Push multiple Values to an Array in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Push multiple Values to an Array in JavaScript
Use the Array.push() method to push multiple values to an array, e.g.
arr.push('b', 'c', 'd');.
The push() method adds one or more values to the end of an array.
const arr = ['a']; arr.push('b', 'c', 'd'); console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
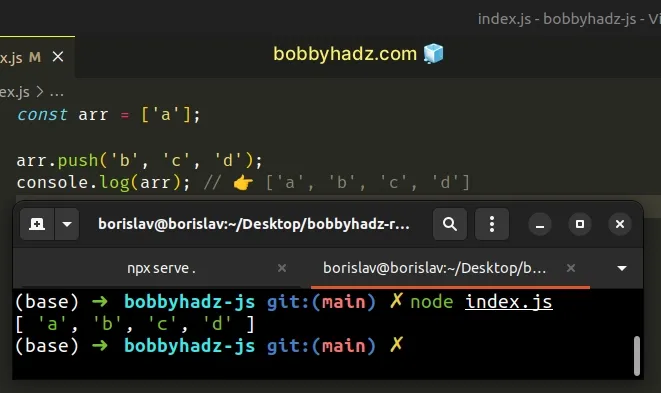
The Array.push() method takes one or more arguments and adds them to the end of the array.
The method changes the contents of the original array and returns the array's new length.
push() method doesn't return the array, it returns the array's new length.If the values you need to push into the array are stored in another array, use the spread syntax (...).
const arr = ['a']; const values = ['b', 'c', 'd']; arr.push(...values); console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
We used the spread syntax (...) to unpack the values in the call to the
Array.push() method.
You can imagine that the spread syntax (...) unpacked the array and passed its
values as multiple, comma-separated arguments to the Array.push() method.
# Push multiple Values to an Array using spread syntax (...)
Alternatively, you can use the spread syntax (...).
The spread syntax can be used to unpack the values of the original array followed by one or more additional values.
let arr = ['a']; arr = [...arr, 'b', 'c', 'd']; console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
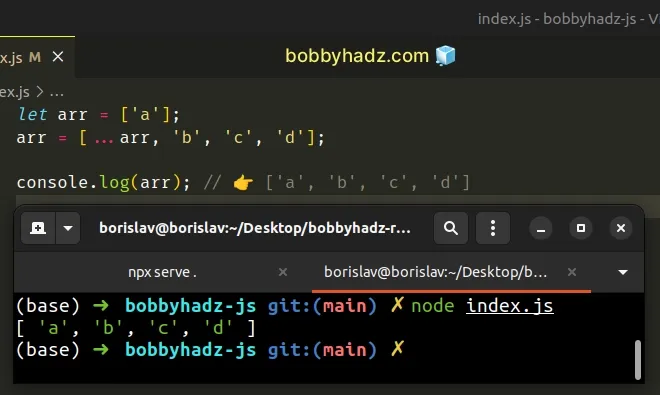
Notice that we used the let keyword to declare the arr variable. Had we
declared the variable using const, we wouldn't be able to reassign it.
In this case, we unpack the contents of the arr array into a new array and add
3 more values to the end of the new array.
If the values you need to push into the array are stored in another array, use the spread syntax (...) to unpack them.
let arr = ['a']; const values = ['b', 'c', 'd']; arr = [...arr, ...values]; console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
We used the spread syntax (...) 2 times in the same statement.
We first unpack the arr array into a new array and then unpack the values
array into the new array.
If you want to push the values to the beginning of the array, change the order in which the arrays are unpacked.
let arr = ['a']; const values = ['b', 'c', 'd']; arr = [...values, ...arr]; console.log(arr); // 👉️ [ 'b', 'c', 'd', 'a' ]
# Push multiple Values to an Array using splice()
Alternatively, you can use the splice() method.
