Format a number to 2 Decimal places in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Format a number to 2 Decimal places in JavaScript
Use the toFixed() method to format a number to 2 decimal places, e.g.
num.toFixed(2).
The toFixed method takes a parameter, representing how many digits should
appear after the decimal and returns the result.
const num1 = 13.505; const result1 = num1.toFixed(2); console.log(result1); // 👉️ 13.51 // ------------------------------------ const num2 = 13.504; const result2 = num2.toFixed(2); console.log(result2); // 👉️ 13.50 // ------------------------------------ const str1 = '13.1'; const result3 = parseFloat(str1).toFixed(2); console.log(result3); // 👉️ 13.10
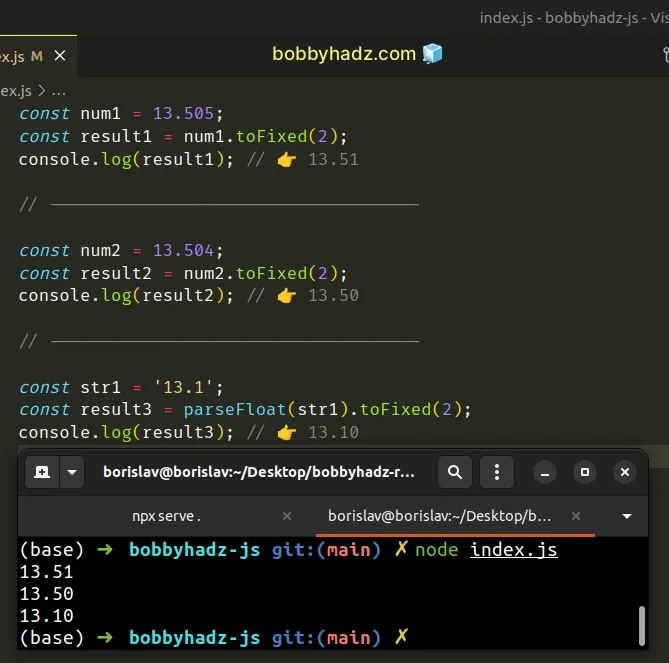
The Number.toFixed() method formats a number to the specified number of decimal places.
The only parameter the toFixed() method takes is how many digits should appear
after the decimal point.
const num = 3.456789; console.log(num.toFixed(1)); // 👉️ 3.5 console.log(num.toFixed(2)); // 👉️ 3.46 console.log(num.toFixed(3)); // 👉️ 3.457 console.log(num.toFixed(4)); // 👉️ 3.4568
The toFixed method:
- rounds the number if necessary
- pads the decimal places with zeros if necessary
# Use parseFloat to convert a string to a number before calling toFixed
The toFixed method should only be called on a number. If you have a number
wrapped in a string, call the parseFloat() function first.
const str1 = '13.1'; const result3 = parseFloat(str1).toFixed(2); console.log(result3); // 👉️ 13.10
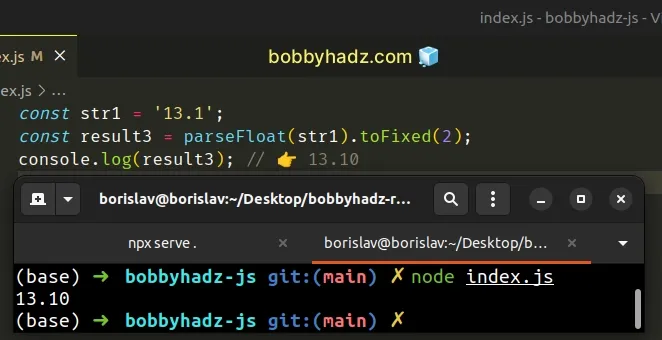
The parseFloat() function parses a string to a floating-point number.
console.log(parseFloat('6.178')); // 👉️ 6.178 console.log(typeof parseFloat('6.178')); // 👉️ number
You can define a reusable function that takes care of the conversion and formats the number to 2 decimal places.
function format2Decimals(str) { return parseFloat(str).toFixed(2); } console.log(format2Decimals('6.45678')); // 👉️ 6.46 console.log(format2Decimals(6)); // 👉️ 6.00 console.log(format2Decimals('6.4')); // 👉️ 6.40 console.log(format2Decimals('6.509')); // 👉️ 6.51
The function takes a number as a parameter and formats the number to 2 decimal places.
