Get the Decimal Part of a Number in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Get the Decimal Part of a Number in JavaScript
To get the decimal part of a number:
- Use the
toString()method to convert the number to a string. - Use the
split()method to split the string on the dot. - Convert the array element at index
1to a number to get the decimal part.
function getDecimalPart(num) { if (Number.isInteger(num)) { return 0; } const decimalStr = num.toString().split('.')[1]; return Number(decimalStr); } console.log(getDecimalPart(12.345)); // 👉️ 345 console.log(getDecimalPart(-1.23)); // 👉️ 23 console.log(getDecimalPart(1)); // 👉️ 0
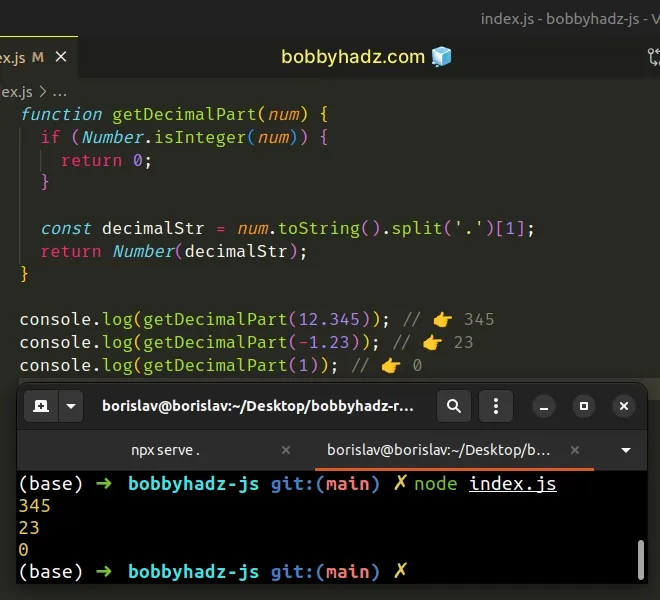
The getDecimalPart function takes a number as a parameter and returns the
decimal part of the number.
If you need to get the number of digits after the decimal, use the following function instead.
function digitsAfterDecimal(num) { if (Number.isInteger(num)) { return 0; } const arr = num.toString().split('.'); return arr[1].length; } console.log(digitsAfterDecimal(1)); // 👉️ 0 console.log(digitsAfterDecimal(1.0)); // 👉 0 console.log(digitsAfterDecimal(1.1)); // 👉️ 1 console.log(digitsAfterDecimal(1.123)); // 👉️ 3 console.log(digitsAfterDecimal(1.1234)); // 👉️ 4
The digitsAfterDecimal function takes a number as a parameter and returns the
number of digits after the decimal.
We used the Number.isInteger() method to check if the passed-in number is an integer.
0 straight away as it has no decimal part.Here are some examples of using the Number.isInteger() method.
console.log(Number.isInteger(5)); // 👉️ true console.log(Number.isInteger(-5)); // 👉️ true console.log(Number.isInteger(5.0)); // 👉️ true console.log(Number.isInteger(5.5)); // 👉️ false console.log(Number.isInteger('5')); // 👉️ false
Notice that numbers like 5.00 are considered integers because 5.00 is the
same as 5.
JavaScript automatically drops any insignificant trailing zeros from numbers.
console.log(5.00 === 5); // 👉️ true
Now that we know the number isn't an integer, we convert it to a string and call the String.split() method on it to split it on the dot.
The split method takes a separator as a parameter and splits the string into
an array of substrings.
console.log('1.37'.split('.')); // 👉️ ['1', '37'] console.log('-3.58'.split('.')); // 👉️ ['-3', '58']
The decimal part of the number is stored in the array at index 1. However, we
have to convert it back to a number before returning from the function.
function getDecimalPart(num) { if (Number.isInteger(num)) { return 0; } const decimalStr = num.toString().split('.')[1]; return Number(decimalStr); } console.log(getDecimalPart(12.345)); // 👉️ 345 console.log(getDecimalPart(-1.23)); // 👉️ 23 console.log(getDecimalPart(1)); // 👉️ 0
JavaScript indexes are zero-based, so the first element in the array has an
index of 0 and the last element has an index of array.length -1.
# Get the Decimal Part of a Number using the modulo % operator
An alternative approach is to use the modulo operator.
When used with a divisor of 1, the modulo operator returns the decimal part of
the number.
function getDecimalPart(num) { return num % 1; } console.log(getDecimalPart(3.137)); // 👉️ 0.137 console.log(getDecimalPart(1.37)); // 👉️ 0.37000000000001 console.log(getDecimalPart(5)); // 👉️ 0
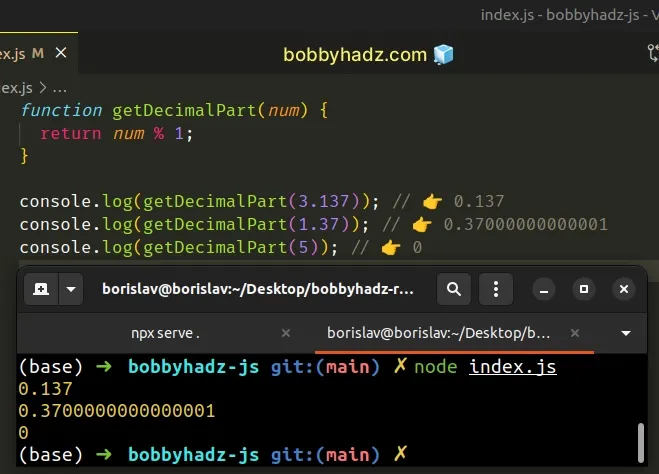
We used the modulo (%) operator to get the remainder of dividing the number by 1.