The splice() method will add the provided values to the end of the array.
const arr = ['a']; arr.splice(arr.length, 0, 'b', 'c', 'd'); console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
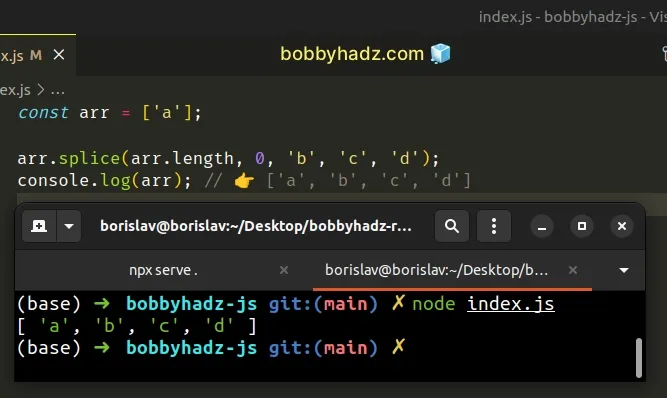
We passed the following arguments to the Array.splice method:
- Start index - the index at which to start changing the array.
- Delete count - how many elements to delete from the array from the start index onwards.
- One or more values to add to the array from the start index onwards.
We want to insert the elements at the end of the array, so we passed the array's length as the start index.
We don't want to delete any elements, so we supplied 0 for the delete
count argument.
This approach achieves the same result as the push() method, however, it is a
bit more verbose and indirect.
If the multiple values you want to push into the array are stored in another array, use the spread syntax (...).
const arr = ['a']; const values = ['b', 'c', 'd']; arr.splice(arr.length, 0, ...values); console.log(arr); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd' ]
We used the spread syntax (...) to unpack the values array in the call to the
Array.splice() method.
# Push multiple Values to an Array using unshift()
Alternatively, you can use the Array.unshift() method.
The unshift() method adds one or more elements to the beginning of an array.
const arr = ['d']; arr.unshift('a', 'b', 'c'); console.log(arr); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd' ]

The Array.unshift() method adds one or more elements to the beginning of an array and returns the new length of the array.
unshift() method is the opposite of the push() method because it adds the specified values to the beginning of the array.If your multiple values are stored in another array, use the spread syntax (...)
in the call to the unshift() method.
const arr = ['d']; const values = ['a', 'b', 'c']; arr.unshift(...values); console.log(arr); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd' ]
# Push multiple Values to an Array using concat()
Alternatively, you can use the Array.concat() method.
The Array.concat() method takes an array or multiple values as parameters and
concatenates the values into a new array.
const arr = ['a']; const result = arr.concat('b', 'c', 'd'); console.log(result); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd' ]
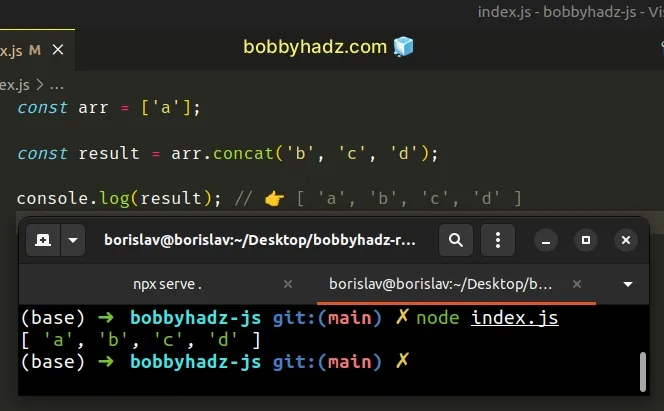
We passed multiple arguments to the Array.concat() method, however, the method can also be called with an array.
const arr = ['a']; const values = ['b', 'c', 'd']; const result = arr.concat(values); console.log(result); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd' ]
Notice that we didn't have to use the spread syntax (...) when calling the
Array.concat() method.
Note that the concat() method concatenates the values into a new array and
returns the new array.
The method doesn't mutate the original array on which it is called.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I'd use the
Array.push() method as I find it quite direct and intuitive.
I've also written an article on how to push an object to an array.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