Note that floating-point numbers don't represent all decimals precisely in binary, which can lead to inconsistent results.
function format2Decimals(str) { return parseFloat(str).toFixed(2); } console.log(format2Decimals('6.005')); // 👉️ 6.00 console.log(format2Decimals('14.005')); // 👉️ 14.01
6.005 to 2 decimal places returns 6.00 whereas 14.01 is returned for 14.005.This issue is very commonly demonstrated by adding the numbers 0.1 and 0.2.
console.log(0.1 + 0.2 === 0.3); // 👉️ false
The sum of 0.1 and 0.2 is equal to 0.30000000000000004 instead of 0.3.
This is because the binary floating-point format cannot accurately represent
numbers like 0.1 or 0.2.
The code gets rounded to the nearest number, resulting in a rounding error.
# The toFixed method returns a string
The toFixed method returns a string. If you need the result to be of type
number, call the parseFloat() method on the string.
const num = 13.5; const str = num.toFixed(2); console.log(typeof str); // 👉️ string const result = parseFloat(str); console.log(result); // 👉️ 13.5 console.log(typeof result); // 👉️ number
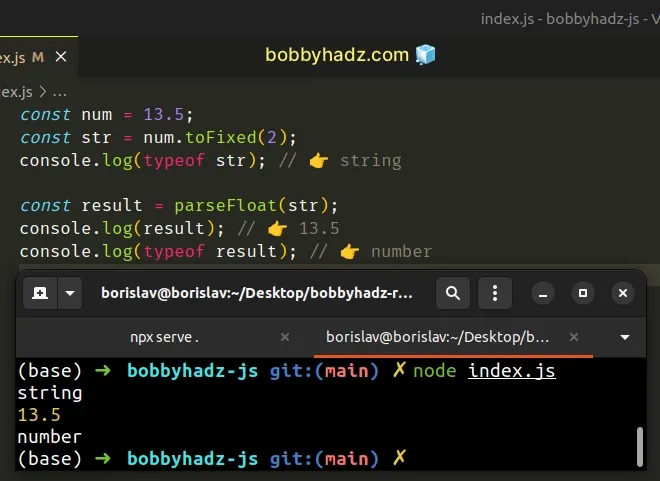
Note that we don't have a trailing zero after converting the string to a number.
You can't have numbers with trailing zeros in JavaScript.
console.log(13.5 === 13.500000000); // 👉️ true console.log(14.4 === 14.400); // 👉️ true
The numbers we compared are equal because the trailing zeros are insignificant.
# Format a number to 2 decimal places using Math.round()
This is a three-step process:
- Multiply the number by
100. - Use the
Math.round()function to round the number to the nearest integer. - Divide the number by
100.
function format2Decimals(str) { const num = parseFloat(str); return Math.round(num * 100) / 100; } console.log(format2Decimals('6.45678')); // 👉️ 6.46 console.log(format2Decimals('7.12345')); // 👉️ 7.12 console.log(format2Decimals('6.000')); // 👉️ 6 console.log(format2Decimals(6)); // 👉️ 6 console.log(format2Decimals('7.1')); // 👉️ 7.1
We first multiply the number by 100 to move the decimal point 2 places to the
right.
const num = 6.45678; console.log(num * 100); // 👉️ 645.678 console.log(Math.round(num * 100)); // 👉️ 646
The Math.round method rounds a number to the nearest integer.
console.log(Math.round(6.45678)); // 👉️ 6 console.log(Math.round(6.55678)); // 👉️ 7
The last step is to divide the result by 100.
const num = 6.45678; console.log(num * 100); // 👉️ 645.678 console.log(Math.round(num * 100)); // 👉️ 646 console.log(Math.round(num * 100) / 100); // 👉️ 6.46
Dividing the result by 100 formats the number to 2 decimal places.
When using this approach, the function returns a number.
function format2Decimals(str) { const num = parseFloat(str); return Math.round(num * 100) / 100; } console.log(typeof format2Decimals('6.45678')); // 👉️ number console.log(format2Decimals('6.45678')); // 👉️ 6.46 console.log(format2Decimals('7.12345')); // 👉️ 7.12 // 🚨 trailing zeros get dropped console.log(format2Decimals('6.000')); // 👉️ 6 console.log(format2Decimals(6)); // 👉️ 6 console.log(format2Decimals('7.1')); // 👉️ 7.1
Since the function returns a number, all insignificant trailing zeros get dropped.
If you need to keep insignificant trailing zeros around, use the toFixed()
method from the previous subheading.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