This gives us the number after the decimal. However, floating-point numbers don't represent all decimals precisely in binary which sometimes leads to inconsistent results.
console.log(0.1 + 0.2 === 0.3); // 👉️ false
The sum of 0.1 and 0.2 is actually equal to 0.30000000000000004 instead of
0.3.
This is because the binary floating-point format cannot accurately represent
numbers like 0.1 or 0.2.
The code gets rounded to the nearest number, resulting in a rounding error.
Alternatively, you can use the String.slice() method
# Get the Decimal Part of a Number using String.slice()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
toString()method to convert the number to a string. - Use the
indexOf()method to get the index of the period. - Use the
Strings.slice()method to get the decimal part of the number.
function getDecimalPart(num) { if (Number.isInteger(num)) { return 0; } const str = num.toString(); const indexOfDot = str.indexOf('.'); return Number(str.slice(indexOfDot + 1)); } console.log(getDecimalPart(12.345)); // 👉️ 345 console.log(getDecimalPart(-1.23)); // 👉️ 23 console.log(getDecimalPart(1)); // 👉️ 0
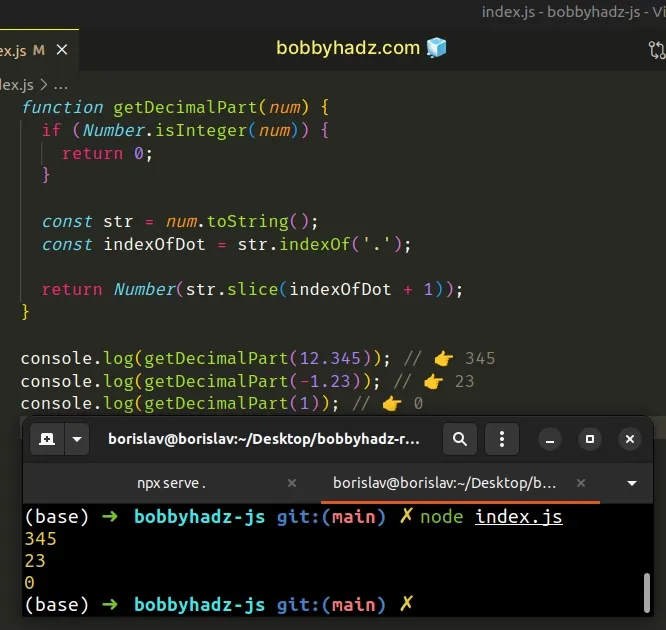
If the number is an integer, we return 0 right away as it doesn't have a
decimal part.
The next step is to convert the number to a string and use the indexOf()
method to get the index of the period.
const num = 12.345; console.log(num.toString().indexOf('.')); // 👉️ 2
The last step is to use the String.slice() method to get the portion of the
string after the period.
The String.slice() method extracts a section of a string and returns it, without modifying the original string.
The String.slice() method takes the following arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| start index | The index of the first character to include in the returned substring |
| end index | The index of the first character to exclude from the returned substring |
When only a single argument is passed to the String.slice() method, the slice
goes to the end of the string.
Notice that we added 1 to the index of the period because the start index
parameter is inclusive and we want to omit the period from the result.
function getDecimalPart(num) { if (Number.isInteger(num)) { return 0; } const str = num.toString(); const indexOfDot = str.indexOf('.'); return Number(str.slice(indexOfDot + 1)); }
When using this approach, there aren't any issues with rounding errors.
You can also use the Math.trunc() method to get the decimal part of a number.
# Get the Decimal Part of a Number using Math.trunc()
This is a two-step process:
- Use the
Math.trunc()method to get the integer part of the number. - Subtract the result from the number.
function getDecimalPart(num) { return num - Math.trunc(num); } console.log(getDecimalPart(3.137)); // 👉️ 0.137 console.log(getDecimalPart(1.234)); // 👉️ 0.23399999999999999 console.log(getDecimalPart(5)); // 👉️ 0
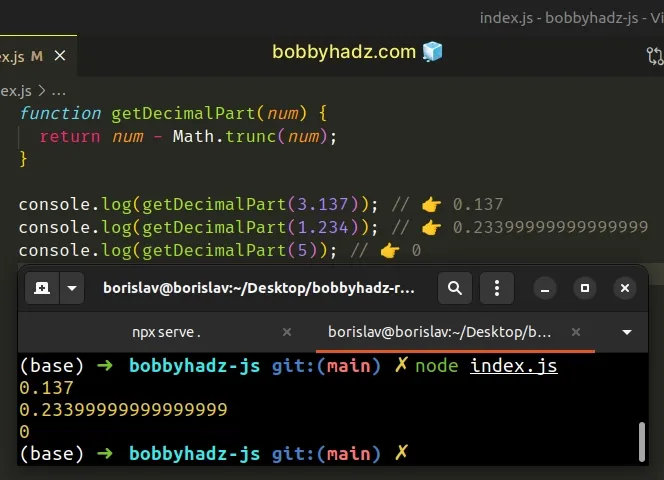
The Math.trunc() method returns the integer part of a number by removing the decimal part.
console.log(Math.trunc(5.9999)); // 👉️ 5 console.log(Math.trunc(5.0001)); // 👉️ 5
The last step is to subtract the result of calling Math.trunc() from the
number.
However, when using this approach you might also encounter rounding errors when dealing with numbers that cannot be accurately represented in binary.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I'd use the
String.split() option as I find it quite direct and intuitive.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

