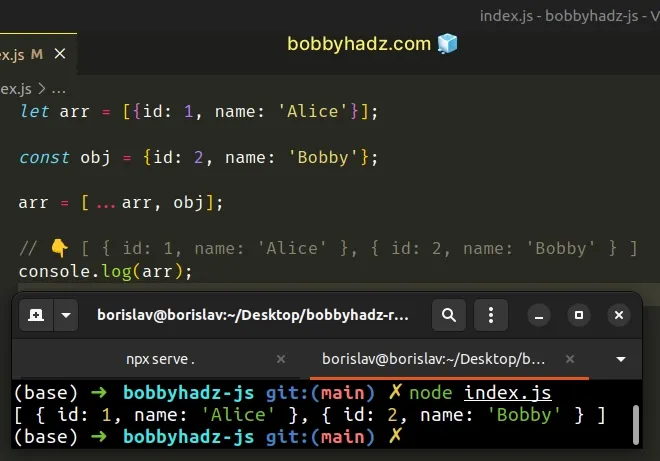
We used the spread syntax (...) to unpack the elements of the array into a new array and added the object at the end.
... syntax unpacks the array's elements (objects) into a new array to which we can add additional objects.Notice that we used the let keyword when declaring the arr variable.
This is important because variables declared using const cannot be reassigned.
You can also unpack the array after the object if you want to add the object at the beginning of the array.
let arr = [{id: 1, name: 'Alice'}]; const obj = {id: 2, name: 'Bobby'}; arr = [obj, ...arr]; // 👇️ [ { id: 2, name: 'Bobby' }, { id: 1, name: 'Alice' } ] console.log(arr);
The order in which the array elements are unpacked is preserved.
# Pushing an Object to an Array using Array.splice()
If you need to push an object into an array at a specific index, use the
Array.splice() method.
The Array.splice() method takes the index at which to insert the object and
the object as arguments.
const arr = [ {id: 1, name: 'Alice'}, {id: 3, name: 'Carl'}, ]; const obj2 = {id: 2, name: 'Bobby'}; arr.splice(1, 0, obj2); // [ // { id: 1, name: 'Alice' }, // { id: 2, name: 'Bobby' }, // { id: 3, name: 'Carl' } // ] console.log(arr);
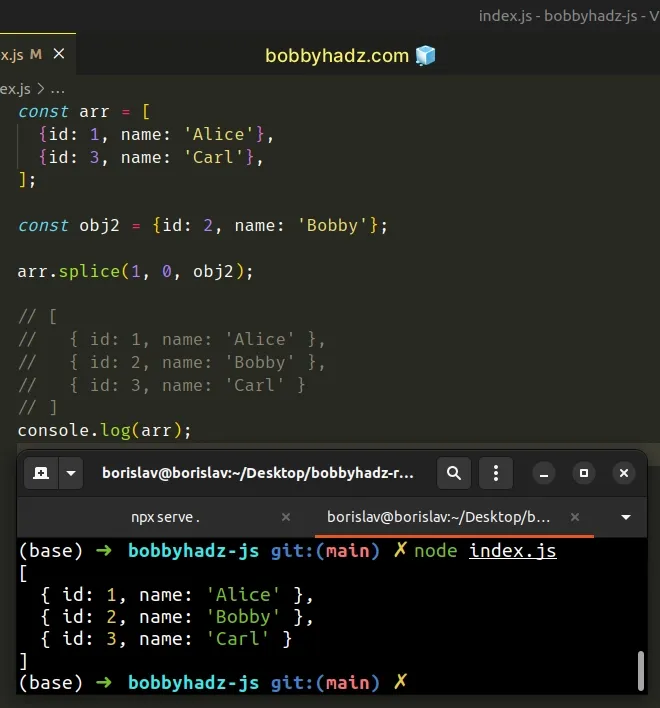
The code sample inserts the object into the array at index 1.
We passed the following arguments to the Array.splice() method:
- The start index - the index at which to start changing the array.
- The delete count - the number of elements to be deleted from the array from the start index onwards.
- The elements to add to the array beginning from start.
We used 1 as the start index to add the object to the array at index 1.
We specified a value of 0 for the delete count argument to not remove any
elements from the array.
Lastly, we passed the object as the third argument to the Array.splice()
method.
You can use the same approach to add multiple objects to the array at the specified index.
const arr = [ {id: 1, name: 'Alice'}, {id: 4, name: 'Dean'}, ]; const obj2 = {id: 2, name: 'Bobby'}; const obj3 = {id: 3, name: 'Carl'}; arr.splice(1, 0, obj2, obj3); // [ // { id: 1, name: 'Alice' }, // { id: 2, name: 'Bobby' }, // { id: 3, name: 'Carl' }, // { id: 4, name: 'Dean' } // ] console.log(arr);
We passed multiple objects to the Array.splice() method and they all got added
to the array starting at index 1.
# Pushing an object to an array using Array.concat
You can also use the Array.concat() method to push an object to an array.
const arr = []; const obj1 = {name: 'Tom'}; const obj2 = {name: 'Alice'}; const arr2 = arr.concat(obj1, obj2); console.log(arr2); // 👉️ [ { name: 'Tom' }, { name: 'Alice' } ]
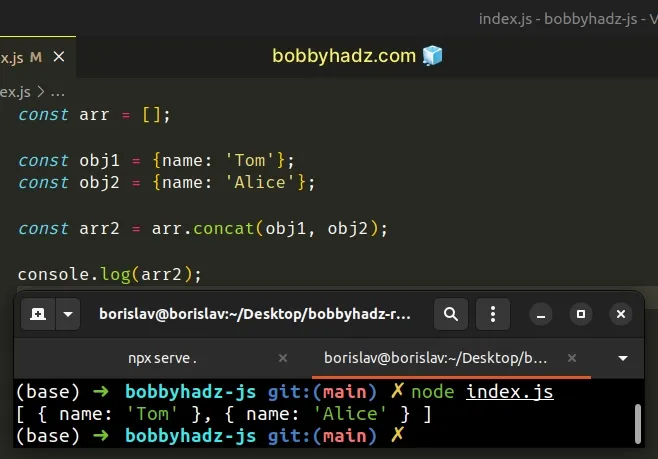
The Array.concat() method is used to merge two or more arrays.
We called the concat() method on the first array and passed it two objects.
The concat() method can be called with as many comma-separated values as
necessary.
The method returns a new array that is first populated by the elements in the array on which it was called.
Then, each of the supplied objects gets added to the new array.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

